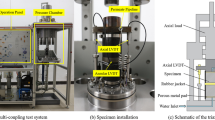
Abstract
For the stability evaluation of excavation engineering located in reservoirs, the combined effect of pore water pressure P and axial stress level ASL on the unloading mechanical properties of rocks is significant to study. The loading and unloading tests were performed on the sandstone under different Ps and ASLs, and a novel method was proposed for evaluating the damage degree caused by the P and the unloading of confining stress during the unloading process of samples. The results showed that the strength and the unloaded amount of the sandstone decrease with the applied ASL and P. The area of cracks generated during the unloading increases with the P and ASL, indicating a higher damage degree under higher P and ASL. The development orientation of the crack is more inclined to the unloading direction under lower ASL and P, due to a larger unloading amount. The damage degree caused by the unloading of confining stress is higher under lower ASL, while the effect of P on the damage degree of samples is greater under higher ASL. It demonstrates that the developed method can be used for evaluating the damage degree of rocks during the unloading process, especially caused by the pore water pressure, while the traditional method cannot.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASL :
-
Axial stress level
- P :
-
Pore water pressure
- σ 3 :
-
Confining stress
- σ 1 :
-
Axial stress
- ε 1 :
-
Axial strain
- F :
-
Increment of deviatoric stress
- d :
-
Unloading amount of confining stress
- \(\Delta \varepsilon {\prime}\) :
-
Axial strain confining stress compliance
- D i :
-
Traditional unloading damage parameter
- D :
-
Developed unloading damage coefficient
- D u :
-
Damage degree caused by the unloading of confining stress
- D p :
-
Damage degree caused by the pore water pressure
References
Chen C, Liu LP, Cong Y (2020a) Experimental investigation on deformation and strength behavior of marble with the complex loading-unloading stress path. Math Probl Eng 2018:8294390
Chen ZH, Huang LQ, Li XB et al (2020b) Influences of the height to diameter ratio on the failure characteristics of marble under unloading conditions. Int J Geomech 9:04020148
Cong Y, Wang ZQ, Zheng YR et al (2020) Effect of unloading stress levels on macro and microfracture mechanisms in brittle rocks. Int J Geomech 20(6):04020066
Deng, H.F., Wang, Z., Li, J.L. (2017) Effect of unloading rate and pore water pressure on mechanical properties of sandstone. Chinese J. Chinese J Rock Mecha Eng 39(11): 1977–1983. (in Chinese)
Huang, X., Liu, Q.S., Lu, X.L. et al. (2013) For deep soft ground TBM excavation surrounding rock mechanics behavior experimental study (II): unloading rate effect and deformation mechanism. Chinese J. Chinese J Rock Mech Eng 36(6): 1–12. (in Chinese)
Li JL, Ha QG, (1997) Three-dimensional numerical simulation of macroscopic mechanical parameters of the Three Gorges unloading rock mass. Chinese J. J Wuhan University of Hydraulic and Electric Power (Yichang) 1997(03): 1–6. (in Chinese)
Li JZ, Lin F, Liu HF et al (2019a) Triaxial experimental study on changes in the mechanical properties of rocks under different rates of confining pressures unloading. Soil Mech Found Eng 56(4):246–252
Li XB, Chen ZH, Weng L (2019b) Unloading responses of pre-flawed rock specimens under different unloading rates. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 29:1516–1526
Li, X.B., Chen, Z.H., Cao, W.Z. (2017) Time-effect properties and mechanisms of marble failure under different unloading rates. Chinese J. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 39(9): 1565–1574. (in Chinese)
Liu SL, Zhu QZ, Shao JF (2020) Deformation and mechanical properties of rock: effect of hydromechanical coupling under unloading conditions. Bull Eng Geol Env 79:5517–5534
Liu, Z.Y., Xiao, M.L., Zhuo, L. et al. (2016) Study on mechanical properties of quartz mica schist with unloading and unloading constitutive. Chinese J. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 38 (S2): 85–91. (in Chinese)
Liu, X.R., Liu, J., Li, D.L. et al. (2017) Mechanical properties and unloading constitutive model of sandstone under different water pressures and initial unloading levels. Chinese J. Chinese Journal of Coal Society 42(10): 2592–2600. (in Chinese)
Qu, S.L., Feng, X.T., Zhang, C.Q. et al. 2010. Different unloading confining pressure rate of deep buried marble unloading mechanical properties test and research. Chinese J. Chinese J Rock Mech Eng 29(9): 1807 - 1817. (in Chinese)
Ren JX, Yun MC, Zhang K et al (2021) Mechanical properties of fine grained granite under different unloading confining pressure rates. Chinese J Science Technology and Engineering 21(29):12672–12678 (in Chinese)
Rong HY, Li GC, Zhao GG et al (2020) Experiment on true triaxial unloading characteristics of deep rock under different stress paths. Chinese J Journal of Coal Society 45(09):3140–3149 (in Chinese)
Rong HY, Li GC, Xu JH et al (2021) Particle flow simulation of failure characteristics of deep rock influenced by sample height-to-width ratios and initial stress level under true-triaxial unloading. Geofluids 2021:6631744
Wang HL, Xu WY, Cai M et al (2017) Gas permeability and porosity evolution of a porous sandstone under repeated loading and unloading conditions. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50:2017–2083
Wang JJ, Liu MN, Jian FX et al (2019) Mechanical behaviors of a sandstone and mudstone under loading and unloading conditions. Environ Earth Sci 78:30
Wang RB, Xu B, Wan Y et al (2020) Characteristics of unloading damage and permeability evolution of sandstone under hydromechanical coupling. Eur J Environ Civ Eng 4:1–10
Wang ML, Li XS, Yang S et al (2022) Research on deformation and fracture characteristics of the fractured rock mass under coupling of heavy rainfall infiltration and mining unloading. Front Earth Sci 2021:792038
Wen, T., Tang, H.M., Fan, Z.Q. et al. 2018. Mechanical properties of rock loading and unloading in Badong Formation and unloading constitutive model. Chinese J. J China University of Mining and Technology 47(04): 768–779. (in Chinese)
Xu H, Feng TX, Yang CX et al (2019) Influence of initial stresses and unloading rates on the deformation and failure mechanism of Jinping marble under true triaxial compression. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 117:90–104
Yang HQ, Liu JF, Zhou XP (2017) Effects of the Loading and unloading conditions on the stress relaxation behavior of pre-cracked granite. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50:1157–1169
Zhang HB, Wang LH, Li JL et al (2021) Mechanical properties of sandstones under initial unloading damage. Adv in Civil Eng 2021:6615846
Zhang Y, Yang YJ, Ma DP (2020) Mechanical characteristics of coal samples under triaxial unloading pressure with different test paths. Shock Vib 2020:8870821
Zhao HG, Liu C, Huang G (2020) Dilatancy behaviour and permeability evolution of sandstone subjected to initial confining pressures and unloading rates. R Soc Open Sci 8:201792
Zhao, G.Y., Dai, B., Dong, L.J., et al. (2015) Study on mechanical properties and strength criteria of rock triaxial unloading under different stress paths. Chinese J. Rock Soil Mech 36(11):3121–3127+3149. (in Chinese)
Zhou KP, Liu TY, Hu ZX (2018) Exploration of damage evolution in marble due to lateral unloading using nuclear magnetic resonance. Eng Geol 244:75–85
Funding
This study is funded by the High Speed Rail Joint Fund (No. U2034203), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42207218), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U23A2045), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (No. 2020CFA049), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2021A1515110723).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, E., Zhang, H., Xiang, G. et al. Combined effect of pore water pressure and axial stress level on the unloading mechanical properties of sandstone. Bull Eng Geol Environ 83, 150 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03651-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03651-8