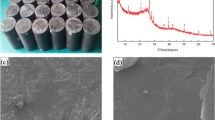
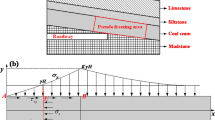
Abstract
The cryogenic cycling freeze–thaw technique demonstrates significant applicability in extracting coalbed methane (CBM) from low-permeability saturated coal seams. However, due to the inability to effectively predict the degree of structural damage to coal-rock at different times and impact radii in practical engineering, it severely affects the efficient extraction of CBM. Therefore, by conducting stepwise low-temperature single-cycle freeze–thaw tests on water-saturated coal-rock specimens at − 196 ℃ (the low temperature of liquid nitrogen), − 45 ℃, − 30 ℃, and − 15 ℃, the damage characteristics of the coal-rock specimens after freeze–thaw are determined and analyzed. Additionally, a physical model is established to calculate the damage range of liquid nitrogen freeze–thaw in coal-rock. Finally, through comparison with existing research results and numerical simulation of liquid nitrogen low-temperature freezing heat transfer, the accuracy of the experiments and physical models is ensured. The research results indicate that with the increase in stepwise low temperatures, the temperature stress caused by temperature changes gradually decreases, leading to a gradual reduction in the freeze–thaw damage to the coal-rock specimen structure. It is calculated that under the − 15 ℃ low-temperature environment, the temperature stress is only 0.72 MPa, which represents the effective temperature for enhancing transparency in freeze–thaw damage to coal-rock structures within a single cycle. Based on the established physical model and combined with experimental results, it is possible to rapidly and accurately predict the degree of damage to coal-rock at different locations, the impact range of liquid nitrogen injection wells, and the time required for heat transfer. This aids researchers in scientifically locating liquid nitrogen injection wells and CBM extraction wells, thereby enhancing work efficiency, reducing costs, and promoting efficient, green CBM extraction.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article. The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article. All data supporting the findings of this study can be obtained from the corresponding author.
References
Aoki K, Hibiya K, Yoshida T (1990) Storage of refrigerated liquefied gases in rock caverns: characteristics of rock under very low temperatures. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 5(4):319–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/0886-7798(90)90126-5
Binal A (2009) A new laboratory rock test based on free three using a steel chamber. Q J Eng Geol and Hydrogeol 42(2):179–198. https://doi.org/10.1144/1470-9236/08-040
Chen WH, Ikehata R (2023) Optimal large-time estimates and singular limits for thermoelastic plate equations with the Fourier law. Mathematical Methods Appl Sci 14:14841–14866. https://doi.org/10.1002/MMA.9349
Cheng L (2009) Experimental research and engineering application of rock mechanical properties under freezing conditions. Xi’an University of Science and Technology, master thesis. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=aHgEko1xHjh7LYwlcJQTUzinyBBDoX6gnTWMigUHzTfdZw4Gzg2A_-UUFovef06XwJgCwfJxnmLCcYr7o8qk9cxSCTp62zzQQ9ptArsJ2RG8P2a2TtW9Ft2jvtEAjHRG2wjxkCyYnxpH8xM0Fi4XA=uniplatform=NZKPTlanguage=CHS(in Chinese)
Du WZ, Niu K,Wang HW et al (2021) Experiment and field application of inhibitior liquid in spontaneous combustion process of coal based on thermogravimetric analysis. J Energ Resour Technol (2). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4048076
Guo X, Zhang TY, Di DJ et al (2021) Gas and water rate forecasting of coalbed methane reservoirs based on the rescaled exponential method. J Energ Resour Technol (5). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4048504
Guo XK (2016) Study on coal-induced penetration of liquid nitrogen. Hebei University of Science and Technology, master’s thesis. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract? v=aHgEko1xHjh7LYwlcJQTUzinyBBDoX6gnTWMigUHzTfdZw4Gzg2A_-UUFovef06XwJgCwfJxnmLCcYr7o8qk9cxSCTp62zzQQ9ptArsJ2RG8P2a2TtW9Ft2jvtEAjHRG2wj xkCyYnxpH8xM0Fi4XA=uniplatform=NZKPTlanguage=CHS (in Chinese)
Jin LX, Cho H, Lee C et al (2018) Experimental research and numerical simulation on cryogenic line chill-down process. Cryogenics 89:42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cryogenics.2017.11.003
Kou HY, Chalana M, Zhou J (2020) Diverse approaches to the preservation of built vernacular heritage: case study of post-disaster reconstruction of the Xijie Historic District in Dujiangyan City China. J Architect Conserv 1:71–86. https://doi.org/10.1080/13556207.2019.1684641
Li HW, Liu J, Wang LG, Ren TJ (2022) Influence of water saturation on curtain formation of frozen wall. Processes 10(10):2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102065
Li Z, Li ZM, Guo J (2011) Heat transfer and flow characteristics of liquid nitrogen laminar fulling films in cryogenic heat transfer. Appl Mech Mater 148–149. https://doi.org/10.4028/WWW.SCIENTIFIC.NET/AMM.148-149.1514
Li B, Ren YJ, Zhang LL et al (2018) Study on the mechanism of liquid nitrogen on penetration of hydrosite. Coal Sci Technol 46(12):145–150. https://doi.org/10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2018.12.023 (in Chinese)
Li HW, Zhang ZH, Wang LG, Liu JG (2021a) Evolution law of mechanical properties of coal sample structure damage caused by cyclic cold leaching. J China Coal Soc (S2):770–776. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.cb21.0516
Li DL, Wang EL, Mao JD et al (2021b). Influence of deposition and fouling on wall temperature distribution in convective path. J Energ Resour Technol (10). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4049319
Li HW, Liu J, Gao XC (2022a) Effect of liquid nitrogen cold loading on coal damage of different water saturation. J Min Saf Eng (39):413–420. https://doi.org/10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2020.0561
Lin HF, Ji PF, KongXG, et al (2023) Progress and prospect of gas extraction technology by underground gas injection displacement for increasing flow in low-permeability coal seam in China. J China Coal Soc 48(2):730–749. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.x022.1260
Lin HF, Luo WR, Li BT et al (2023b) Experimental research on pore damage law of water-contained coal caused by liquid nitrogen freeze-thaw. J Xi’an Univ Sci Technol (01):55–64. https://doi.org/10.13800/j.cnki.xakjdxxb.2023.0107 (in Chinese)
Liu ZX (2019).Study on heat transfer in coal porous medium. China University of Mining and Technology, master’s thesis. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=aHgEko1xHjhmRgHDG45h_IGFjjwHB7Yhlgj2vlbBhhBcAedHngsZHjSTJftLFPOoU-KeLmeM8fDFsrt9vFMSp3hjYsOY6vc4n-5gMf43w8Xl-3BOl9P3Dd_AF0Mg_9LOwxF5eLlWcRtiED1nLQDY4g==uniplatform=NZKPTlanguage=CHS (in Chinese)
Lu X, Zhou Y, Sun S (2022) Temperature field measurement and analyses of friction stir welding of 18 mm thick 2219 aluminum alloy. Exp Tech (49),1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40799-022-00556-7
Noreen S (2022) Experimental data for thermal conductivity and dielectric properties of wood and wood-based materials. Data Brief 42:108027. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DIB.2022.108027
Pan JN, Zhang ZZ, Li M et al (2019) Characteristics of multi-scale pore structure of coal and its influence on permeability. Natural Gas Industry B (4):357–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ngib.2019.01.012
Poulsen BA, Shen B, Williams DJ (2014) Strength reduction on saturation of coal and coal measure rocks with implications for coal pillar strength. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 71:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.06.012
Sellitto A (2020) Phonon- and electron-temperature waves in a Maxwell-Cattaneo heat-conduction theory. J Therm Stresses 1:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/01495739.2020.1820922
Wang LG, Zhang CH (2016) Experimental study on fatigue expansion of liquid nitrogen on hydraulic coal cracking. Experimental mechanisms 31(01):119–126. https://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:SYLX.0.2016-01-015(in Chinese)
Wang SC, Su SJ, Wang DK et al (2023) Experimental study on fracture characteristics of coal due to liquid nitrogen fracturing. Geomech Energ Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GETE.2023.100438
Yang Y, Liu SM (2020) Laboratory study of cryogenic treatment induced pore-scale structural alterations of Illinois coal and their implications on gas sorption and diffusion behaviors. J Petrol Sci Eng (prepublish) 194:107507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107507
Yu CS, Jiang Q, Su N, et al (2021) Predicting the permeability of tight sandstone utilizing experimental and mathematical modeling approaches. J Energ Resour Technol (2). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4048064
Yuan JW, Wang Y, Chen XJ (2022b) Study on the evolution of pore structure of anthracite coal under liquid-nitrogen freeze-thaw cycles. ACS Omega 5:4648–4654. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSOMEGA.1C06784
Yuan JW, Xia JY, Chu SF (2022a) The transformation characteristics of coal pore structure by freeze-thaw cycle. Coal Safety (02):33–39. https://doi.org/10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2022.02.006
Zhang JF, Tang JT, Wang Y (2009) Effect of boundary conditions on the calculation results in finite element simulations. Prog Geophys 24:1905–1911. (in Chinese)
Zhang JC, Si LL, Chen JG et al (2020) Stimulation techniques of coalbed methane reservoirs. Geofluids. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5152646
Zhang ZY, Liu Q, Wu Q et al (2021) Damage evolution of asphalt mixture under freeze-thaw cyclic loading from a mechanical perspective. Int J Fatigue. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105923
Zhang LL, Li B, Ren YJ (2018). Analysis of influencing factors of liquid nitrogen cold-immersed coal-rock. J Safety Environ (04):1290–1295. https://doi.org/10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2018.04.009 (in Chinese)
Zheng TY, Liu XG, Yang ZM et al (2021) Identification of seepage mechanisms for natural gas huff-n-puff and flooding processes in hydrophilic reservoirs with low and ultra-low permeabilities. J Energ Resour Technol (6). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4048526
Acknowledgements
All individuals have consented. We thank Ziheng Zhang for their support with part of the implementation of experiments. We thank Siyang Sun for their support with part of the language correction. All authors have given their consent to the publication of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Projects (Grant No. 2017YFC1503101), the General Programs of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51704142), and the Liaoning Province Doctoral Fund Project (Grant No. 2019-BS-115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, H.L. and L.W.; methodology, L.W.; software, J.L.; validation, H.L., L.W. and J.L.; formal analysis, T.R.; investigation, T.R.; resources, T.R.; data curation, T.R.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, J.L.; visualization, J.L.; supervision, H.L.; project administration, L.W.; funding acquisition, L.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Institutional review board statement.
“Not applicable” for studies not involving humans or animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Wang, L., Li, H. et al. Study on damage characteristics and influence scope of coal-rock saturated with freeze–thaw water. Bull Eng Geol Environ 83, 126 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03636-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03636-7