Abstract
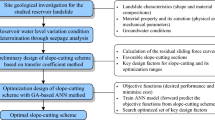
Many loess multi-stage slopes have been constructed in gully land consolidation projects on the Chinese Loess Plateau, which are vulnerable to failure induced by unreasonable excavation or rainfall. However, few studies have analyzed the influence of slope shape parameters and their design optimization on the stability of multi-stage slopes. We selected the Nangou catchment as a case study. Based on detailed field investigations, numerical analysis was conducted to reveal the influence of slope shape parameters (single stage slope height h, single stage slope ratio i, and berm width d) and platform setting on displacement, shear strain, plastic zone distribution, and the factor of safety (FS) of the multi-stage slope. Additionally, the sensitivity analysis method was used to compare and analyze the sensitivity of the slope shape parameters to FS. The results show that FS is negatively correlated with h and i and positively correlated with d. The sensitivity order of slope shape parameters to FS is i > d > h. The setting of a platform separates the shallow plastic zone of the slope into two independent parts to prevent larger landslides. In addition, based on the function relationship of FS with slope height and gradient: FS = a(tanθ)b (where a and b are functions of the slope height), the design optimization of the multi-stage slope with different slope heights and a comprehensive treatment are proposed. The research results could provide theoretical support for the design and prevention of related risks for excavation slopes in gully land consolidation projects.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borgatti L, Soldati M (2005) Geomorphological hazard and human impact in mountain environments: an introduction. Geomorphology 66(1/4):7–11
Derbyshire E (2001) Geological hazards in loess terrain, with particular reference to the loess regions of China. Earth Sci Rev 54(1–3):231–260
Dijkstra TA, Rogers CDF, van Asch TWJ (1995) Cut slope and terrace edge failures in Malan loess, Lanzhou, PR China. In: Proceedings of the XI ECSMFE conference, Copenhagen, pp 61–67
Fan X, Xu Q, Scaringi G, Li S, Peng D (2017) A chemo-mechanical insight into the failure mechanism of frequently occurred landslides in the Loess Plateau, Gansu Province, China. Eng Geol 228:337–345
Gao DB, Ni WK, Zhao ZS (2007) Research on choice of highway loess-cutting high slope styles. Highway (07):94–98 (in Chinese)
Guo Z, Huang Q, Liu Y, Wang Q, Chen Y (2022) Model experimental study on the failure mechanisms of a loess-bedrock fill slope induced by rainfall. Eng Geol 313:106979
He X, Tang K, Zhang X (2004) Soil erosion dynamics on the Chinese Loess Plateau in the last 10,000 years. Mt Res Dev 24(4):342–347
Jeldes IA, Drumm EC, Yoder DC (2015) Design of stable concave slopes for reduced sediment delivery. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 141(2):04014093
Jin Z (2014) The creation of farmland by gully filling on the loess plateau: a double-edged sword. Environ Sci Technol 48(2):883–884
Lei XY (2001) Geo-hazards in Loess Plateau and human activity. Science Press, Beijing, pp 258–264
Li X, Lu Y, Zhang X, Fan W, Lu Y, Pan W (2019) Quantification of macropores of Malan loess and the hydraulic significance on slope stability by X-ray computed tomography. Environ Earth Sci 78(16):1–19
Li Y (2018) A review of shear and tensile strengths of the Malan Loess in China. Eng Geol 236:4–10
Li Y, Shi W, Aydin A, Beroya-Eitner MA, Gao G (2020) Loess genesis and worldwide distribution. Earth Sci Rev 201:102947
Li ZQ, Oyediran IA, Tang C, Hu RL, Zhou YX (2014) FEM application to loess slope excavation and support: case study of Dong Loutian coal bunker, Shuozhou, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 73(4):1013–1023
Lin ZG, Xu ZJ, Zhang MS (2008) Loess in China and landslides in loess slopes. Taylor & Francis group, CRC Press, London, pp 129–144
Liu Y, Fu B, Lü Y, Wang Z, Gao G (2012) Hydrological responses and soil erosion potential of abandoned cropland in the Loess Plateau, China. Geomorphology 138:404–414
Liu Y, Huang QB (2007) Centrifuge model test on the deformation mechanism of loess cut slope. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 34(3):59–62
Peng J, Fan Z, Wu D, Huang Q, Wang Q, Zhuang J, Che W (2019) Landslides triggered by excavation in the Loess Plateau of China: a case study of Middle Pleistocene loess slopes. J Asian Earth Sci 171:246–258
Peng JB, Fan ZJ, Wu D, Zhuang JQ, Dai FC, Chen WW, Zhao C (2015) Heavy rainfall triggered loess-mudstone landslide and subsequent debris flow in Tianshui, China. Eng Geol 186:79–90
Peng JB, Sun P, Igwe O, Li XA (2018) Loess caves, a special kind of geo-hazard on Loess Plateau, northwestern China. Eng Geol 236:79–88
Rost KT (2001) Late Holocene loess deposits and dust accumulation in the alpine meadow belt of the Wutai Shan, China. Quatern Int 76–7:85–92
Shao X, Zhang H, Tan Y (2018) Collapse behavior and microstructural alteration of remolded loess under graded wetting tests. Eng Geol 233:11–22
Tu XB, Kwong AKL, Dai FC, Tham LG, Min H (2009) Field monitoring of rainfall infiltration in a loess slope and analysis of failure mechanism of rainfall-induced landslides. Eng Geol 105:134–150
Wang, G., 1992. Relationship between the origin of loess landslides and the human activities in China. In: Sixth International Symposium on Landslides. Landslides, vol. 1, pp. 263–268
Wang HB, Zhou B, Wu SR, Shi JS, Li B (2011) Characteristic analysis of large-scale loess landslides: a case study in Baoji City of Loess Plateau of Northwest China. Nat Hazard 11:1829–1837
Wang J, Xu Y, Ma Y, Qiao S, Feng K (2018) Study on the deformation and failure modes of filling lope in loess filling engineering: a case study at a loess mountain airport. Landslides 15(12):2423–2435
Wang JJ, Liang Y, Zhang HP et al (2014) A loess landslide induced by excavation and rainfall. Landslides 11(1):141–152
Wu TH, Kokesh CM, Trenner BR, Fox PJ (2014) Use of live poles for stabilization of a shallow slope failure. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 140(10):05014001
Xie Q, Huang Q, Liu Y, Wang Z, Yu D, Peng J (2023) Strength behaviors of undisturbed Malan loess under rainfall leaching in Yan’an area, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82(2):53
Xu L, Dai FC, Gong QM, Tham LG, Min H (2012) Irrigation-induced loess flow failure in Heifangtai Platform, north-west China. Environ Earth Sci 66(6):1707–1713
Xu L, Dai FC, Tham LG, Tu XB, Min H, Zhou YF, Wu CX, Xu K (2011) Field testing of irrigation effects on the stability of a cliff edge in loess, North-west China. Eng Geol 120:10–17
Yu D, Huang Q, Kang X et al (2023) The unsaturated seepage process and mechanism of internal interfaces in loess-filled slopes during intermittent rainfall. J Hydrol 619:129317
Zhang B, He C, Burnham M, Zhang L (2016) Evaluating the coupling effects of climate aridity and vegetation restoration on soil erosion over the Loess Plateau in China. Sci Total Environ 539:436–449
Zhang F, Pei X, Chen W, Liu G, Liang S (2014) Spatial variation in geotechnical properties and topographic attributes on the different types of shallow landslides in a loess catchment, China. Eur J Environ Civ Eng 18(4):470–488
Zhang FY, Zhao CX, Lourenco SDN, Dong SM, Jiang Y (2021) Factors affecting the soil-water retention curve of Chinese loess. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80:717–729
Zhang MS, Liu J (2010) Controlling factors of loess landslides in western China. Environ Earth Sci 59:1671–1680
Zhang X, Li P, Li ZB, Yu G (2017) Characteristics and formation mechanism of the July 25, 2013, Tianshui group-occurring geohazards. Environ Earth Sci 76(5):1–17
Zhou JX, Zhu CY, Zheng JM, Wang XH, Liu ZH (2002) Landslide disaster in the loess area of China. J For Res 13(2):157–161
Zhou P, Wen AB, Zhang XB, He XB (2013) Soil conservation and sustainable eco-environment in the Loess Plateau of China. Environ Earth Sci 68(3):633–639
Zhuang JQ, Peng JB (2014) A coupled slope cutting—a prolonged rainfall-induced loess landslide: a 17 October 2011 case study. Bull Eng Geol Environ 73(4):997–1011
Zhuang JQ, Peng JB, Zhu Y, Leng YQ, Zhu XH, Huang WL (2021) The internal erosion process and effects of undisturbed loess due to water infiltration. Landslides 18:629–638
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42041006, 41790443), the National Key Research and Development Program, China (No. 2017YFD0800501), and the Innovation Capability Support Program of Shaanxi (No. 2021TD-50, 2021TD-51).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Z., Huang, Q., Liu, Y. et al. Stability analysis and design optimization of multi-stage slope in gully land consolidation projects on the Loess Plateau. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 431 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03451-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03451-6