Abstract
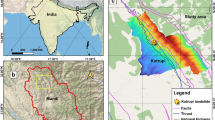
High-speed remote landslides have been the focus of landslide research because of their fast movement, long sliding distance, and large damage range. This paper takes the Donghekou landslide as an example and establishes a more reasonable 3D model based on high-precision DEM data. Under the premise of considering the landslide initiation mechanism, the complete dynamic process of Donghekou landslide initiation-acceleration-impact fold-deceleration accumulation is reproduced by PFC3D numerical simulation software. The numerical simulation results are consistent with the actual situation. The results show that the Donghekou landslide took about 20 s from the moment of initiation to the moment of impact with the barrier, about 25 s from the start of impact with the barrier to the complete departure from the barrier, and about 19 s from the end of impact to deposition. The maximum velocity of about 58.5 m/s and the maximum displacement of about 2159.0 m are typical of ultra-high-speed remote landslides. The maximum displacement and maximum velocity of the slide show a decreasing pattern from head to tail and from surface to base, except for the distribution of the maximum displacement at the head, which does not show a clear pattern. Divide the sliding mass into left and right parts, for sliding mass with the same longitudinal position: the left side has the maximum velocity and the right side has the maximum displacement.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data, models, and codes generated or used during the study appear in the published article.
References
Anbarasu K, Sengupta A, Gupta S, Sharma SP (2010) Mechanism of activation of the Lanta Khola landslide in Sikkim Himalayas. Landslides 7:135–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-009-0193-0
Cui SH, Wang GH, Pei XJ, Huang RQ, Kamai T (2016) On the initiation and movement mechanisms of a catastrophic landslide triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan (Ms 8.0) earthquake in the epicenter area. Landslides 14(3):805–819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0754-y
Djerbal L, Melbouci B (2012) Le glissement de terrain d’Ain El Hammam (Algerie): causes et evolution. Bull Eng Geol Env 71(3):587–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-012-0423-x
Erismann TH (1979) Mechanisms of large landslides. Rock Mech 12(1):15–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01241087
Fang H, Pei LZ, Xiang LZ (2011) Study on kinematic velocity of high-speed and long-range landslides induced by Wenchuan earthquake. J Disaster Prev Mitig Eng 31(2):212–217. https://doi.org/10.13409/j.cnki.jdpme.2011.02.015
Gu CZ, Hu XW, Luo G, Niu YB, Hu HY (2012a) Setting-out mechanism of landslide induced by earthquake. J Southwest Jiaotong Univ 47(04):567–572. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2012.04.005
Gu CZ, Yang HF, Hu XW, Zeng JX, Luo G (2012b) Analysis of energy conversion of earthquake-induced landslide based on fuzzy synthetic evaluation. Rock Soil Mech 33(S1):297–302. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2012.s1.009
Huang T, Ding MT, She T, Tian SJ, Yang JT (2017) Numerical simulation of a high-speed landslide in Chenjiaba, Beichuan. China Journal of Mountain of Science 14(11):13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-017-4516-7
Li XP, He SM, Luo Y, Wu Y (2012) Simulation of the sliding process of Donghekou landslide triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake using a distinct element method. Environ Earth Sci 65:1049–1054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-0953-8
Ma SY, Xu C, Xu XW, He XL, Qian HT, Jiao QS, Gao W, Yang HN, Gui YL, Zhang PF, Li K, Mo HR, Liu J, Liu XW (2020) Characteristics and causes of the landslide on July 23, 2019 in Shuicheng, Guizhou Province, China. Landslides 17:1441–1452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01374-x
Notti D, Wrzesniak A, Dematteis N, Lollino P, Fazio NL, Zucca F, Giordan D (2021) A multidisciplinary investigation of deep-seated landslide reactivation triggered by an extreme rainfall event: a case study of the Monesi di Mendatica landslide, Ligurian Alps. Springer Berlin Heidelberg 18(7):2341-2365.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01651-3
Song YX, Huang D, Cen DF (2016) Numerical modelling of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake-triggered Daguangbao landslide using a velocity and displacement dependent friction law. Eng Geol 215:50–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.11.003
Take WA, Bolton MD, Wong PCP, Yeung FJ (2004) Evaluation of landslide triggering mechanisms in model fill slopes. Landslides 1(3):173–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-004-0025-1
Wang FW, Dai ZL, Zhang S (2017) Experimental study on the motion behavior and mechanism of submarine landslides. Bull Eng Geol Env 77(3):1117–1126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1143-z
Wang G, Huang RQ, Lourenco SDN, Kamai T (2014) A large landslide triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan (M8.0) earthquake in Donghekou area: phenomena and mechanisms. Eng Geol 182(B):148–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.07.013
Xu WJ, Xu Q, Wang YJ (2013) The mechanism of high-speed motion and damming of the Tangjiashan landslide. Eng Geol 157:8–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.01.020
Yuan RM, Tang CL, Hu JC, Xu XW (2014) Mechanism of the Donghekou landslide triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake revealed by discrete element modeling. Nat Hazard 14(5):1195–1205. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-14-1195-2014
Zhang YS, Guo CB, Lan HX, Zhou NJ, Yao X (2015) Reactivation mechanism of ancient giant landslides in the tectonically active zone: a case study in Southwest China. Environ Earth Sci 74(2):1719–1729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4180-6
Zhao XY, Hu K, Burns SF, Hu HT (2019) Classification and sudden departure mechanism of high-speed landslides caused by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8083-9
Zhao YP, Xu M, Liu XS, Luo B (2021a) Study on the initiation mechanism of bedding rock landslide under seismic load. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 40(S1):2692–2700. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.1098
Zhao WH, Xia XL, Su XL, Liang QH, Liu XW, Ju NP (2021b) Movement process analysis of the high-speed long-runout Shuicheng landslide over 3-D complex terrain using a depth-averaged numerical model. Landslides 181:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01695-5
Zhou JW, Cui P, Fang H (2013) Dynamic process analysis for the formation of Yangjiagou landslide-dammed lake triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake, China. Landslides 10(3):331–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0387-3
Zou ZX, Tang HM, Xiong CR, Su AJ, Robert EC (2017) Kinetic characteristics of debris flows as exemplified by field investigations and discrete element simulation of the catastrophic Jiweishan rockslide, China. Geomorphology 295:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.06.012
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41772163).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Yue, G., Lin, H. et al. An improved inversion of Donghekou landslide considering “starting-elastic-impulsive” acceleration mechanism. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 375 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03402-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03402-1