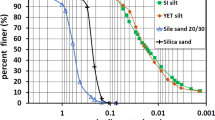
Abstract
The influence of groundwater on sandy dolomite stratum renders it highly susceptible to disasters, resulting in frequent water inrush accidents during tunnel construction. Advanced dewatering is crucial in enhancing tunnel face stability. It is found that sandy dolomite comprises a porous permeable medium consisting of dolomite sand and dolomite powder, characterized by low shear resistance and deformation resistance. Through the fluid–solid coupling model test device developed, it has been proven that the release of pore water pressure via advanced dewatering substantially enhances the stability of the tunnel face in water-rich sandy dolomite stratum prone to seepage failure. By conducting fluid–solid coupling analysis, the impact of drainage pipe length on the dewatering effect is investigated, and the improvement in tunnel face stability due to varying drainage pipe lengths is evaluated using the limit equilibrium analysis method. It is observed that drainage pipes reduce the range of slip body in front of the tunnel face and mitigate seepage forces by dissipating pore water pressure, consequently enhancing tunnel face stability and reducing extrusion deformation. However, there exists an efficiency limit regarding drainage pipe length. For initial water levels of 30, 50, 80, and 120 m, it is recommended to employ advanced drainage pipes of 20, 25, 30, and 40 m or more, respectively.























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper.
References
Anagnostou G (2012) The contribution of horizontal arching to tunnel face stability. Geotechnic 35:34–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/gete.201100024
Bischoff JL, Juliá R, Shanks WC III, Rosenbauer RJ (1994) Karstification without carbonic acid: bedrock dissolution by gypsum-driven dedolomitization. Geology 22:995–998. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022%3c0995:KWCABD%3e2.3.CO;2
Chen YY (2009) Study on grouting reinforcement technology of Karst Tunnel. Dissertation, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing (in Chinese)
Chen TM (2021) Surface dewatering excavation and soft foundation reinforcement technology for water-rich loess tunnel in Dongzhi Tableland: a case study of Yima No.1 Tunnel on Yinchuan-Xi’an High-Speed Railway. Tunnel Construction 41:1015–1023
He Y, Sun B, Wang M (2021) Study on stability of tunnel surrounding rock and precipitation disaster mitigation in flowing sand body. Geofluids 2021:6043807. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6043807
Hui H, Bowen Z, Yanyan Z et al (2018) The mechanism and numerical simulation analysis of water bursting in filling Karst Tunnel. Geotech Geol Eng 36:1197–1205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-017-0386-6
Huang Z, Li X, Li S, Zhao K, Xu H, Wu R (2018) Research and development of similar material for liquid-solid coupling and its application in tunnel water-inrush model test. J Cent South Univ (Science and Technology) 49(12):029–3039. https://doi.org/10.11817/j.issn.1672−7207.2018.12.017
Huang M, Li Y, Shi Z, Lu X (2022) Face stability analysis of shallow shield tunneling in layered ground under seepage flow. Tunn Undergr Space Tech 119:104201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2021.104201
Jiang Y, Zhou P, Zhou F et al (2022) Failure analysis and control measures for tunnel faces in water-rich sandy dolomite formations. Eng Fail Anal 138:106350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106350
Jin Q, Qi Y, Li Z et al (2022) Research and application of modified cement grouting materials for gushing water disaster in Karst Conduit. Geotech Geol Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02254-y
Li MG, Chen JJ, Xia XH et al (2020) Statistical and hydro-mechanical coupling analyses on groundwater drawdown and soil deformation caused by dewatering in a multi-aquifer-aquitard system. J Hydrol 589:125365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125365
Li S, Qi Y, Li Z et al (2021) A novel treatment method and construction technology of the pipeline gushing water geohazards in karst region. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 113:103939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2021.103939
Liu J, Chen W, Yuan J et al (2018) Groundwater control and curtain grouting for tunnel construction in completely weathered granite. Bull Eng Geol Env 77:515–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1003-x
Liu W, Zhu J, Zhang H et al (2022) Geological conditions of saturated soft loess stratum and influence of tunnel excavation and dewatering system on its groundwater environment. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81:128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02624-z
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China (2010) Code for design of concrete structures (GB 50010–2010), 1st edn. China architecture & building press, Beijing (in Chinese)
National Railway Administration of the People’s Republic of China (2016) Code for Design of Railway Tunnel (TB 10003–2016). China railway publishing house, Beijing (in Chinese)
Pan D, Li S, Xu Z et al (2019) Experimental and numerical study of the water inrush mechanisms of underground tunnels due to the proximity of a water-filled karst cavern. Bull Eng Geol Env 78:6207–6219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01491-5
Perazzelli P, Leone T, Anagnostou G (2014) Tunnel face stability under seepage flow conditions. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 43:459–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2014.03.001
Rivers JM, Kaczmarek SE (2020) Dologrus: the impact of meteoric-water-controlled diagenesis following early-marine dolomitization. Sedimentology 67:3317–3332. https://doi.org/10.1111/sed.12742
Sedghi MM, Zhan H (2021) On inflow to a tunnel in a fractured double-porosity aquifer. Groundwater 59:562–570. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.13079
Shi CH, Jiang J, Lei MF, Peng LM (2017) Optimal design of construction dewatering of underground engineering with the consideration of dynamic dewatering process. J Railw Sci Eng 14:1597–1605 https://doi.org/10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.2017.08.005
Wang K, Li SC, Zhang QS et al (2016) Development and application of new similar materials of surrounding rock for a fluid-solid coupling model test. Rock Soil Mech 37:2521–2533 https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2016.09.012
Wang M, Xu W, Mu H, Mi J, Wu Y, Wang Y (2022a) Study on construction and reinforcement technology of dolomite sanding tunnel. Sustainability 14:9217. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159217
Wang Y, Chen F, Sui W et al (2022b) Large-scale model test for studying the water inrush during tunnel excavation in fault. Bull Eng Geol Env 81:238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02733-9
Wang J, Long Y, Gao F et al (2022c) Transparent soil test evaluation of vertical–horizontal mixed curtain during dewatering. Acta Geotech 17:3293–3313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-021-01436-x
Wu GJ, Chen WZ, Yuan JQ, Yang DS, Bian HB (2017) Formation mechanisms of water inrush and mud burst in a migmatite tunnel: a case study in China. J Mt Sci 14:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-016-4070-8
Wu B, Sun WT, Cai GW, Meng GW (2022) Reliability analysis of shallow-buried tunnel construction adjacent to karst cave. Comput Geotech 145:104673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2022.104673.
Yang W, Fang Z, Yang X et al (2018) Experimental study of influence of karst aquifer on the law of water inrush in tunnels. Water 10:1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091211
Yang W, Fang Z, Wang H et al (2019) Analysis on water inrush process of tunnel with large buried depth and high water pressure. Processes 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7030134
Zhao W, Shen A, Qiao Z et al (2018) Genetic types and distinguished characteristics of dolomite and the origin of dolomite reservoirs. Pet Explor Dev 45:983–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30103-4
Zhang LX (2012) Study on formation mechanism and engineering characteristics of dolomite karst sanding, dissertation. Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu (in Chinese)
Zhang ZY, Wang ST, Wang LS (2016) Principles of engineering geological analysis. Geological publishing house, Beijing, China
Zhang J, Li S, Zhang Q et al (2019) Mud inrush flow mechanisms: a case study in a water-rich fault tunnel. Bull Eng Geol Env 78:6267–6283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01508-z
Zhang Y, Yi L, Zhang L et al (2022) Causation identification and control measures of deformation by integrated dewatering-excavation process simulation of a T-shaped deep foundation pit. Water 14:535. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040535
Zhao J, Tan Z, Wang X et al (2022) Engineering characteristics of water-bearing weakly cemented sandstone and dewatering technology in tunnel excavation. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 121:104316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2021.104316
Zhou P, Jiang Y, Zhou F et al (2022) Disaster mechanism of tunnel face with large section in sandy dolomite stratum. Eng Fail Anal 131:105905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105905
Zingg S, Anagnostou G (2018) Tunnel face stability and the effectiveness of advance drainage measures in water-bearing ground of non-uniform permeability. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51:187–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1312-1
Zou C, Lei SY, Zhang WX (2019) Dewatering model test of advanced deep hole in deep-buried tunnel. J Traffic Transp Eng 19:42–52 https://doi.org/10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2019.05.005
Funding
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant number 52278417] and the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST [Grant number 2022QNRC001].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Li, J., Zhou, F. et al. Study of advanced dewatering and its influence on tunnel in water rich and sandy dolomite stratum. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 364 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03381-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03381-3