Abstract
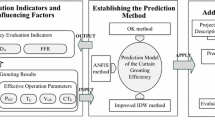
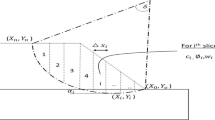
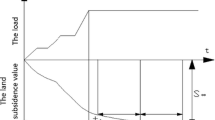
The operational safety of high-speed railways (HSRs) mainly relies on the flatness of their track surfaces. In recent years, continuous and stable subgrade uplift deformations in red-bed mudstone strata have occurred beneath several HSRs in southwest China, severely affecting the regular operation of HSRs. This study proposed a method for predicting the subgrade uplift intensity of the Chengdu-Chongqing passenger dedicated line (CCPDL) and determined the subgrade uplift mechanisms of the CCPDL through mudstone creep experiments, mineral composition analysis, and the statistical analysis of monitoring data on the uplift. Five parameters were selected as prediction indices, namely the excavation height of the subgrade center, dip angle, the characteristics of sandstone-mudstone interbeds, saturated uniaxial compressive strength, and mudstone expansibility. The weights of these five indices were determined using both subjective and objective weighting methods. The relationships between prediction indices and actual uplift intensities were analyzed using the ideal point method (IPM). Then, the optimal prediction model was proposed through precision and error analyses. Finally, the feasibility and applicability of the prediction model proposed in this study were verified through engineering case analyses. The prediction model proposed in this study can be used as a reference for similar engineering challenges in red-bed areas.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data supporting the findings of this study can be accessed upon request. Interested researchers are invited to contact the corresponding author.
References
Banimahd M, Woodward P, Kennedy J, Medero G (2013) Three-dimensional modelling of high speed ballasted railway tracks. Proc Inst Civil Eng-Transp 166(2):113–123
Chen NY, Liu Y, Chen HQ, Cheng JJ (2017) Detecting communities in social networks using label propagation with information entropy. Phys a-Stat Mech Its Appl 471:788–798
Dai ZJ, Guo JH, Yu F, Zhou Z, Li J, Chen SX (2021) Long-term uplift of high-speed railway subgrade caused by swelling effect of red-bed mudstone: case study in Southwest China. Bull Eng Geol Env 80(6):4855–4869
Diakoulaki D, Mavrotas G, Papayannakis L (1995) Determining Objective Weights in Multiple Criteria Problems - the Critic Method. Comput Oper Res 22(7):763–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0548(94)00059-H
Du H, Wang G, Deng GC, Cao C (2018) Modelling the effect of mudstone cuttings on rheological properties of KCl/Polymer water-based drilling fluid. J Pet Sci Eng 170:422–429
Eren M, Kadir S, Zucca C, Aksit I, Kaya Z, Kapur S (2014) Pedogenic manganese oxide coatings (calcium buserite) on fracture surfaces in Tortonian (Upper Miocene) red mudstones, southern Turkey. Catena 116:149–156
Feit GN, Malinnikova ON, Zykov VS, Rudakov VA (2002) Prediction of rockburst and sudden outburst hazard on the basis of estimate of rock-mass energy. J Min Sci 38(1):61–63
He F, Xu XN, Chen R, Zhu LY (2016) Interval efficiency improvement in DEA by using ideal points. Measurement 87:138–145
Hendry MT, Martin CD, Barbour SL (2013) Measurement of cyclic response of railway embankments and underlying soft peat foundations to heavy axle loads. Can Geotech J 50(5):467–480
Hillier S (2000) Accurate quantitative analysis of clay and other minerals in sandstones by XRD: comparison of a Rietveld and a reference intensity ratio (RIR) method and the importance of sample preparation. Clay Miner 35(1):291–302
Jia J, Yu F, Tan Y, Gao X (2021) Experimental investigations on rheological properties of mudstone in kilometer-deep mine. Advances in Civil Engineering 2021:6615379
Jian LM, Zhao XY, Wu J, et al (2022) Preparation, properties and grouting process simulation of cement-based grout for loose deposits. Constr Build Mater 360:129596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129596
Jiang G, Chen W, Liu X, Yuan S, Wu L, Zhang C (2018) Field study on swelling-shrinkage response of an expansive soil foundation under high-speed railway embankment loads. Soils Found 58(6):1538–1552
Jin K, Cheng YP, Wang L, Dong J, Guo PK, An FH, Jiang LM (2015) The effect of sedimentary redbeds on coalbed methane occurrence in the Xutuan and Zhaoji Coal Mines, Huaibei Coalfield, China. Int J Coal Geol 137:111–123
Larasati A, Yeh MY (2016) Does more attractive choice always decrease choice deferral? The moderating effect of ideal point. Int J Hosp Manag 54:43–51
Li AD, He Z, Zhang Y (2016) Bi-objective variable selection for key quality characteristics selection based on a modified NSGA-II and the ideal point method. Comput Ind 82:95–103
Li A, Niu F, Xia C et al (2019) Water migration and deformation during freeze-thaw of crushed rock layer in Chinese high-speed railway subgrade: Large scale experiments. Cold Reg Sci Technol 166:102841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2019.102841
Liu W, Chen J, Chen L et al (2022) Nonlinear deformation behaviors and a new approach for the classification and prediction of large deformation in tunnel construction stage: a case study. Eur J Environ Civil Eng 26(5):2008-2036. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2020.1744482
Lu Y, L Wang (2017) Effect of water and temperature on short-term and creep mechanical behaviors of coal measures mudstone. Environ Earth Sci 76(17):597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6941-x
Moore GD (1996) Improved Hamiltonian for Minkowski Yang-Mills theory. Nucl Phys B 480(3):689–726
Murray CA, Take WA, Hoult NA (2015) Measurement of vertical and longitudinal rail displacements using digital image correlation. Can Geotech J 52(2):141–155
Saaty TL (2004) Decision making — the analytic hierarchy and network processes (AHP/ANP). J Syst Sci Syst Eng 13(1):1–35
Shan Y, Albers B, Savidis SA (2013) Influence of different transition zones on the dynamic response of track-subgrade systems. Comput Geotech 48:21–28
Sun Q, Indraratna B, Nimbalkar S (2015) Deformation and degradation mechanisms of railway ballast under high frequency cyclic loading. J Geotech Geoenviron 142:04015056. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001375
SY/T 5163-2018 (2018) Analysis method for clay minerals and ordinary non-clay minerals in sedimentary rocks by the X-ray diffraction. People's Republic of China Oil and Gas Industry Standards. China Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing
Tan XD, Kodama KP, Chen HL, Fang DJ, Sun DJ, Li YA (2003) Paleomagnetism and magnetic anisotropy of cretaceous red beds from the Tarim basin, northwest China: Evidence for a rock magnetic cause of anomalously shallow paleomagnetic inclinations from central Asia. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 108(B2)
Tang AM, Cui YJ, Trinh VN, Szerman Y, Marchadier G (2009) Analysis of the railway heave induced by soil swelling at a site in southern France. Eng Geol 106(1-2):68–77
Wang R, Cheng JJ, Gao L, et al (2021) Research on the swelling mechanism of high-speed railway subgrade and the induced railway heave of ballastless tracks. Transportation Geotechnics 27:100470
Wang XG, Lian BQ, Wang JD, Feng WK, Gu TF (2020) Creep damage properties of sandstone under dry-wet cycles. J Mt Sci 17(12):3112–3122
Xi C, Han M, Hu X, et al (2022) Effectiveness of newmark-based sampling strategy for coseismic landslide susceptibility mapping using deep learning, support vector machine, and logistic regression. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81(5):174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02664-5
Xu C, Liu XL, Wang EZ, Zheng YL, Wang SJ (2018a) Rockburst prediction and classification based on the ideal-point method of information theory. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 81:382–390
Xu JB, Chen JP, Wu SL, Pan YH, Wang W, Luo QQ (2018b) Prediction of large deformation behavior in tunnels based on AHP-FUZZY method and numerical simulation method. Geotech Geol Eng 36(1):151–163
Xu C, Hu C, Liu X et al (2017) Information entropy in predicting location of observation points for long tunnel. Entropy 19(7):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19070332
Zhang LW, Zhang XY, Wu J, Zhao DK, Fu H (2020) Rockburst prediction model based on comprehensive weight and extension methods and its engineering application. Bull Eng Geol Env 79(9):4891–4903
Zhong ZB, Li AH, Deng RG, Wu PP, Wang K, Chen MH, Fu ZQ (2020) Study on time-dependent upheaval deformation mechanisms of red-bed soft rock subgrade of high-speed railways. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 39(02):327–340
Zhou H, Chen SK, Li HR, Liu T, Wang HL (2021) Rockburst prediction for hard rock and deep-lying long tunnels based on the entropy weight ideal point method and geostress field inversion: a case study of the Sangzhuling Tunnel. Bull Eng Geol Environ
Zhou KP, Lin Y, Hu JH, Zhou YL (2016) Grading prediction of rockburst intensity based on entropy and normal cloud model. Rock and Soil Mechanics 37:596–602
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments.
Funding
This study was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41672295).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, H., Zhao, X., Wünnemann, B. et al. A method for predicting the subgrade uplift intensity along a high-speed railway track in red-bed areas in China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 303 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03301-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03301-5