Abstract
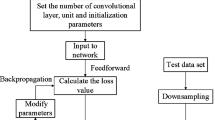
The recognition of tensile and shear cracks during hard rock cracking is critical for early warning of rockbursts in deep rock engineering. However, direct observation of cracking inside hard rocks by imaging equipment is difficult. A sound-based machine learning method for crack-type recognition in hard rock is therefore proposed. First, the sound signals of tensile and shear cracks in granite are obtained by Brazilian tension and shear tests, respectively. Then, the spectrogram conversion of the two kinds of signals is conducted to build a dataset. Next, a deep learning network EfficientNet is used to automatically extract the features of the spectrograms. Last, these deep learning–based features are used to construct a classification model of the crack types by a shallow machine learning method CatBoost. The experiments showed that the combination of two learning methods achieves high accuracy. We further validated the performance of the proposed method in laboratory cases involving biaxial and triaxial compression, as well as in real-world cases. The results indicate that the proposed method can accurately analyze the failure process of rocks by recognizing crack types. The proposed method is straightforward to implement and can provide a sound basis for making informed decisions on early warning of rockbursts.

























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The code used in the study is provided as supplementary material, while the supporting data is temporarily not publicly available due to the nature of the research.
References
Abadi M, Barham P, Chen J et al (2016) TensorFlow: a system for large-scale machine learning. Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Conference on Operating Systems Design and Implementation. USENIX Association, USA, pp 265–283. https://www.usenix.org/conference/osdi16/technical-sessions/presentation/abadi
Altman NS (1992) An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonparametric regression. Am Stat 46:175–185. https://doi.org/10.1080/00031305.1992.10475879
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Cai M, Kaiser PK, Morioka H et al (2007) FLAC/PFC coupled numerical simulation of AE in large-scale underground excavations. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 44:550–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.09.013
Chen J, Feng X (2006) True triaxial experimental study on rock with high geostress. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 25:1537–1543
Dahl GE, Yu D, Deng L, Acero A (2011) Context-dependent pre-trained deep neural networks for large-vocabulary speech recognition. IEEE Trans Audio, Speech, Lang Process 20:30–42. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2011.2134090
Du X, Cai Y, Wang S, Zhang L (2016) Overview of deep learning. 2016 31st Youth Academic Annual Conference of Chinese Association of Automation (YAC). IEEE, pp 159–164. https://doi.org/10.1109/YAC.2016.7804882
Farhidzadeh A, Mpalaskas AC, Matikas TE et al (2014) Fracture mode identification in cementitious materials using supervised pattern recognition of acoustic emission features. Constr Build Mater 67:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.05.015
Feng X, Zhang C, Chen B et al (2012) Dynamical control of rockburst evolution process. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 31:1983–1997. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.10.004
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 770–778. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Hinton G, Deng L, Yu D et al (2012) Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: the shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal Process Mag 29:82–97. https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2012.2205597
Hu X, Su G, Chen G et al (2019) Experiment on rockburst process of borehole and its acoustic emission characteristics. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:783–802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1613-z
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 7132–7141. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745
Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ (2017) Densely connected convolutional networks. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 2261–2269. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.243
Krizhevsky A, Hinton G (2009) Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. Technical report, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario. https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/learning-features-2009-TR.pdf
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2017) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun ACM 60:84–90. https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
Kumar BR, Vardhan H, Govindaraj M, Vijay G (2013) Regression analysis and ANN models to predict rock properties from sound levels produced during drilling. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 58:61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.10.002
Latif S, Rana R, Khalifa S, et al (2020) Deep representation learning in speech processing: challenges, recent advances, and future trends. arXiv preprint arXiv:200100378. https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.00378
Linares H (2012) Caso Estallido de Rocas. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S7Zy0V0C-VA. Accessed 22 Feb 2021
Łopatka K, Zwan P, Czyżewski A (2010) Dangerous sound event recognition using support vector machine classifiers. Advances in multimedia and network information system technologies. Springer, pp 49–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14989-4_5
Natekin A, Knoll A (2013) Gradient boosting machines, a tutorial. Front Neurorob 7:21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbot.2013.00021
Nilsback M-E, Zisserman A (2008) Automated flower classification over a large number of classes. 2008 Sixth Indian Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics & Image Processing. IEEE, pp 722–729. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICVGIP.2008.47
Phoon K-K, Ching J, Cao Z (2022) Unpacking data-centric geotechnics. Undergr Space 7:967–989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.undsp.2022.04.001
Phoon K-K, Zhang W (2022) Future of machine learning in geotechnics. Georisk: Assess Manage Risk Eng Syst Geohazards 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/17499518.2022.2087884
Prokhorenkova L, Gusev G, Vorobev A et al (2018) CatBoost: unbiased boosting with categorical features. Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 6639–6649. https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.5555/3327757.3327770
Purwins H, Li B, Virtanen T et al (2019) Deep learning for audio signal processing. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process 13:206–219. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTSP.2019.2908700
Qian Q (2012) Challenges faced by underground projects construction safety and countermeasures. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 31:1945–1956
Quinlan JR (1986) Induction of decision trees. Mach Learn 1:81–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00116251
Reynolds DA (2009) Gaussian mixture models. Encyclopedia of. Biometrics 741:659–663. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-73003-5_196
Rish I (2001) An empirical study of the naive Bayes classifier. IJCAI 2001 Workshop on Empirical Methods in Artificial Intelligence, pp 41–46. https://www.cc.gatech.edu/home/isbell/classes/reading/papers/Rish.pdf
Russenes BF (1974) Analyses of rockburst in tunnels in valley sides. M.S. thesis, Norwegian Institute of Technology. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?cluster=13704180236568480419
Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M et al (2018) Mobilenetv 2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp 4510–4520. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00474
Schuller B, Rigoll G, Lang M (2003) Hidden Markov model-based speech emotion recognition. 2003 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. p I–401. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME.2003.1220939
Sharif Razavian A, Azizpour H, Sullivan J, Carlsson S (2014) CNN features off-the-shelf: an astounding baseline for recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern. pp 512–519. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2014.131
Steinwart I, Christmann A (2008) Support vector machines. Springer, New York
Su G, Feng X, Wang J et al (2017a) Experimental study of remotely triggered rockburst induced by a tunnel axial dynamic disturbance under true-triaxial conditions. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50:2207–2226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1218-y
Su G, Jiang J, Zhai S, Zhang G (2017b) Influence of tunnel axis stress on strainburst: an experimental study. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50:1551–1567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1181-7
Su G, Shi Y, Feng X et al (2018) True-triaxial experimental study of the evolutionary features of the acoustic emissions and sounds of rockburst processes. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51:375–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1344-6
Su G, Gan W, Zhai S, Zhao G (2020) Acoustic emission precursors of static and dynamic instability for coarse-grained hard rock. J Cent South Univ 27:2883–2898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4516-6
Su G, Zhao G, Jiang J, Hu X (2021) Experimental study on the characteristics of microseismic signals generated during granite rockburst events. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80:6023–6045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02295-2
Su G, Huang J, Xu H, Qin Y (2022) Extracting acoustic emission features that precede hard rock instability with unsupervised learning. Eng Geol 306:106761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106761
Tan Y (1992) A new classifcation of rockburst intensity. Geol Rev 38:439–443. https://doi.org/10.16509/j.georeview.1992.05.007
Tan M, Le Q (2019) Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. International Conference on Machine Learning, pp 6105–6114. https://proceedings.mlr.press/v97/tan19a.html
Tan M, Chen B, Pang R et al (2019) Mnasnet: Platform-aware neural architecture search for mobile. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 2815–2823. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00293
Testa A, Gallo D, Langella R (2004) On the processing of harmonics and interharmonics: Using Hanning window in standard framework. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 19:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRD.2003.820437
Tokozume Y, Harada T (2017) Learning environmental sounds with end-to-end convolutional neural network. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp 2721–2725. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2017.7952651
Vacher M, Serignat J-F, Chaillol S (2007) Sound classification in a smart room environment: an approach using GMM and HMM methods. The 4th IEEE Conference on Speech Technology and Human-Computer Dialogue (SpeD 2007). Publishing House of the Romanian Academy, Bucharest, pp 135–146. https://hal.science/hal-00957418/document
Wang Q, Ju N, Du L et al (2016) Research on rockburst prediction and engineering measures of long and deep-lying tunnels. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 43:88–100. https://doi.org/10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2016.06.14
Wang C, Hou X, Liu Y (2021) Three-dimensional crack recognition by unsupervised machine learning. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54:893–903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02287-w
Yandex AB, Lempitsky V (2015) Aggregating local deep features for image retrieval. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp 1269–1277. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.150
Yang B, Qin S, Xue L et al (2017) A physical self-similarity law describing the accelerated failure behavior of rocks. Chin J Geophys 60:1746–1760. https://doi.org/10.6038/cjg20170512
Yosinski J, Clune J, Nguyen A et al (2015) Understanding neural networks through deep visualization. arXiv preprint arXiv:150606579. https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.06579
Zhang C, Feng X, Zhou H et al (2012) Case histories of four extremely intense rockbursts in deep tunnels. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45:275–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-011-0218-6
Zhang J, Phoon KK, Zhang D et al (2021) Deep learning-based evaluation of factor of safety with confidence interval for tunnel deformation in spatially variable soil. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 13:1358–1367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.09.001
Zhang H, Wu S, Zhang Z, Han L (2023) Rock joint roughness determination method based on deep learning of time–frequency spectrogram. Eng Appl Artif Intell 117:105505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105505
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 52169021 and 51869003), the Innovative Team and Outstanding Talent Program of Colleges and Universities in Guangxi (Grant No. 202006) and the Interdisciplinary Scientific Research Foundation of Guangxi University (Grant No. 2022JCA004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, G., Qin, Y., Xu, H. et al. A sound-based machine learning method for crack-type recognition in hard rock. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 252 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03291-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03291-4