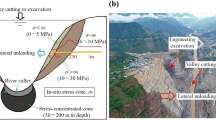
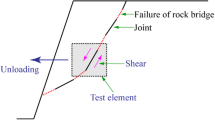
Abstract
The catastrophic mechanism of rock masses with discontinuities under excavations and river incisions is very complex. Based on this engineering background, a standard direct shear test under unloading normal stress is performed on sandstone specimens containing nonpersistent joints to investigate their shear behaviors. The results obtained are compared and discussed with those of conventional direct shear tests. An overall instantaneous coalescence under unloading conditions is presented on the rock bridge without a precursor, while the failure under loading conditions is a segmented progressive coalescence. This overall cracking behavior, driven by tensile damage, triggers a constant dilation rate. The cohesion is smaller and the internal friction angle is larger at a larger continuity factor under unloading conditions, while the relationship under loading conditions is the opposite. The evolution mechanism of the shear strength parameter affected by the continuity factor is revealed by analyzing the damage degree of the rock bridge per unit length. Interestingly, there is a polished and scratched area on the failure plane under unloading conditions, while the failure plane is smooth with some polishing without striated scratches under loading conditions. These failure plane characteristics reflect the basement sliding behavior of a rockslide. The striated scratch-like gullies are caused by tensile damage from the analysis of the microscopic three-dimensional topography. This investigation reveals the failure mechanism of rock masses under tensile-shear stress conditions.























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are within the paper.
References
Anderson TL (2005) Fracture mechanics: fundamentals and applications. CRC Taylor & Francis, New York
Asadizadeh M, Moosavi M, Hossaini MF, Masoumi H (2018) Shear strength and cracking process of non-persistent jointed rocks: an extensive experimental investigation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(2):415–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1328-6
Bahaaddini M, Sharrock G, Hebblewhite BK (2013) Numerical investigation of the effect of joint geometrical parameters on the mechanical properties of a non-persistent jointed rock mass under uniaxial compression. Comput Geotech 49:206–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2012.10.012
Bai Q, Young RP (2020) Numerical investigation of the mechanical and damage behaviors of veined gneiss during true-triaxial stress path loading by simulation of in situ conditions. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(1):133–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01898-2
Ban LR, Du WS, Jin TW, Qi CZ, Li XZ (2021) A roughness parameter considering joint material properties and peak shear strength model for rock joints. Int J Min Sci Technol 31(3):413–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2021.03.007
Barton N (1973) Review of a new shear-strength criterion for rock joints. Eng Geol 7:287–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(73)90013-6
Cai M, Kaiser PK (2005) Assessment of excavation damaged zone using a micromechanics model. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 20(4):301–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2004.12.002
Chen GQ, Li TB, Zhang GF, Yin HY, Zhang H (2014) Temperature effect of rock burst for hard rock in deep-buried tunnel. Nat Hazards 72(2):915–926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1042-6
Chen ZQ, He C, Ma GY, Xu GW, Ma CC (2019) Energy damage evolution mechanism of rock and its application to brittleness evaluation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(4):1265–1274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1681-0
Chen GQ, Tang P, Huang RQ, Wang D (2020a) Critical tension crack depth in rockslides that conform to the three-section mechanism. Landslides 18(1):79–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01471-x
Chen QZ, Liu YM, Pu SY (2020b) Strength characteristics of nonpenetrating joint rock mass under different shear conditions. Adv Civ Eng 2020:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3579725
Chen GQ, Li H, Tao Wei, Zhu J (2021) Searching for multistage sliding surfaces based on the discontinuous dynamic strength reduction method. Eng Geol 286:106086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106086
Cheng Y, Wong LNY, Zou CJ (2015) Experimental study on the formation of faults from en-echelon fractures in Carrara Marble. Eng Geol 195:312–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.06.004
Du YT, Li TC, Li WT, Ren YD, Wang G, He P (2020) Experimental study of mechanical and permeability behaviors during the failure of sandstone containing two preexisting fissures under triaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(8):3673–3697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02119-x
Eberhardt E, Stead D, Coggan JS (2004) Numerical analysis of initiation and progressive failure in natural rock slopes-the 1991 Randa rockslide. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(1):69–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00076-5
Einstein HH (2021) Fractures: tension and shear. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54(7):3389–3408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02243-8
Einstein HH, Veneziano D, Baecher GB, O’Reilly KJ (1983) The effect of discontinuity persistence on rock slope stability. Int J Rock Mech Sci Geomech Abstr 20(5):227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(83)90003-7
Fan X, Kulatilake PHSW, Chen X (2015) Mechanical behavior of rock-like jointed blocks with multi-non-persistent joints under uniaxial loading: a particle mechanics approach. Eng Geol 190:17–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.02.008
Feng XT, Ding WX (2007) Experimental study of limestone micro-fracturing under a coupled stress, fluid flow and changing chemical environment. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 44(3):437–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.07.012
Feng XT, Yang CX, Kong R, Zhao J, Zhou YY, Yao ZB, Hu L (2021) Excavation-induced deep hard rock fracturing: methodology and applications. J Rock Mech Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.12.003
Gao L, Gao F, Zhang ZZ, Xing Y (2020) Research on the energy evolution characteristics and the failure intensity of rocks. Int J Min Sci Techno 30(5):705–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2020.06.006
Gehle C, Kutter HK (2003) Breakage and shear behaviour of intermittent rock joints. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40(5):687–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00060-1
Ghazvinian A, Sarfarazi V, Schubert W, Blumel M (2012) A study of the failure mechanism of planar non-persistent open joints using PFC2D. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45(5):677–693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0233-2
Guo SF, Qi SW, Zhan ZF, Zheng BW (2017) Plastic-strain-dependent strength model to simulate the cracking process of brittle rocks with an existing non-persistent joint. Eng Geol 231:114–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.10.008
Hajiabdolmajid V, Kaiser PK, Martin CD (2003) Mobilised strength components in brittle failure of rock. Geotechnique 53(3):327–336. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.53.3.327.37280
Hu W, McSaveney MJ (2018) A polished and striated pavement formed by a rock avalanche in under 90 s mimics a glacially striated pavement. Geomorphology 320:154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.08.011
Huang RQ (2008) Geodynamical process and stability control of high rock slope development. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 27(8):1525–1544. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.08.002 (in Chinese)
Huang RQ (2012a) Mechanisms of large-scale landslides in China. B Eng Geol Environ 71(1):161–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-011-0403-6
Huang RQ (2012b) Engineering geology for high rock slopes. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Huang RQ, Huang D (2014) Evolution of rock cracks under unloading condition. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47(2):453–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0429-0
Huang D, Li YR (2014) Conversion of strain energy in triaxial unloading tests on marble. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 66:160–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2013.12.001
Huang D, Gu DM, Yang C, Huang RQ, Fu GY (2016) Investigation on mechanical behaviors of sandstone with two preexisting flaws under triaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(2):375–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0757-3
Huang D, Guo YQ, Cen DF, Zhong Z, Song YX (2020) Experimental investigation on shear mechanical behavior of sandstone containing a pre-existing flaw under unloading normal stress with constant shear stress. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(8):3779–3792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02136-w
ISRM (2015) ISRM suggested methods for rock characterization, testing and monitoring: 2007–2014. Springer, Cham, Switzerland
Jennings JE (1970) A mathematical theory for the calculation of the stability of open cut mines. In: Johannesburg (ed) Proceedings of the symposium on the theoretical background to the planning of open pit mines. AA Balkema Cape Town, pp 87–102
Ji YL, Wu W, Zhao ZH (2019) Unloading-induced rock fracture activation and maximum seismic moment prediction. Eng Geol 262:105352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105352
Kemeny J (2003) The time-dependent reduction of sliding cohesion due to rock bridges along discontinuities: a fracture mechanics approach. Rock Mech Rock Eng 36(1):27–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-002-0032-2
Lajtai EZ (1969) Shear strength of weakness planes in rock. Int J Rock Mech Sci Geomech Abstr 6(5):499–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(69)90016-3
Lee H, Jeon S (2011) An experimental and numerical study of fracture coalescence in pre-cracked specimens under uniaxial compression. Int J Solids Struct 48(6):979–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2010.12.001
Li HQ, Wong LNY (2012) Influence of flaw inclination angle and loading condition on crack initiation and propagation. Int J Solids Struct 49(18):2482–2499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2012.05.012
Li SY, He TM, Yin XC (2010) The introduction of rock fracture mechanics. University of Science and Technology of China Press, Hefei (in Chinese)
Li ZG, Xu GL, Dai YY, Zhao X, Fu YP (2021) Effects of foliation on deformation and failure mechanism of silty slates. Int J Rock Mech Min 141:104703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104703
Lin H, Ding X, Yong R et al (2019) Effect of non-persistent joints distribution on shear behavior. CR Mecanique 347(6):477–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crme.2019.05.001
Liu YM, Chen QZ, Chen HY, Ou X, Wu DF, Tian XC (2021) Experimental study on influence of joint surface morphology on strength and deformation of nonthrough jointed rock masses under direct shear. Adv Civ Eng 2021:2581382. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2581382
Malmgren L, Saiang D, Töyrä J, Bodare A (2007) The excavation disturbed zone (EDZ) at Kiirunavaara mine, Sweden-by seismic measurements. J Appl Geophys 61(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2006.04.004
Martin CD, Chandler NA (1994) The progressive fracture of Lac du Bonnet granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 31(6):643–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(94)90005-1
Massey CI, Petley DN, McSaveney MJ (2013) Patterns of movement in reactivated landslides. Eng Geol 159:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.03.011
Meng FZ, Zhou H, Wang ZQ, Zhang CQ, Li SJ, Zhang LM, Kong L (2018) Characteristics of asperity damage and its influence on the shear behavior of granite joints. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(2):429–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1315-y
Meng FZ, Wong LNY, Zhou H, Wang ZQ, Zhang LM (2020) Asperity degradation characteristics of soft rock-like fractures under shearing based on acoustic emission monitoring. Eng Geol 266:105392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105392
Sarfarazi V, Ghazvinian A, Schubert W, Blumel M, Nejati HR (2014) Numerical simulation of the process of fracture of echelon rock joints. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47(4):1355–1371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0450-3
Sarfarazi V, Haeri H, Shemirani AB, Zhu Z (2017) Shear behavior of non-persistent joint under high normal load. Strength Mater 49(2):320–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11223-017-9872-6
Schuster K, Alheid HJ, Böddener D (2001) Seismic investigation of the Excavation damaged zone in Opalinus Clay. Eng Geol 61(2–3):189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(01)00054-0
Shi H, Zhang HQ, Song L (2020) Evolution of sandstone shear strength parameters and its mesoscopic mechanism. Geomech Eng 20(1):29–41. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2019.20.1.029
Tang P, Chen GQ, Huang RQ, Zhu J (2020) Brittle failure of rockslides linked to the rock bridge length effect. Landslides 17(4):793–803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01323-3
Tian JJ, Xu DJ, Liu TH (2020) An experimental investigation of the fracturing behaviour of rock-like materials containing two V-shaped parallelogram flaws. Int J Min Sci Technol 30(6):777–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2020.07.002
Twidale CR (1973) On the origin of sheet jointing. Rock Mech Rock Eng 5:163–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01238046
Vazaios I, Vlachopoulos N, Diederichs MS (2019) Assessing fracturing mechanisms and evolution of excavation damaged zone of tunnels in interlocked rock masses at high stresses using a finite-discrete element approach. J Rock Mech Geotech 11(4):701–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2019.02.004
Vergara MR, Jan MV, Lorig L (2016) Numerical model for the study of the strength and failure modes of rock containing non-persistent joints. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(4):1211–1226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0824-9
Wong RHC, Chau KT (1998) Crack coalescence in rock-like material containing two cracks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 35:147–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0148-9062(97)00303-3
Wong RHC, Leung WL, Wang SW (2001) Shear strength studies on rock-like models containing arrayed open joints. DC Rocks 2001–38th U.S. Symposium on Rock Mechanics (USRMS). OnePetro
Wu FQ, Liu T, Liu JY, Tang XL (2009) Excavation unloading destruction phenomena in rock dam foundations. B Eng Geol Environ 68(2):257–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-009-0202-5
Wu W, Zou Y, Li X, Zhao J (2014) An unload-induced direct-shear model for granular gouge friction in rock discontinuities. Rev Sci Instrum 85(9):093902. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4894207
Wu LZ, Li B, Huang RQ, Wang QZ (2016) Study on Mode I-II hybrid fracture criteria for the stability analysis of sliding overhanging rock. Eng Geol 209:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.04.022
Wu W, Zhao ZH, Duan K (2017) Unloading-induced instability of a simulated granular fault and implications for excavation-induced seismicity. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 63:154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2017.01.002
Xie HP, Ju Y, Li LY (2005) Criteria for strength and structural failure of rocks based on energy dissipation and release principles. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 24:3003–3010. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.17.001 (in Chinese)
Yang XX, Kulatilake PHSW (2019) Laboratory investigation of mechanical behavior of granite samples containing discontinuous joints through direct shear tests. Arab J Geosci 12(3):79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4278-3
Yang SQ, Huang YH, Tian WL, Yin PF, Jing HW (2019a) Effect of high temperature on deformation failure behavior of granite specimen containing a single fissure under uniaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(7):2087–2107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1725-5
Yang SQ, Yin PF, Zhang YC, Chen M, Zhou XP, Jing HW, Zhang QY (2019b) Failure behavior and crack evolution mechanism of a non-persistent jointed rock mass containing a circular hole. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 114:101–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.12.017
Yong R, Ye J, Li B, Du SG (2018) Determining the maximum sampling interval in rock joint roughness measurements using Fourier series. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 101:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.11.008
Zhang XP, Wong LNY (2013) Crack initiation, propagation and coalescence in rock-like material containing two flaws: a numerical study based on bonded-particle model approach. Rock Mech Rock Eng 46(5):1001–1021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0323-1
Zhang HQ, Tannant DD, Jing HW, Nunoo S, Niu SJ, Wang SY (2015) Evolution of cohesion and friction angle during microfracture accumulation in rock. Nat Hazards 77(1):497–510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1592-2
Zhang K, Cao P, Ma G, Wang W, Fan W, Li K (2016) Strength, fragmentation and fractal properties of mixed flaws. Acta Geotech 11(4):901–912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-015-0403-y
Zhao YL, Zhang LY, Wang WJ, Pu CZ, Wan W, Tang JZ (2016) Cracking and stress–strain behavior of rock-like material containing two flaws under uniaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(7):2665–2687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-0932-1
Zhao WH, Frost JD, Huang RQ, Yan M, Jin LD (2017a) Distribution and quantitative zonation of unloading cracks at a proposed large hydropower station dam site. J Mt Sci-Engl 14(10):2106–2121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-017-4431-y
Zhao YL, Zhang LY, Wang WJ, Tang JZ, Lin H, Wan W (2017b) Transient pulse test and morphological analysis of single rock fractures. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 91:139–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.11.016
Zhong Z, Huang D, Zhang YF, Ma GW (2020) Experimental study on the effects of unloading normal stress on shear mechanical behaviour of sandstone containing a parallel fissure pair. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(4):1647–1663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01997-0
Zhou XP, Cheng H, Feng YF (2014) An experimental study of crack coalescence behaviour in rock-like materials containing multiple flaws under uniaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47(6):1961–1986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0511-7
Zhou XP, Bi J, Qian QH (2015) Numerical simulation of crack growth and coalescence in rock-like materials containing multiple pre-existing flaws. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48(3):1097–1114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-014-0627-4
Zhu TT, Huang D (2019) Experimental investigation of the shear mechanical behavior of sandstone under unloading normal stress. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 114:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.01.003
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41972284 and 42090054) and the State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection Independent Research Project (SKLGP2020Z005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, C., Chen, G., Li, T. et al. Shear behaviors of rock masses containing nonpersistent joints affected by normal stress rebound under excavations and river incisions. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 171 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03209-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03209-0