Abstract
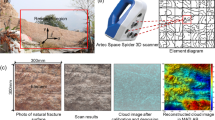
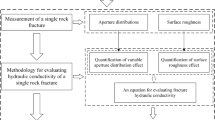
Fracture surface morphology, mechanical and hydraulic properties are related to fracture size. One of the core issues in the size effect is the representative elementary surface, which determines the size of the test specimens in the laboratory and facilitates the application of test results to the field. In this study, the size effect on surface morphology and permeability of rock fractures is investigated, and the representative elementary surface size for the surface morphology and the permeability was determined based on the asperity height data of fracture surfaces obtained by 3D laser scanning in the field. The roughness of fracture surfaces varies significantly at small fracture surface sizes. As the fracture surface size continues to increase, the fracture surface roughness tended toward a relatively stable state. The critical size for fracture surface roughness stability in the study, which is called the representative elementary surface, is 300–400 mm. The size effect on the permeability of rock fractures was investigated, and the results show that fracture permeability tended toward a relatively stable state with increasing fracture size, which was the same as the fracture surface roughness. The representative elementary surface size for fracture permeability is less than 100 mm in the study, which is also less than that for fracture surface roughness with the same coefficient of variation. This result indicated that a lower coefficient of variation might provide the best estimate of the representative elementary surface for fracture permeability compared with the fracture surface roughness.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alameda-Hernández P, Jiménez-Perálvarez J, Palenzuela JA, El Hamdouni R, Irigaray C, Cabrerizo MA, Chacón J (2014) Improvement of the JRC calculation using different parameters obtained through a new survey method applied to rock discontinuities. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47:2047–2060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0532-2
Babanouri N, Karimi Nasab S, Sarafrazi S (2013) A hybrid particle swarm optimization and multi-layer perceptron algorithm for bivariate fractal analysis of rock fractures roughness. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 60:66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.12.028
Baghbanan A, Jing L (2007) Hydraulic properties of fractured rock masses with correlated fracture length and aperture. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 44:704–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.11.001
Barton N (1973) Review of a new shear-strength criterion for rock joints. Eng Geol 7:287–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(73)90013-6
Belem T, Homand-Etienne F, Souley M (2000) Quantitative parameters for rock joint surface roughness. Rock Mech Rock Eng 33:217–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s006030070001
Berkowitz B (2002) Characterizing flow and transport in fractured geological media: a review. Adv Water Resour 25:861–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0309-1708(02)00042-8
Brown SR (1987) Fluid flow through rock joints: the effect of surface roughness. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 92:1337–1347. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB092iB02p01337
Brown SR, Scholz CH (1985) Broad bandwidth study of the topography of natural rock surfaces. J Geophys Re Solid Earth 90:12575–12582. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB090iB14p12575
Chen S, Zhu w, Liu S, Zhang F, Guo L (2015a) Anisotropy and Size Effects of Surface Roughness of Rock Joints. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 34:57–66
Chen SJ, Zhu WC, Yu QL, Liu XG (2016) Characterization of anisotropy of joint surface roughness and aperture by variogram approach based on digital image processing technique. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49:855–876. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0795-x
Chen T, Feng X-T, Cui G, Tan Y, Pan Z (2019) Experimental study of permeability change of organic-rich gas shales under high effective stress. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 64:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2019.01.014
Chen Y-F, Zhou J-Q, Hu S-H, Hu R, Zhou C-B (2015b) Evaluation of Forchheimer equation coefficients for non-Darcy flow in deformable rough-walled fractures. J Hydrol 529:993–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.09.021
Dou Z, Sleep B, Zhan H, Zhou Z, Wang J (2019) Multiscale roughness influence on conservative solute transport in self-affine fractures. Int J Heat Mass Transf 133:606–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.12.141
Esmaieli K, Hadjigeorgiou J, Grenon M (2010) Estimating geometrical and mechanical REV based on synthetic rock mass models at Brunswick Mine. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47:915–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.05.010
Fakhimi A, Gharahbagh EA (2011) Discrete element analysis of the effect of pore size and pore distribution on the mechanical behavior of rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 48:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.08.007
Fardin N, Stephansson O, Jing LR (2001) The scale dependence of rock joint surface roughness. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 38:659–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(01)00028-4
Feng P, Zhao J, Dai F, Wei M, Liu B (2022) Mechanical behaviors of conjugate-flawed rocks subjected to coupled static–dynamic compression. Acta Geotech 17:1765–1784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-021-01322-6
Giwelli AA, Sakaguchi K, Matsuki K (2009) Experimental study of the effect of fracture size on closure behavior of a tensile fracture under normal stress. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46:462–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.11.008
Huang N, Jiang Y, Liu R, Li B (2017) Estimation of permeability of 3-D discrete fracture networks: an alternative possibility based on trace map analysis. Eng Geol 226:12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.05.005
Huang NA, Jiang Y, Liu R, Xia Y (2018) Size effect on the permeability and shear induced flow anisotropy of fractal rock fractures. Fractals 26:1840001. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218348X18400017
Jing L, Stephansson O (2007) Fundamentals of discrete element method for engineering: Theory and Applications. Elsevier Science
Koyama T, Jing L (2007) Effects of model scale and particle size on micro-mechanical properties and failure processes of rocks—a particle mechanics approach. Eng Anal Bound Elem 31:458–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2006.11.009
Kulatilake PHSW, Balasingam P, Park J, Morgan R (2006) Natural rock joint roughness quantification through fractal techniques. Geotech Geol Eng 24:1181–1202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-005-1219-6
Lei Q, Latham J-P, Tsang C-F, Xiang J, Lang P (2015) A new approach to upscaling fracture network models while preserving geostatistical and geomechanical characteristics. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 120:4784–4807. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JB011736
Li B, Mo Y, Zou L, Liu R, Cvetkovic V (2020a) Influence of surface roughness on fluid flow and solute transport through 3D crossed rock fractures. J Hydrol 582:124284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124284
Li Y, Sun S, Yang H (2020b) Scale dependence of waviness and unevenness of natural rock joints through fractal analysis. Geofluids 2020:8818815. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8818815
Li Y, Zhang Y (2015) Quantitative estimation of joint roughness coefficient using statistical parameters. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 77:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.03.016
Liang Z, Wu N, Li Y, Li H, Li W (2019) Numerical study on anisotropy of the representative elementary volume of strength and deformability of jointed rock masses. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:4387–4402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01859-9
Lin H, Xie S, Yong R, Chen Y, Du S (2019) An empirical statistical constitutive relationship for rock joint shearing considering scale effect. Comptes Rendus Mécanique 347:561–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crme.2019.08.001
Liu J, Wang Z, Qiao L, Li W, Yang J (2021) Transition from linear to nonlinear flow in single rough fractures: effect of fracture roughness. Hydrogeol J 29:1343–1353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-020-02297-6
Liu R, Huang N, Jiang Y, Jing H, Yu L (2020) A numerical study of shear-induced evolutions of geometric and hydraulic properties of self-affine rough-walled rock fractures. Int J Rock Mech Mining Sci 127:104211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104211
Liu R, Li B, Jiang Y, Huang N (2016) Review: Mathematical expressions for estimating equivalent permeability of rock fracture networks. Hydrogeol J 24:1623–1649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-016-1441-8
Liu R, Yu L, Jiang Y, Wang Y, Li B (2017) Recent developments on relationships between the equivalent permeability and fractal dimension of two-dimensional rock fracture networks. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 45:771–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2017.06.013
Luo S, Zhao Z, Peng H, Pu H (2016) The role of fracture surface roughness in macroscopic fluid flow and heat transfer in fractured rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 87:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.05.006
Nigon B, Englert A, Pascal C, Saintot A (2017) Multiscale characterization of joint surface roughness. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 122:9714–9728. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JB014322
Odling NE (1994) Natural fracture profiles, fractal dimension and joint roughness coefficients. Rock Mech Rock Eng 27:135–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01020307
Özvan A, Dinçer İ, Acar A, Özvan B (2014) The effects of discontinuity surface roughness on the shear strength of weathered granite joints. Bull Eng Geol Env 73:801–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-013-0560-x
Pandey SN, Vishal V, Chaudhuri A (2018) Geothermal reservoir modeling in a coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical approach: a review. Earth-Sci Rev 185:1157–1169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.09.004
Qian J, Zhan H, Luo S, Zhao W (2007) Experimental evidence of scale-dependent hydraulic conductivity for fully developed turbulent flow in a single fracture. J Hydrol 339:206–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.03.015
Raven KG, Gale JE (1985) Water Flow in a Natural Rock Fracture as a Function of Stress and Sample Size. Int J Rock Mech Mining Sci Geomecha Abstracts 22:251–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(85)92952-3
Rong G, Peng J, Wang X, Liu G, Hou D (2013) Permeability tensor and representative elementary volume of fractured rock masses. Hydrogeol J 21:1655–1671. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-013-1040-x
Singh H, Cai J (2018) Screening improved recovery methods in tight-oil formations by injecting and producing through fractures. Int J Heat Mass Transf 116:977–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.09.071
Song L, Jiang Q, Li L-f, Liu C, Liu X-p, Xiong J (2020) An Enhanced Index for Evaluating Natural Joint Roughness Considering Multiple Morphological Factors Affecting the Shear Behavior. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:2037–2057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01700-1
Song L, Jiang Q, Li Y, Yang C, Zhong S, ZHang M (2017) Study on the Stability of Statistical Parameters of the Rock Nature Discontinuities Morphology and Anisotropic Based on Different Interval Point-Cloud Data. Rock Soil Mech 38:1–13
Sutopo, Arihara N, Sato K, Abbaszadeh M (2002) Representative elementary volume of naturally fractured reservoirs evaluated by flow simulation. J Jpn Pet Inst 45:156–168. https://doi.org/10.1627/jpi.45.156
Tatone BSA, Grasselli G (2010) A new 2D discontinuity roughness parameter and its correlation with JRC. Int J Rock Mech Mining Sci 47:1391–1400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.06.006
Thomas TR (1981) Characterization of Surface Roughness Precision Engineering 3:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-6359(81)90043-X
Tsang YW, Witherspoon PA (1983) The dependence of fracture mechanical and fluid flow properties on fracture roughness and sample size. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 88:2359–2366. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB088iB03p02359
Ueng T-S, Jou Y-J, Peng IH (2010) Scale effect on shear strength of computer-aided-manufactured joints. J GeoEng 5:29–37. https://doi.org/10.6310/jog.2010.5(2).1
Vogler D, Settgast RR, Annavarapu C, Madonna C, Bayer P, Amann F (2018) Experiments and simulations of fully hydro-mechanically coupled response of rough fractures exposed to high-pressure fluid injection. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 123:1186–1200. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JB015057
Wang C, Jiang Y, Liu R, Wang C, Zhang Z, Sugimoto S (2020) Experimental study of the nonlinear flow characteristics of fluid in 3D rough-walled fractures during shear process. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:2581–2604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02068-5
Wang M, Chen Y-F, Ma G-W, Zhou J-Q, Zhou C-B (2016) Influence of surface roughness on nonlinear flow behaviors in 3D self-affine rough fractures: lattice Boltzmann simulations. Adv Water Resour 96:373–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.08.006
Wang Z, Li W, Bi L, Qiao L, Liu R, Liu J (2018a) Estimation of the REV size and equivalent permeability coefficient of fractured rock masses with an emphasis on comparing the radial and unidirectional flow configurations. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51:1457–1471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1422-4
Wang Z, Li W, Qiao L, Liu J, Yang J (2018b) Hydraulic properties of fractured rock mass with correlated fracture length and aperture in both radial and unidirectional flow configurations. Comput Geotech 104:167–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2018.08.017
Wei M, Dai F, Liu Y, Jiang R (2022) A fracture model for assessing tensile mode crack growth resistance of rocks. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.03.001
Wei M, Dai F, Liu Y, Li A, Yan Z (2021) Influences of loading method and notch type on rock fracture toughness measurements: from the perspectives of t-stress and fracture process zone. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54:4965–4986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02541-9
Witherspoon PA, Wang JSY, Iwai K, Gale JE (1980) Validity of Cubic Law for fluid flow in a deformable rock fracture. Water Resour Res 16:1016–1024. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR016i006p01016
Wu C, Chu J, Wu S, Hong Y (2019) 3D characterization of microbially induced carbonate precipitation in rock fracture and the resulted permeability reduction. Eng Geol 249:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.12.017
Yan F, Ban L, Qi C, Shan R, Yuan H (2020) Research on the anisotropy, size effect, and sampling interval effect of joint surface roughness. Arab J Geosci 13:399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05330-w
Yang ZY, Di CC, Yen KC (2001) The effect of asperity order on the roughness of rock joints. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 38:745–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(01)00032-6
Young NL, Simpkins WW, Reber JE, Helmke MF (2020) Estimation of the representative elementary volume of a fractured till: a field and groundwater modeling approach. Hydrogeol J 28:781–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-019-02076-y
Zhang G, Karakus M, Tang H, Ge Y, Zhang L (2014) A new method estimating the 2D Joint Roughness Coefficient for discontinuity surfaces in rock masses. Int J Rock Mech Mining Sci 72:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.09.009
Zhao L et al (2020) A practical photogrammetric workflow in the field for the construction of a 3D rock joint surface database. Eng Geol 279:105878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105878
Zhao L, Zhang S, Huang D, Zuo S, Li D (2018) Quantitative characterization of joint roughness based on semivariogram parameters. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 109:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.06.008
Zou L, Håkansson U, Cvetkovic V (2020) Radial propagation of yield-power-law grouts into water-saturated homogeneous fractures. Int J Rock Mech Mining Sci 130:104308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104308
Zou L, Jing L, Cvetkovic V (2015) Roughness decomposition and nonlinear fluid flow in a single rock fracture. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 75:102–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.01.016
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China with No. 42177157 and 51779045, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities with Nos. N2001025, N2001026 and N2101005, Applied Basic Research Program of Liaoning Province with No. 2022020363-JH2/1013, Innovative Talents Support Program of Sciences & Technologies of Shenyang Young and Middle-aged Scientists with No. RC210405, and Shenyang Science and Technology Program with No. 22-322-3-17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Wang, Z., Qiao, L. et al. Representative elementary surface for morphology and permeability of natural rock fractures. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 159 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03184-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03184-6