Abstract
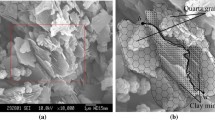
The grouting reinforcement strength of fracture surface is closely related to the microscopic behavior of slurry-rock interface. In this work, the spreading and penetration dynamics of nanosilica sol (NSS) droplets on granite, sandstone, and marble which cover the main types of rocks in nature were studied by experiments and numerical simulations. The control experiments were carried out by changing NSS and rock into distilled water and impermeable steel. The results show that the spreading behavior of granite and sandstone are similar because they are both porous rocks with similar mineral compositions. Based on the experimental data, two new scaling laws describing the maximum spreading factor as a function of the Reynolds number and the Weber number were proposed. The numerical models are validated against experimental data at the same condition. Following that, a parametric study is undertaken at various velocities, droplet initial diameters, equilibrium contact angles, porosity, and roughness. As the contact angle varies from 30° to 150°, the maximum spreading factor has a decrease of 49.7%, while the dimensionless penetration depth increases after decreasing. When the porosity ranges from 0.2 to 0.4, the dimensionless penetration depth has a significant increase of 138.7%. Besides, the dimensionless penetration depth increases after decreasing as the roughness gets higher. The results also show that the penetration depth has a negative correlation with the maximum spreading factor which reveals that there is a competitive mechanism of spreading and penetration.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek S, Yong K (2020) Impact dynamics on SLIPS: effects of liquid droplet’s surface tension and viscosity. Appl Surf Sci 506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144689
Bouchard DJ, Chandra S (2020) Infiltration of impacting droplets into porous substrates. Exp Fluids 61(11). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-020-03056-9
Brackbill JU, Kothe DB, Zemach C (1992) A continuum method for modeling surface tension. J Comput Phys 100(2):335–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9991(92)90240-y
Cetiner A, Evren B, Budakli M, Arik M, Ozbek A (2020) Spreading behavior of droplets impacting over substrates with varying surface topographies. Colloids Surf A:606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125385
Clanet C, BÉGuin C, Richard D, QuÉRÉ D (2004) Maximal deformation of an impacting drop. J Fluid Mech 517:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022112004000904
Davis SH, Hocking LM (1999) Spreading and imbibition of viscous liquid on a porous base. Phys Fluids 11(1):48–57. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.869901
Deendarlianto TY, Kohno M, Hidaka S, Wakui T, Majid AI, Widyaparaga A (2016) The effects of the surface roughness on the dynamic behavior of the successive micrometric droplets impacting onto inclined hot surfaces. Int J Heat Mass Transf 101:1217–1226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.05.132
Du Y, Liu J, Li Y, Du J, Wu X, Min Q (2021) Numerical study on droplets impacting solid spheres: effect of fluid properties and sphere diameter. Colloids Surf A:625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126862
Eggers J, Fontelos MA, Josserand C, Zaleski S (2010) Drop dynamics after impact on a solid wall: theory and simulations. Phys Fluids 22(6). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3432498
Fu F, Li P, Wang K, Wu R (2019) Numerical simulation of sessile droplet spreading and penetration on porous substrates. Langmuir 35(8):2917–2924. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b03472
Gothäll R, Stille H (2009) Fracture dilation during grouting. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 24(2):126–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2008.05.004
Guo C, Sun Y, Zhao D (2021) Experimental study of droplet impact on superheated cylindrical surfaces. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2020.110263
Hapgood KP, Litster JD, Biggs SR, Howes T (2002) Drop penetration into porous powder beds. J Colloid Interface Sci 253(2):353–366. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2002.8527
Holman RK, Cima MJ, Uhland SA, Sachs E (2002) Spreading and infiltration of inkjet-printed polymer solution droplets on a porous substrate. J Colloid Interface Sci 249(2):432–440. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2002.8225
Hung YL, Wang MJ, Liao YC, Lin SY (2011) Initial wetting velocity of droplet impact and spreading: Water on glass and parafilm. Colloids Surf A 384(1–3):172–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2011.03.061
Kumar SM, Deshpande AP (2006) Dynamics of drop spreading on fibrous porous media. Colloids Surf A 277(1–3):157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2005.11.056
Lee JB, Laan N, de Bruin KG, Skantzaris G, Shahidzadeh N, Derome D, Bonn D (2015) Universal rescaling of drop impact on smooth and rough surfaces. J Fluid Mech 786. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2015.620
Lee JB, Radu AI, Vontobel P, Derome D, Carmeliet J (2016) Absorption of impinging water droplet in porous stones. J Colloid Interface Sci 471:59–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.03.002
Lee JS, Bang CS, Mok YJ, Joh SH (2000) Numerical and experimental analysis of penetration grouting in jointed rock masses. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 37(7):1027–1037. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1365-1609(00)00040-x
Li J, Zhang H, Liu Q (2019) Dynamics of a successive train of monodispersed millimetric-sized droplets impact on solid surfaces at low Weber number. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 102:81–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2018.08.029
Lin S, Zhao B, Zou S, Guo J, Wei Z, Chen L (2018) Impact of viscous droplets on different wettable surfaces: impact phenomena, the maximum spreading factor, spreading time and post-impact oscillation. J Colloid Interface Sci 516:86–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.12.086
Luo P, Zhong N, Khan I, Wang X, Wang H, Luo Q, Guo Z (2019) Effects of pore structure and wettability on methane adsorption capacity of mud rock: insights from mixture of organic matter and clay minerals. Fuel 251:551–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.04.072
Malgarinos I, Nikolopoulos N, Marengo M, Antonini C, Gavaises M (2014) VOF simulations of the contact angle dynamics during the drop spreading: standard models and a new wetting force model. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 212:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.07.004
Negeed ES, Hidaka S, Kohno M, Takata Y (2013) Effect of the surface roughness and oxidation layer on the dynamic behavior of micrometric single water droplets impacting onto heated surfaces. Int J Therm Sci 70:65–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2013.03.004
Pasandideh-Fard M, Qiao YM, Chandra S, Mostaghimi J (1996) Capillary effects during droplet impact on a solid surface. Phys Fluids 8(3):650–659. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.868850
Reis NC, Griffiths RF, Santos JM (2004) Numerical simulation of the impact of liquid droplets on porous surfaces. J Comput Phys 198(2):747–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2004.01.024
Ríos-López I, Evgenidis S, Kostoglou M, Zabulis X, Karapantsios TD (2018) Effect of initial droplet shape on the tangential force required for spreading and sliding along a solid surface. Colloids Surf A 549:164–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.04.004
Roisman IV (2009) Inertia dominated drop collisions. II. An analytical solution of the Navier–Stokes equations for a spreading viscous film. Phys Fluids 21(5). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3129283
Salem TK, Budaklı M, Şahan O, Arık M (2018) An experimental and analytical study on the influence of superhydrophobic micro-textured surfaces on liquid wetting phenomena. Colloids Surf A 555:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.06.084
Sari A, Al Maskari NS, Saeedi A, Xie Q (2020) Impact of surface roughness on wettability of oil-brine-calcite system at sub-pore scale. J Mol Liq 299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112107
Shen YJ, Wei X, Yang GS, Wang YZ, Jia HL, Zhang H, Zhang H (2020) Freeze-thaw degradation model and experimental analysis of rock-concrete interface bond strength. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 39(3):480–490
Starov VM, Zhdanov SA, Kosvintsev SR, Sobolev VD, Velarde MG (2003) Spreading of liquid drops over porous substrates. Adv Coll Interface Sci 104(1–3):123–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0001-8686(03)00039-3
Su W, Liu Y, Yang H, Pi J, Chai R, Li C (2019) New insights into the mechanism of wettability alteration during low salinity water flooding in carbonate rocks. J Dispersion Sci Technol 40(5):695–706. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2018.1478306
Wal RLV, Berger GM, Mozes SD (2005) The splash/non-splash boundary upon a dry surface and thin fluid film. Exp Fluids 40(1):53–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-005-0045-1
Wang GX, Matthys EF (2002) Experimental determination of the interfacial heat transfer during cooling and solidification of molten metal droplets impacting on a metallic substrate: effect of roughness and superheat. Int J Heat Mass Transf 45(25):4967–4981. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0017-9310(02)00199-0
Wang Y, Wang Y, Wang S (2020) Droplet impact on cylindrical surfaces: effects of surface wettability, initial impact velocity, and cylinder size. J Colloid Interface Sci 578:207–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.06.004
Wenzel RN (2002) Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind Eng Chem 28(8):988–994. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50320a024
Yarin AL (2006) Drop impact dynamics: splashing, spreading, receding, bouncing. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 38(1):159–192. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.fluid.38.050304.092144
ZadraŽIl A, Stepanek F, Matar OK (2006) Droplet spreading, imbibition and solidification on porous media. J Fluid Mech 562. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022112006000875
Zhao B, Wang X, Zhang K, Chen L, Deng X (2017) Impact of viscous droplets on superamphiphobic surfaces. Langmuir, 33(1), 144–151. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b03862
Funding
This research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 12072363).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Weihong Peng, Yawen Jing, and Donghui Zhao designed the study. Weihong Peng, Yawen Jing, and Donghui Zhao carried out the experiment and simulation. Weihong Peng, Yawen Jing, Donghui Zhao, and Yunchao Qi analyzed simulation results. Weihong Peng, Yawen Jing, and Donghui Zhao wrote the paper. Weihong Peng and Hongmei Cheng reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, W., Jing, Y., Zhao, D. et al. Spreading and penetration dynamics of nanosilica sol droplets impacting on porous rocks. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81, 496 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02995-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02995-3