Abstract
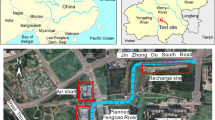
The main components of the confined aquifer in Tianjin are silt and silty sand. In addition, when the recharge of a shallow confined aquifer is used in deep excavation engineering to control the subsidence caused by pressure relief, the recharge cone and well loss require attention. Pressure recharge is often used to improve the efficiency of recharging. However, in the process of pressure recharge, the phenomena of recharge failure and water burst easily appear. In this study, single-well pumping, natural recharge, and pressure recharge tests were conducted at a green field site. Pressure recharge can further improve the recharge efficiency and reduce the number of recharge wells and the cost of recharge. Compared with clay sealing of the well wall’s outer hole, grouting sealing with slurry cement can significantly improve the recharge pressure and efficiency. The water level rise is close to the water level drawdown in the aquifer farther than 5 m from the recharge/pumping well based on the monitoring results. However, close to the recharge/pumping well in the aquifer, the water level rise in recharge is higher than the drawdown in pumping. In particular, the well loss in the recharge test is much greater than that in the pumping test because aquifer clogging occurs in recharge at the same flow rate. Based on the field test results, an equation to predict the well loss in recharge of the third confined aquifer in the Tianjin area is proposed.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett ME, Taylor S (2004) Retrofit of storm water treatment controls in a highway environment. The 5th International Conference On Sustainable Techniques and Strategies in Urban Water Management. Lyon, France, 243–250
Bhusari V, Katpatal YB, Kundal P (2016) An innovative artificial recharge system to enhance groundwater storage in basaltic terrain: example from Maharashtra, India. Hydrogeol J 24(5):1273–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-016-1387-x
Bouri S, Dhia HB (2010) A thirty-year artificial recharge experiment in a coastal aquifer in an arid zone: the Teboulba aquifer system (Tunisian Sahel). CR Geosci 342(1):60–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crte.2009.10.008
Budhu M, Adiyaman IB (2010) Mechanics of land subsidence due to groundwater pumping. Int J Numer Anal Meth Geomech 34(14):1459–1478. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.863
Cooper HH, Jacob CE (1946) A generalized graphical method for evaluating formation constants and summarizing well field history. Transaction American Geophysical Union 27(4):526–534. https://doi.org/10.1029/TR027i004p00526
Dong Y, Zhao P, Zhou W (2011) Effect of artificial aquifer recharge on hydraulic conductivity using single injection well. Int Symposium Water Resource Environ Protect 2011 Xi'an
Driscoll FG (1986) Groundwater and wells: St. Paul, Minnesota: Johnson Filtration Systems
Healy RW, Cook PG (2002) Using groundwater levels to estimate recharge. Hydrogeol J 10(1):91–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-001-0178-0
Hegeman PS, Hallford DL, Joseph JA (1993) Well test analysis with changing wellbore storage. SPE Form Eval 8(03):201–207. https://doi.org/10.2118/21829-PA
Henry C, Minier JP, Lefèvre G (2012) Towards a description of particulate fouling: From single particle deposition to clogging. Adv Coll Interface Sci 185:34–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2012.10.001
Kim J, Kim J, Lee J, Yoo H (2018) Prediction of transverse settlement trough considering the combined effects of excavation and groundwater depression. Geomech Eng 15(3):851–859. https://doi.org/10.12989/GAE.2018.15.3.851
Kim Y, Moon JS (2020) Change of groundwater inflow by cutoff grouting thickness and permeability coefficient. Geomech Eng 21(2):165–170. https://doi.org/10.12989/GAE.2020.21.2.165
Kuroda K, Hayashi T, Do AT, Canh VD, Nga TTV, Funabiki A, Takizawa S (2017) Groundwater recharge in suburban areas of Hanoi, Vietnam: effect of decreasing surface-water bodies and land-use change. Hydrogeol J 25(3):727–742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-016-1528-2
Lerner DN (1990) Groundwater recharge in urban areas. Atmospheric Environment Part b Urban Atmosphere 24(1):29–33
Liu XL, Zhu JL (2009) A study of clogging in geothermal reinjection wells in the Neogene sandstone aquifer. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology 36(5):138–141. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2009.05.031
Longe EO (2011) Groundwater resources potential in the coastal plain sands aquifers, Lagos, Nigeria. Res J Environ Earth Sci 3(1):1–7. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ezechiel_Longe/publication/49605116_Groundwater_Resources_Potential_in_the_Coastal_Plain_Sands_Aquifers_Lagos_Nigeria/links/0a85e5308a75c980a2000000.pdf
Moon J, Fernandez G (2010) Effect of excavation-induced groundwater level drawdown on tunnel inflow in a jointed rock mass. Eng Geol 110(3–4):33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.09.002
Nie JY, Zhu NW, Zhao K, Wu L, Hu YH (2011) Analysis of the bacterial community changes in soil for septic tank effluent treatment in response to bio-clogging. Water Sci Technol 63(7):1412–1417. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2011.319
Page D, Miotlinski K, Dillon P, Taylor R, Wakelin S, Levett K, Barry K, Pavelic P (2011) Water quality requirements for sustaining aquifer storage and recovery operations in a low permeability fractured rock aquifer. J Environ Manage 92(10):2410–2418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.04.005
Powrie W, Roberts TOL (1995) Case history of a dewatering and recharge system in chalk. Geotechnique 45(4):599–609. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1995.45.4.599
Preene M (2012) Groundwater lowering in construction: a practical guide to dewatering. CRC Press
Rorabaugh MI (1953) Graphical and theoretical analysis of step-drawdown test of artesian well. Proc Am Soc Civil Eng ASCE, 79(12):1–23. https://cedb.asce.org/CEDBsearch/record.jsp?dockey=0354261
Sarma D, Xu Y (2017) The recharge process in alluvial strip aquifers in arid Namibia and implication for artificial recharge. Hydrogeol J 25(1):123–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-016-1474-z
Sayana VBM, Arunbabu E, Kumar LM, Ravichandran S, Karunakaran K (2010) Groundwater responses to artificial recharge of rainwater in Chennai, India: a case study in an educational institution campus. Indian J Sci Technol 3(2):124–130. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.908.6953&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Scanlon BR, Healy RW, Cook PG (2002) Choosing appropriate techniques for quantifying groundwater recharge. Hydrogeol J 10(1):18–39
Shen SL, Wu YX, Xu YS, Hino T, Wu HN (2015) Evaluation of hydraulic parameters from pumping tests in multi-aquifers with vertical leakage in Tianjin. Comput Geotech 68:196–207
Shi XQ, Jiang SM, Xu HX, Jiang F, He ZF, Wu JC (2016) The effects of artificial recharge of groundwater on controlling land subsidence and its influence on groundwater quality and aquifer energy storage in Shanghai, China. Environmental Earth Sciences 75(3):195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5019-x
Simmers I (1988) Estimation of natural groundwater recharge, NATO ASI Series C Vol 222, Reidel, Dordrecht
Singh SK (2002) Well loss estimation: variable pumping replacing step drawdown test. J Hydraul Eng 128(3):343–348. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2002)128:3(343)
Todd DK (1980) Groundwater Hydrology. John Wiley
Wang JX, Wu YB, Zhang XS, Liu Y, Yang TL, Feng B (2012) Field experiments and numerical simulations of confined aquifer response to multi-cycle recharge–recovery process through a well. J Hydrol 464:328–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.07.018
Wu HN, Shen SL, Yang J (2017) Identification of tunnel settlement caused by land subsidence in soft deposit of Shanghai. J Perform Constr Facil ASCE 31(6). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0001082
Ye XY, Geng DQ, Du XQ, Wang FG, Cao DJ (2011) Integrated technique of artificial recharge in engineering dewatering. Global Geology 30(1):90–97. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000185
Yuan Y, Xu YS, Shen JS, Wang BZF (2018) Hydraulic conductivity estimation by considering the existence of piles: a case study. Geomech Eng 14(5):467–477. https://doi.org/10.12989/GAE.2018.14.5.467
Zeng CF (2014) Study on deformation mechanism, behavior and control strategy of excavation and ground under dewatering. Tianjin University, Tianjin
Zhang YQ, Li MG, Wang JH, Chen JJ, Zhu YF (2017) Field tests of pumping-recharge technology for deep confined aquifers and its application to a deep excavation. Eng Geol 228:249–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.08.019
Zheng G, Cao JR, Cheng XS, Ha D, Wang FJ (2018) Experimental study on the artificial recharge of semiconfined aquifers involved in deep excavation engineering. J Hydrol 557:868–877
Zheng G, Ha D, Loaiciga H et al (2019) Estimation of the hydraulic parameters of leaky aquifers based on pumping tests and coupled simulation/optimization: verification using a layered aquifer in Tianjin, China. Hydrogeol J 27(8):3081–3095
Zheng G, Zeng CF, Diao Y, Xue XL (2014) Test and numerical research on wall deflections induced by pre-excavation dewatering. Comput Geotech 62: 244-256
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant numbers 52178343 and 51708206 and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under grant number 2019T120797.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Li, Q., Cheng, X. et al. Study on artificial recharge and well loss in confined aquifers using theoretical and back-analysis calculations of hydrogeological parameters from recharge and pumping tests. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81, 483 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02988-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02988-2