Abstract
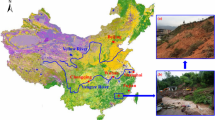
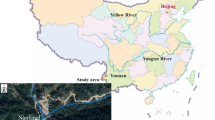
Due to topographical restrictions, transmission towers will inevitably be erected in areas prone to frequent geological disasters such as steep slope failure. Taking the Yanzi tower foundation landslide as the research object, the failure process of the tower foundation in a landslide and the corresponding failure mode under rainfall were studied through physical model testing and numerical theoretical analysis. Firstly, the planned design and testing process of the physical model test of the tower foundation landslide under rainfall were introduced. Secondly, the failure process of the tower foundation at different positions of landslide under rainfall was revealed. Then, the failure mode of the tower foundation landslide under rainfall was proposed. Finally, the failure mode of the tower foundation under rainfall was determined. According to the observed displacement of the tower foundation during a landslide in the model test, the instability of the toe of the landslide caused by scouring caused traction damage to the landslide. The tower foundations on the landslide and outside the trailing edge of the landslide became unstable and collapsed along with the landslide, while the tower foundation below the landslide remained stable. During the deformation stage of the landslide, there was no shear failure and no tipping damage to the tower foundation. If the potential landslide on which the tower foundation is located is unstable under heavy rainfall, the tower foundation may slide along with the potential landslide passing through the bottom of the tower foundation, which is consistent with the result of physical testing.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askarinejad A, Akca D, Springman SM (2018) Precursors of instability in a natural slope due to rainfall: a full-scale experiment. Landslides 15(15):1745–1759
Askarinejad A, Casini F, Bischof P, Beck A, Springman SM (2012) Rainfall induced instabilities: a field experiment on a silty sand slope in northern Switzerland. Riv Ital Geotec 46:50–71
Cao L, Zhang J, Wang Z, Liu F, Liu Y, Zhou Y (2019) Dynamic response and dynamic failure mode of the slope subjected to earthquake and rainfall. Landslides 16:1467–1482
Chen Y, Xu D (2013) FLAC/FLAC3D basics and engineering examples, 2nd edn. China WaterPower Press, Beijing
Cotecchia F, Tagarelli V, Pedone G, Ruggieri G, Guglielmi S, Santaloia F (2019) Analysis of climate-driven processes in clayey slopes for the early-warning system design. Proc Inst Civil Eng Geotech Eng 172:465–780
Elkamhawy E, Wang HB, Zhou B, Yang ZY (2018) Failure mechanism of a slope with a thin soft band triggered by intensive rainfall. Environ Earth Sci 77:340
Fredlund DG, Rahardjo H (1993) Soil mechanics for unsaturated soils. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Fredlund DG, Xing A (1994) Equations for the soil-water characteristic curve. Can Geotech J 31(4):521–532
Fu X, Li H, Wang J (2019) Failure analysis of a transmission tower subjected to combined wind and rainfall excitations. Struct Design Tall Spec Build. https://doi.org/10.1002/tal.1615
Fu X, Li HN, Li G, Dong ZQ (2020). Fragility analysis of a transmission tower under combined wind and rain loads. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics 199:104098
Gan JJ, Zhang YX (2020) Analysis of model tests of rainfall-induced soil deposit landslide. Advances in Civil Engineering 3:1–13
Hu X, Zhang M, Sun M, Huang K, Song Y (2015) Deformation characteristics and failure mode of the Zhujiadian landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Bull Eng Geol Env 74(1):1–12
Liu X, Wang Y, Li DQ (2020a) Numerical simulation of the 1995 rainfall-induced Fei Tsui Road landslide in Hong Kong: new insights from hydro-mechanically coupled material point method. Landslides 17(3):2755–2775
Liu Y, Wang C, Gao G, Wang P, Hou Z, Jiao Q (2020b) Analysis of the instability conditions and failure mode of a special type of translational landslide using long-term monitoring data: a case study of the Wobaoshi landslide (in Bazhong, China). Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 20:1305–1319
Lourenço SDN, Sassa K, Fukuoka H (2006) Failure process and hydrologic response of a two layers physical model: implications for rainfall-induced landslides. Geomorphology 73:115–130
Pirone M, Papa R, Nicotera MV, Urciuoli G (2015) In situ monitoring of the groundwater field in an unsaturated pyroclastic slope for slope stability evaluation. Landslides 12:259–276
Prakoso WA, Kulhawy FH (2001) Contribution to piled raft foundation design. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 127(1):1–24
Sitarenios P, Casini F, Askarinejad A, Springman SM (2019) Hydro-mechanical analysis of a surficial landslide triggered by artificial rainfall: the Ruedlingen field experiment. Géotechnique, Ahead of Print. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.18.P.188
Song X, Tan Y (2020) Experimental study on failure of temporary earthen slope triggered by intense rainfall. Eng Fail Anal 116:104718
Sun P, Wang G, Wu LZ, Igwe O, Zhu E (2019) Physical model experiments for shallow failure in rainfall-triggered loess slope, Northwest China. Bull Eng Geol Env 78(6):4363–4382
Tagarelli V, Cotecchia F (2020) The effects of slope initialization on the numerical model predictions of the slope-vegetation-atmosphere interaction. Geosciences 10(85):1–24
Tommasi P, Boldini D, Caldarini G, Coli N (2013) Influence of infiltration on the periodic re-activation of slow movements in an overconsolidated clay slope. Can Geotech J 50(1):54–67
Tran ATP, Kim AR, Cho GC (2019) Numerical modeling on the stability of slope with foundation during rainfall. Geomechanics and Engineering 17(1):109–118
van Genuchten MT (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44(5):892–898
Vassallo R, Grimaldi GM, Di Maio C (2015) Pore water pressures induced by historical rain series in a clayey landslide: 3D modeling. Landslides 12:731–744
Wang G, Sassa K (2003) Pore-pressure generation and movement of rainfall-induced landslides: effects of grain size and fine-particle content. Eng Geol 69(1–2):109–125
Wang H, Luo J, Xu T, Li H, Li B, Zhu H, Xue Y (2010) Questionnaire survey and analysis of natural disaster defense techniques of power grids in China. Automation of Electric Power Systems 23(5–10):118
Wang J, Xiao L, Zhang J, Zhu Y (2019) Deformation characteristics and failure mechanisms of a rainfall-induced complex landslide in Wanzhou County, Three Gorges Reservoir. China Landslides 17(2):419–431
Xie Q, Sun L (2012) Failure mechanism and retrofitting strategy of transmission tower structures under ice load. J Constr Steel Res 74:26–36
Xie Q, Sun L (2013) Experimental study on the mechanical behavior and failure mechanism of a latticed steel transmission tower. J Struct Eng 139(6):1009–1018
Zhang C, Zhang M, Zhang T, Dai Z, Wang L (2020) Influence of intrusive granite dyke on rainfall-induced soil slope failure. Bull Eng Geol Env 79:5259–5276
Zhang S, Zhang X, Pei X, Wang S, Huang R, Xu Q, Wang Z (2019) Model test study on the hydrological mechanisms and early warning thresholds for loess fill slope failure induced by rainfall. Eng Geol 258:105135
Zhang Q, Wu H, Chen J, Chen L, Wu X (2008) Developing characteristics and countermeaures of geological hazards in Badong. Hubei Resources Environment & Engineering 22(6):591–595
Zhang ZP, Fu XD, Sheng Q, Du Y, Zhou YQ, Huang JH (2021) Stability of cracking deposit slope considering parameter deterioration subjected to rainfall. Int J Geomechanics 21(7):05021001. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0002045
Acknowledgements
A special acknowledgement should be expressed to the China-Pakistan Joint Research Center on Earth Sciences, which supported the implementation of this study.
Funding
The work reported in this paper is financially supported by the National Key R&D Programme of China (2018YFC0809400), the International Partnership Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. 131551KYSB20180042), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51779250).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Sheng, Q., Chen, J. et al. The failure mode of transmission tower foundation on the landslide under heavy rainfall: a case study on a 500-kV transmission tower foundation on the Yanzi landslide in Badong, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81, 125 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02628-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02628-9