Abstract
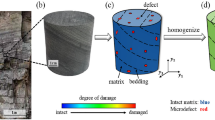
Shale is one of the most widely distributed and common types of surrounding rock in underground structures such as tunnels. However, the mechanical strength of shale decreases significantly under the combined action of stress and osmotic pressure. In this study, we conducted triaxial compression tests under variable osmotic and confining pressures to evaluate the mechanical behavior of shale under a combination of stress and seepage. The peak mechanical strength of shale decreased as the osmotic pressure increased, which resulted in five different macro failure modes corresponding to different levels of osmotic pressures. Furthermore, high confining pressures induced failure of the compression band which considerably inhibited permeability, with stages of shale fracture developing in correspondence with changes in the permeability. The minimum permeability of shale occurred before the expansion point. While the confining pressure played an important role in the growth of cracks, the osmotic pressure had a relatively weak effect. The quantitative relationship between permeability, axial strain, and volumetric strain found in this study sufficiently reflects the evolution law of shale permeability during the deformation and failure processes. Based on these results, we developed a new damage constitutive model for rock under osmotic pressure by introducing statistical damage theory. The model can reflect the stress–strain relationship better under different confining and osmotic pressures, can accurately capture the key points of the mechanical response, and depends on parameters that are simple to calculate, which is important for engineering applications.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht D, Reitenbach V (2015) Investigations on fluid transport properties in the North-German Rotliegend tight gas sandstones and applications. Environ Earth Sci 73:5791–5799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4322-x
Andersson P, Byegard J, Tullborg EL, Doe T, Hermanson J, Winberg A (2004) In situ tracer tests to determine retention properties of a block scale fracture network in granitic rock at the sp Hard Rock Laboratory Sweden. J Contam Hydrol 70:271–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2003.09.009
Baud P, Klein E, Wong TF (2004) Compaction localization in porous sandstones: spatial evolution of damage and acoustic emission activity. J Struct Geol 26:603–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2003.09.002
Bruno MS, Nakagawa FM (1991) Pore pressure influence on tensile fracture propagation in sedimentary rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 28:261–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(91)90593-B
Cao WG, Zhang C, He M (2016) Statistical damage simulation method of strain softening deformation process for rocks considering characteristics of void compaction stage. Chin J Geotech Eng 38:1754–1761. https://doi.org/10.11779/CJGE201610002
Cao WG, Zhao H, Li X (2012) A statistical damage simulation method for rock full deformation process with consideration of the deformation characteristics of residual strength phase. Chin Civil Eng J 32:647–654. https://doi.org/10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2012.06.001
Cha SS, Lee JY, Amantini E, Lee KK (2006) Engineering characterization of hydraulic properties in a pilot rock cavern for underground LNG storage. Eng Geol 84:229–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6701(06)81589-4
Chu Z, Wu Z, Wang Z, Weng L, Liu Q, Fan L (2022) Micro-mechanism of brittle creep in saturated sandstone and its mechanical behavior after creep damage. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 149:104994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104994
Dada A, Muradov K, Davies D (2017) Temperature transient analysis models and workflows for vertical dry gas wells. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 45:207–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2017.05.017
Dan M, Qiang L, Matthew H, Yu WJE (2017) Experimental Investigation of Stress Rate and Grain Size on Gas Seepage Characteristics of Granular Coal. Energies 10:527–542. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10040527
Emerson DW (1990) Notes on mass properties of rocks density, porosity, permeability. Explor Geophys 21:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1071/EG990209
Fang Z, Harrison JP (2001) A mechanical degradation index for rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 38:1193–1199. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(01)00070-3
Feng H, Zhu HH, Xu QW, Cai YC, Zhuang XY (2013) The effect of weak interlayer on the failure pattern of rock mass around tunnel–Scaled model tests and numerical analysis. Tunn under Sp Tech 35:207–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2012.06.014
Gao YF, Huang WP, Qu GL, Wang B, Cui XH, Fan QZ (2017) Perturbation effect of rock rheology under uniaxial compression. J Cent South Univ 24:1684–1695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3575-9
Geng Z, Bonnelye A, Chen M, Jin Y, Dick P et al (2018) Time and Temperature Dependent Creep in Tournemire Shale. Solid Earth 123:9658–9675. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JB016169
Geng Z, Bonnelye A, David C, Dick P, Schubnel A (2021) Pressure solution compaction during creep deformation of Tournemire shale: implications for temporal sealing in shales. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 126:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JB021370
Hamiel Y, Lyakhovsky V, Agnon A (2005) Rock dilation, nonlinear deformation, and pore pressure change under shear. Earth Planet Sci Lett 237:577–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.06.028
Heiland J (2003) Laboratory testing of coupled hydro-mechanical processes during rock deformation. Hydrogeol J 11:122–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-002-0236-2
Hou J, Guo Z, Li J, Zhao L (2020) Study on triaxial creep test and theoretical model of cemented gangue-fly ash backfill under seepage-stress coupling. Constr Build Mater 273:121722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121722
Hu DW, Zhou H, Zhang F, Shao JF (2010) Evolution of poroelastic properties and permeability in damaged sandstone. Int J Rock Mech Min 47:962–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.06.007
Jiang T, Shao JF, Xu WY, Zhou CB (2010) Experimental investigation and micromechanical analysis of damage and permeability variation in brittle rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47:703–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.05.003
Katsman R, Aharonov E (2006) A study of compaction bands originating from cracks, notches and compacted defects. J Struct Geol 28:508–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2005.12.007
Kawabata K, Tanaka H, Kitamura Y, Ma KF (2009) Apparent activation energy and rate-limiting process estimation from natural shale deformed by pressure solution in shallow subduction zone. Earth Planet Sci Lett 287:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2009.07.032
Lemaitre J (1984) How to use damage mechanics. Nucl Eng Des 80:233–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-5493(84)90169-9
Lespinasse M, Sausse J (2000) Quantification of fluid flow: hydro-mechanical behaviour of different natural rough fractures. J Geochem Explor 69:483–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6742(00)00111-4
Li P, Lu W, Long Y, Yang Z, Li J (2008) Seepage analysis in a fractured rock mass: The upper reservoir of Pushihe pumped-storage power station in China. Eng Geol 97:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.12.005
Li SP, Wu DX, Xie WH (1997) Effect of confining pressure, pore pressure and specimen dimension on permeability of Yinzhuang sandstone. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 34:175. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0148-9062(97)00205-2
Liu D, Liu C, Kang Y (2018) Mechanical behavior of Benxi Formation limestone under triaxial compression: a new post-peak constitutive model and experimental validation. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77:1701–1715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1193-2
Liu D, Pu H, Ju Y, Cao LL, Lu JF (2019) A new nonlinear viscoelastic-plastic seepage-creep constitutive model considering the influence of confining pressure. Therm Sci 23:116–116. https://doi.org/10.2298/TSCI180621116L
Liu K, Vardon PJ, Hicks MA, Arnold P (2016) Combined effect of hysteresis and heterogeneity on the stability of an embankment under transient seepage. Eng Geol 219:140–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.11.011
Louis C (1974) Rock Hydraulics. Springer, Vienna, pp 36–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-4109-0_16
Mark C (2016) Coal bursts in the deep longwall mines of the United States. Int J Coal Sci Technol 3:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-016-0102-9
Martin CD, Chandler NA (1994) The progressive fracture of Lacdu Bonnet granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 31:643–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(94)90005-1
Meng QX, Wang HL, Xu WY, Cai M (2016) Experimental Research on Permeability Evolution with Microcrack Development in Sandstone under Different Fluid Pressures. J Geotech Geoenviron 142:04016014. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001462
Mollema PN, Antonellini MA (1996) Compaction bands: a structural analog for anti-mode I cracks in Aeolian sandstones. Tectonophysics 267:209–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-1951(96)00098-4
Neuman SP, Tartakovsky DM (2009) Perspective on theories of non-Fickian transport in heterogeneous media. Adv Water Resour 32:670–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2008.08.005
Parisio F, Vilarrasa V, Laloui L (2018) Hydro-mechanical Modeling of Tunnel Excavation in Anisotropic Shale with Coupled Damage-Plasticity and Micro-dilatant Regularization. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51:3819–3833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1569-z
Pluymakers A, Spiers CJ (2015) Compaction creep of simulated anhydrite fault gouge by pressure solution: theory v experiments and implications for fault sealing. Geol Soc London Spec Publ 409:107–124. https://doi.org/10.1144/SP409.6
Pu H, Cao L, Qiu Y, Qiu P (2015) Study of overlying strata creep affected by seepage in backfilling mining process. J Min Saf Eng 32:846–852. https://doi.org/10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2015.05.023
Raghavan R, Chen C (2013) Fractured-well performance under anomalous diffusion. SPE Reserv Eval Eng 16:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-017-0820-5
Rutter EH (1983) Pressure solution in nature theory and experiment. J Geol Soc London 140:725–740. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsjgs.140.5.0725
Sun JL, Wang F, Li ZQ, Ren DR, Yu MY (2022) A new hybrid copula-based nonparametric Bayesian model for risk assessments of water inrush. Qual Reliab Eng Int. https://doi.org/10.1002/qre.3053
Wang HL, Xu WY, Jia CJ, Cai M, Meng QX (2016) Experimental Research on Permeability Evolution with Microcrack Development in Sandstone under Different Fluid Pressures. J Geotech Geoenviron 142:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001462
Wang JA, Park HD (2002) Fluid permeability of sedimentary rocks in a complete stress–strain process. Eng Geol 63:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(01)00088-6
Wu F, Zhang H, Zou Q, Li C, Gao R (2020) Viscoelastic-plastic damage creep model for salt rock based on fractional derivative theory. Mech Mater 150:103600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmat.2020.103600
Wu K, Shao Z, Qin S, Zhao N, Chu Z (2021) An improved non-linear creep model for rock applied to tunnel displacement prediction. Int J Appl Mech 13(8):2150094. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1758825121500940
Xu P, Yang SQ (2016) Permeability evolution of sandstone under short-term and long-term triaxial compression. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 85:152–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.03.016
Yang TH, Jia P, Shi WH, Wang PT, Liu HL, Yu QL (2014) Seepage–stress coupled analysis on anisotropic characteristics of the fractured rock mass around roadway. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 43:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2014.03.005
Yarushina VM, David B, Oristaglio ML (2013) Rock deformation models and fluid leak-off in hydraulic fracturing. Geophys J Int 194:1514–1526. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggt199
Yu J, Li H, Chen X (2013) Triaxial experimental study of associated permeability-deformation of sandstone under hydro-mechanical coupling. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 32:1203–1211. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2013.06.014
Zeng Z, Li X, Shi L, Bing B, Ying W (2014) Experimental study of the laws between the effective confining pressure and mudstone permeability. Energy Procedia 63:5654–5663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.11.598
Zhang JC, Bai M, Roegiers JC, Wang JX, Liu TQ (2000) Experimental determination of stress-permeability relationship. In: 4th North American Rock Mechanics, Symposium, p 817–822. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1713511
Zhang JW, Song ZX, Wang SY (2021) Mechanical behavior of deep sandstone under high stress-seepage coupling. J Cent South Univ 28:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4791-x
Zhao JH, Yin LM, Guo WL (2018) Stress–seepage coupling of cataclastic rock masses based on digital image technologies. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51:2355–2372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1474-5
Zhou GL, Tham LG, Lee P, Tsui Y (2001) A phenomenological constitutive model for rocks with shear failure mode. Int J Numer Anal Met 25:391–414. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.135
Funding
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2020YJS114), Traffic Science and Technology Project of Yunnan Province([2020]50), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71771020, 71631007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yu Mingyuan: conceptualization. Baoguo Liu: methodology. Zhaofei Chu: review. Jinglai Sun: validation. Tingbang Deng: investigation. Qi Wang: data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, M., Liu, B., Chu, Z. et al. Permeability, deformation characteristics, and damage constitutive model of shale under triaxial hydromechanical coupling. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81, 85 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02584-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02584-4