Abstract
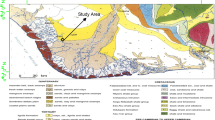
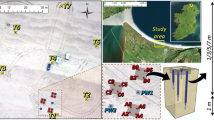
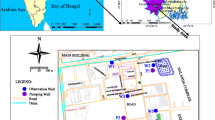
Various studies have described upon importance of the performance of multilevel slug tests to assess hydraulic conductivity of aquifer sediment. For this study, slug tests were performed at 33 locations in 107 numbers of observation wells under six physiographic divisions in the Bengal Basin, Bangladesh. The objective of this paper is to evaluate the potential of multilevel slug tests to determine depth distribution and vertical variations of hydraulic conductivity in layered aquifer systems of the Bengal Basin that can be utilized for resource assessment. The studied aquifer sediments are dominated by unconsolidated fine and very fine sand with lenses of clay and silty clay aquitards. The hydraulic conductivity values commonly correspond with the lithology and their settlements. The unconsolidated sand in the Active and Tidal Delta contains high hydraulic conductivity values of up to 24.4 m/day. Older sediments in the Teppera Surface and Coastal Plain show lower average hydraulic conductivity. Very low hydraulic conductivities in few wells indicate the heterogeneities as well as poor development of these newly installed wells. Individual layers have relatively uniform grain size with well sorted sands, and their hydraulic conductivity values have a small variation, while sediments from multiple layers have variations in grain size with anisotropic signature and their hydraulic conductivity values, in many cases, vary by orders of magnitude. However, multilevel slug tests can provide considerable information about vertical variations in hydraulic conductivity under the right conditions. Although the slug tests were performed with precaution, unknown uncertainties in the well during the operation may influence the values of hydraulic conductivity. A more accurate values of the conductivity variations can be achieved by placing thin, low-conductivity layers in the sand pack that reduces vertical flow. Selection of drilling procedure and the techniques of measurement and analysis are also important to get good results. Factors like leakage and partial penetration should also be minimal for optimum results





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and materials have been generated under the above mentioned research and knowledge management project of the Bangladesh Water Development Board, leaded by the first author Dr. Anwar Zahid, Director, Ground Water Hydrology, Bangladesh Water Development Board.
References
Aggarwal PK, Basua R, Poreda RJ, et al (2000) Isotope hydrology of groundwater in Bangladesh: implications for characterization and mitigation of arsenic in groundwater. IAEA-TC Proj BGD/8/016 61
Al-Hussainy R, Ramey HJ, Crawford PB (1966) The flow of real gases through porous media. J Pet Technol. https://doi.org/10.2118/1243-a-pa
Bouwer H (1989) The Bouwer and Rice slug test—an update. Groundwater. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1989.tb00453.x
Bouwer H, Rice RC (1976) A slug test for determining hydraulic conductivity of unconfined aquifers with completely or partially penetrating wells. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR012i003p00423
Butler JJ Jr, Bohling GC, Hyder Z, McElwee CD (1994) The use of slug tests to describe vertical variations in hydraulic conductivity. J Hydrol 156(1994):137–162
Butler, Jr. JJ (1997) The Design, Performance, and Analysis of Slug Tests
Butler JJ, Healey JM (1998) Relationship between pumping-test and slug-test parameters: scale effect or artifact? Ground Water. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1998.tb01096.x
Butler JJ, McElwee CD, Liu W (1996) Improving the quality of parameter estimates obtained from slug tests. Ground Water. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1996.tb02029.x
BWDB-UNDP (1982) Groundwater survey: the hydrogeological conditions of Bangladesh. UNDP Technical Report DP/UN/BGD-74–009/1, 113p
Chen X, Mi H, He H, Liu R, Gao M, Huo A, Cheng D (2014) Hydraulic conductivity variation within and between layers of a high floodplain profile. J Hydrol 515:147–155
Chirlin GR (1989) A critique of the Hvorslev method for slug test analysis: the fully penetrating well. Groundw Monit Remediat. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6592.1989.tb01147.x
Dax A (1987) A note on the analysis of slug tests. J Hydrol 91:153–177
DPHE-BGS (2001) Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Bangladesh. British Geological Survey (BGS), Department of Public Health Engineering (DPHE), Br Geol Surv Tech Rep WC/00/19
DPHE-BGS (1999) Groundwater studies for arsenic contamination in Bangladesh. Final Report, Rapid Investigation Phase. Department of Public Health Engineering, Government of Bangladesh. Mott MacDonald and British Geological Survey
GWTF (2002) Report of the Ground Water Task Force, Ministry of Local Govt. Rural Dev. And Co-operatives, Govt. of the Peoples Republic of Bangladesh, 77p
Hvorslev MJ (1951) Time lag and soil permeability in groundwater observations. US Army 6 Corps of Engineers Waterways Experiment Station Bulletin No 36
Hossain J, Salehin M, Mourin MM (2017) Impact of storm surge flooding on groundwater salinity in the polder protected and non-polder area of coastal aquifer in Bangladesh. Int Conf Disaster Risk Mitigation 0–4
Hyder Z, Butler JJ, McElwee CD, Liu W (1994) Slug tests in partially penetrating wells. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/94WR01670
Jiao JJ, Leung C man (2003) Spreadsheets for the analysis of aquifer-test and slug-test data. Ground Water
Leap DI (1984) A simple pneumatic device and technique for performing rising water level slug tests. Groundw Monit Remediat. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6592.1984.tb00905.x
McElwee CD (2002) Improving the analysis of slug tests. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00214-7
McElwee CD (2001) Application of a nonlinear slug test model. Ground Water. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2001.tb02364.x
McElwee CD, Butler JJ Jr, Bohling GC, Liu W (1995) Sensitivity analysis of slug tests Part 2. Observation wells. J Hydrol 164:69–87
Melville JG, Molz FJ, Guven O, Widdowson MA (1991) Multilevel slug tests with comparisons to tracer data. Ground Water 29(6):897–907
Method ST (2002) (Field Procedure) for instantaneous change in head (Slug) tests for determining hydraulic properties of aquifiers 1. TEST. https://doi.org/10.1520/D4044-96R08.2
Ujang PM, Lawrence CJ, Hale CP, Hewitt GF (2006) Slug initiation and evolution in two-phase horizontal flow. Int J Multiph Flow. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2005.11.005
Yeh HD, Chen YJ (2007) Determination of skin and aquifer parameters for a slug test with wellbore-skin effect. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.05.029
Zahid A, Afzal Hossain AFM, Hazrat Ali M, Islam K, Abbassi SU (2018) Monitoring the coastal groundwater of Bangladesh. In: Mukherjee A. (eds) Groundwater of South Asia. Springer Hydrogeology, Springer pp 431–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3889-1_26
Zahid A, Hassan MQ, Ahmed KMU (2015) Simulation of flowpaths and travel time of groundwater through arsenic-contaminated zone in the multi-layered aquifer system of Bengal Basin. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3447-7
Acknowledgements
Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB), Ministry of Water Resources and Bangladesh Climate Change Trust (BCCT), Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change are highly acknowledged for supporting the study under Climate Change Trust Fund project to assess coastal water resources. Aminur Rahman, M. Jahangir Alam, Nur Ahmed, and all other hydrogeologists of the project team are acknowledged for their participation in the slug test activities. Farzana Bashar is acknowledged for editing literature of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for this project of Bangladesh Water Development Board has been provided by the Bangladesh Climate Change Trust, Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate change of the Bangladesh Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Anwar Zahid leaded, guided, and actively participated the research activities as well as prepared the manuscript. Sara Nowreen and M. Jakir Hossain were engaged to review the manuscript. M. Kamrul Islam, M. Rashedul Hasan, and Salah Uddin Abbassi participated in the field research activities and analyzed the slug test data using appropriate software.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahid, A., Nowreen, S., Islam, M.K. et al. Assessment of hydraulic conductivity in the multi-layered aquifer system of the Bengal Basin, Bangladesh, by performing slug tests. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80, 5941–5955 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02294-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02294-3