Abstract
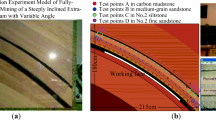
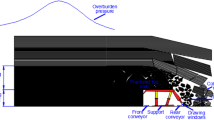
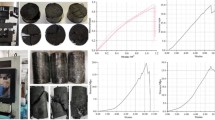
Coal face spalling is a major issue affecting the safety of a large-cutting-height mining face, especially in deep mining. In order to analyze failure mechanisms and propose corresponding stability control measures in a large-cutting-height longwall face, panel 1303, with a mining depth of 860 m, which is arranged and advanced distances of 300 m and over 1000 m along the dip and strike directions of a coal seam, respectively, was selected as the engineering background. In addition to uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) tests, triaxial compression tests under different confining pressures and loading methods were carried out to investigate the deformation characteristics of the coal specimens. A mechanical model, the “coal face support roof”, was established to illustrate the factors affecting the stability of the coal face. Combined with numerical simulation, the dominant factor was obtained, and the stress distribution around the coal face at different advance distances was revealed. Based on the coal face failure mechanism, the pertinent in situ measures of “manila + grouting” reinforcement technology for controlling coal face spalling were proposed. The results showed that the coal face spalling depended mainly on vertical cyclic loading and horizontal unloading in both initial and periodic weighting. In terms of deep mining, the surrounding stress distribution played a vital role in coal face failure and instability. Specifically, two dimensions of loading conditions were found in the front 3 m of the coal face, and the principal stress σxx of the coal body was significantly less than the other two principal stresses in the front 8 m of the coal face. In addition, the horizontal principal stress σyy was greater than the vertical principal stress σzz. Therefore, the horizontal principal stress and strength of the coal body were the prominent influencing factors in the large-cutting-height coal face. The mining height and support system working resistance were also of great importance with respect to the stability of the coal face to some degree. Lastly, “manila + grouting” reinforcement technology proposed in this study resulted in 70–80% reduced potential for the occurrence of coal face spalling and in the degree of failure of the coal face, as well as grouting cost could be saved of 30–40% compared with pure grouting measures.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguado MBD, González C (2009) Influence of the stress state in a coal bump-prone deep conalbed: a case study. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(2):333–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.07.005
Alejano LR, Ramírez-Oyanguren P, Taboada J (1999) FDM predictive methodology for subsidence due to flat and inclined coal seam mining. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 36(4):475–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0148-9062(99)00022-4
Asadi A, Shakhriar K, Goshtasbi K (2004) Profiling function for surface subsidence prediction in mining inclined coal seams. J Min Sci 40(2):142–146. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOMI.0000047856.91826.76
Cai MF, HE MC, Liu DY (2013) Rock mechanics and engineering. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Chang JC, Xie GX, Zhang XH (2015) Analysis of coal face spalling mechanism of fully-mechanized top-coal caving face with great mining height in the extra-thick coal seam. Rock Soil Mech 36(3):803–808. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2015.03.026
Christopher M (2016) Coal bursts in the deep longwall mines of the United States. Int J Coal Sci Technol 3(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-016-0102-9
Fan X, Kulatilake PHSW, Chen X (2015) Mechanical behavior of rock-like jointed blocks with multi-non-persistent joint under uniaxial loading: a particle mechanics approach. Eng Geol 190:17–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.02.008
Gao FQ, Stead D (2014) The application of a modified Voronoi logic to brittle fracture modelling at the laboratory and field scale. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 68:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.02.003
Gao F, Stead D, Kang H (2014a) Simulation of roof shear failure in coal mine roadways using an innovative UDEC trigon approach. Comput Geotech 61(3):33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.04.009
Gao F, Stead D, Kang H, Wu Y (2014b) Discrete element modelling of deformation and damage of a roadway driven along an unstable goaf–a case study. Int J Coal Geol 127(7):100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2014.02.010
He MC, Sousa LR, Miranda T, Zhu GL (2015) Rockburst laboratory tests database-application of data mining technique. Eng Geol 185:116–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.12.008
Huang BX, Li HT, Liu CY, Xing SJ, Xue WC (2011) Rational cutting height for large cutting height fully mechanized top-coal caving. Min Sci Technol 21:457–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mstc.2011.05.020
Iannacchione AT, Tadolini SC (2016) Occurrence, predication, and control of coal burst events in the U.S. Int J Min Sci Technol 26:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2015.11.008
Kazerani T (2013) Effect of micromechanical parameters of microstructure on compressive and tensile failure process of rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 64:44–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2013.08.016
Kong DZ, Yang SL, Gao L, Ma ZQ (2017) Determination of support capacity based on coal face stability control. J China Coal Soc 42(3):590–596. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2016.1296
Li XP, Kang TH, Yang YK, Li H, Li CY, Wu LL, Du MZ (2015) Analysis of coal face slip risk and caving depth based on bishop method. J China Coal Soc 40(7):1498–1504. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.0912
Li XH, Ju MH, Yao QL, Zhou J, Chong ZH (2016) Numerical investigation of the effect of the location of critical rock block fracture on crack evolution in a gob-side filling wall. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(3):1041–1058. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0783-1
Lisjak A, Grasselli G (2014) A review of discrete modeling techniques for fracturing processes in discontinuous rock masses. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 6:301–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2013.12.007
Mazaira A, Konicek P (2015) Intense rockburst impacts in deep underground construction and their prevention. Can Geotech J 52:1426–1439. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2014-0359
Pang YH, Wang GF (2017) Hydraulic support protecting board analysis based on coal face spalling “tensile cracking-sliding” mechanical model. J China Coal Soc 42(8):1941–1950. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2016.1696
Peng SS, Chiang HS (1984) Longwall mining. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York
Suorineni FT, Mgumbwa JJ, Kaiser PK, Thibodeau D (2014) Mining of orebodies under shear loading part 2–failure modes and mechanisms. Min Technol 123(4):240–249. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743286314Y.0000000072
Wang JC, Wang L, Guo Y (2014) Determining the support capacity based on roof and coal face control. J China Coal Soc 39(8):1619–1624. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.9027
Wang JC, Wang ZH, Kong DZ (2015) Failure and prevention mechanism of coal face in hard coal. J China Coal Soc 40(10):2243–2250. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.6013
Wang JC, Yang SL, Kong DZ (2016) Failure mechanism and control technology of Longwall coal face in large-cutting-height mining method. Int J Min Sci Technol 26(1):111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2015.11.018
Wang G, Wu MM, Wang R, Xu H, Song X (2017) Height of the mining-induced fractured zone above a coal face. Eng Geol 216:140–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.11.024
Xuan DY, Xu JL, Wang BL, Teng H (2016) Investigation of fill distribution in post-injected longwall overburden with implications for grout take estimation. Eng Geol 206:71–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.04.007
Yang SL, Kong DZ (2015) Flexible reinforcement mechanism and its application in the control of spalling at large mining height coal face. J China Coal Soc 40(6):1361–1367. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.0271
Yang SL, Kong DZ, Yang JH, Meng H (2015) Coal face stability and grouting reinforcement technique in fully mechanized caving face during topple mining. J Min Saf Eng 32(5):827–833,839. https://doi.org/10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2015.05.020
Yao QL, Li XH, Sun BY, Ju MH, Chen T, Zhou J, Liang S, Qu QD (2017) Numerical investigation of the effects of coal seam dip angle on coal face stability. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 100:298–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.10.002
Zhang L, Einstein HH (2004) Using RQD to estimate the deformation modulus of rock masses. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(2):337–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00100-X
Zhao TB, Guo WY, Tan YL, Lu CP, Wang CW (2017) Case histories of rock bursts under complicated geological conditions. Bull Eng Geol Environ 2:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1014-7
Zhou H, Meng FZ, Zhang CQ, Hu DW, Yang FJ, Lu JJ (2015) Analysis of rockburst mechanisms induced by structural planes in deep tunnels. Bull Eng Geol Environ 74(4):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-014-0696-3
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge financial support from the Scientific Research Foundation of Guizhou Provincial Department of Science & Technology and Guizhou University (QianKehe LH [2017]7280), Annual Academic Training and Special Innovation Program of Guizhou University in 2017 (Guizhou Kehe [2017]5788), the Fund of Key Laboratory of Safety and High-efficiency Coal Mining, Ministry of Education (JYBSYS2017101) and the China Scholarship Council. The authors would also like to thank the editors and anonymous reviewers for their valuable time and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
(1) Proposed coal face failure mechanism and transfer process of a stress state
(2) σyy > σzz > σxx in the front 8 m of a coal face.
(3) Illustrated the main constraints and secondary factors affecting the stability of a coal face.
(4) Proposed a new technology, “manila + grouting” reinforcement into a coal face.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, DZ., Cheng, ZB. & Zheng, SS. Study on the failure mechanism and stability control measures in a large-cutting-height coal mining face with a deep-buried seam. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78, 6143–6157 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01523-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01523-0