Abstract
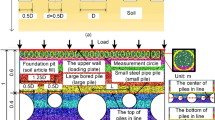
The largest coal bunker in China will be built in the Dong Loutian loess region to store coal, and the long V-shaped loess slope of the bunker, more than 60 m in depth, will be excavated. The finite element method of numerical simulation is applied (using linear elastic and hardening soil models) to simulate stability of the excavation slope and deformation with and without reinforcement, with a view to predict the deformation trend, design the reinforcement scheme, decrease the unrealistically large heave at the base of excavation and horizontal displacement of the excavation slope, and ensure the safety of the project. The simulation results show that the stress field redistributes after excavation and reinforcement, and the horizontal displacement of the slope is inhibited effectively, while the soil at the base of the bunker should be emphatically compacted and supported by piles. The field-measured data are in better agreement with the results calculated from the hardening-soil model and the combined support mode of anchor and soil nail. Thus, the results can be used to determine the key deformation range and reinforcing areas for engineering design.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ataei M, Bodaghabadi S (2008) Comprehensive analysis of slope stability and determination of stable slopes in the Chador–Malu iron ore mine using numerical and limit equilibrium methods. J China Univ Min Technol 18(4):488–493
Brencich A (2010) A Deep trench, landslide and effects on the foundations of a residential building: A case study. Eng Struct 32:1821–1829
Chen XP (2011) Research on stability of an excavated high slope. Appl Mech Mater 90:377–382 (in Chinese)
Chen JX, Xuan JJ, Qiao X (2011) Numerical simulation of support action of systematic anchorage bolts in shallow-buried loess tunnel. J Chang’an Univ (Nat Sci Edn) 31(1):59–62 (in Chinese)
Guo J, Wang QC (2012) The numerical simulation analysis of excavation process of loess tunnel. Adv Mater Res 383:6594–6600
Koner R, Chakravarty D (2010) Discrete element approach for mine dump stability analysis. Min Sci Technol 20(2010):0809–0813
Koner R, Chakravarty D, Singh AK, Chakravarty K (2008) Application of numerical methods for assessment of slope stability. Mine Tech 29(1):3–10
Li ZQ, Tang C, Hu RL (2013) Research on model fitting and strength characteristics of critical state for expansive soil. J Civil Eng Manag 19(1):9–15
Mansour Z, Chik Z, Taha MR (2010) Predicting the geotechnical performance of Lisan Marl using finite element analysis, Dead Sea area. Nat Hazards 54:931–947
Nezar AH, Abdallah I, Husein M (2008) Stability analysis of slopes using the finite element method and limiting equilibrium approach. Bull Eng Geol Environ 67:471–478
Singh TN, Gulati A, Dontha L, Bhardwaj V (2008) Evaluating cut slope failure by numerical analysis a case study. Nat Hazards 47:263–279
Song HW, Duan YY, Yang J (2010) Numerical simulation on bolted rock joint shearing performance. Min Sci Technol 20(3):460–465
Wang C, Tannant DD, Lilly PA (2003) Numerical analysis of the stability of heavily jointed rock slopes using PFC2D. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40:415–424
Xu S, Zhao T (2013) The loess slope stability study. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on systems engineering and modeling (ICSEM-13), Atlantis Press, France, pp 0036–0039
Yin SH, Wu AX (2006) Experimental study of preferential solute transportation during dump leaching. J China Univ Min Technol 16(4):416–420
Zhang KY, Ai YB (2012) Comparison and application of different elasto-plastic constitutive models in FEM analysis of and excavated soil slope. J Civil Eng Manag 18(6):802–810
Zhou X, Chen H (2010) Application of discrete element method in stability analysis for rock slope based on strength reduction. In: Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IE&EM), IEEE, pp 1497–1501
Zhou YD, Cheuk CY, Yham LG (2009) An embedded bond-slip model for finite element modeling of soil–nail interaction. Comput Geotech 36:1090–1097
Acknowledgments
This research is financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41102186, 41072226, 41330643); Opening fund of State Key Laboratory for Geomechanics and Deep Underground Engineering (China University of Mining and Technology) (SKLGDUEK 1006); Opening fund of State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection (Chengdu University of Technology) (SKLGP2011K001); the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Simulation and Regulation of Water Cycle in River Basin (China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research), Grant No. IWHR-SKL-201217.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z.Q., Oyediran, I.A., Tang, C. et al. FEM application to loess slope excavation and support: case study of Dong Loutian coal bunker, Shuozhou, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 73, 1013–1023 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-013-0564-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-013-0564-6