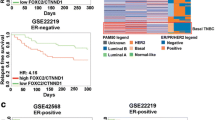
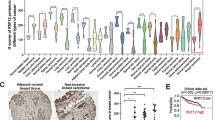
Abstract
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a well-known growth factor that induces cancer cell migration and invasion. Previous studies have shown that SMAD ubiquitination regulatory factor 1 (SMURF1), an E3 ubiquitin ligase, regulates cell motility by inducing RhoA degradation. Therefore, we examined the role of SMURF1 in EGF-induced cell migration and invasion using MDA-MB-231 cells, a human breast cancer cell line. EGF increased SMURF1 expression at both the mRNA and protein levels. All ErbB family members were expressed in MDA-MB-231 cells and receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors specific for the EGF receptor (EGFR) or ErbB2 blocked the EGF-mediated induction of SMURF1 expression. Within the signaling pathways examined, ERK1/2 and protein kinase C activity were required for EGF-induced SMURF1 expression. The overexpression of constitutively active MEK1 increased the SMURF1 to levels similar to those induced by EGF. SMURF1 induction by EGF treatment or by the overexpression of MEK1 or SMURF1 resulted in enhanced cell migration and invasion, whereas SMURF1 knockdown suppressed EGF- or MEK1-induced cell migration and invasion. EGF treatment or SMURF1 overexpression decreased the endogenous RhoA protein levels. The overexpression of constitutively active RhoA prevented EGF- or SMURF1-induced cell migration and invasion. These results suggest that EGFinduced SMURF1 plays a role in breast cancer cell migration and invasion through the downregulation of RhoA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asanuma, K., Yanagida-Asanuma, E., Faul, C., Tomino, Y., Kim, K., and Mundel, P. (2006). Synaptopodin orchestrates actin organization and cell motility via regulation of RhoA signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 485–491.
Balz, L.M., Bartkowiak, K., Andreas, A., Pantel, K., Niggemann, B., Zanker, K.S., Brandt, B.H., and Dittmar, T. (2012). The interplay of HER2/HER3/PI3K and EGFR/HER2/PLC-gamma1 signalling in breast cancer cell migration and dissemination. J. Pathol. 227, 234–244.
Barr, S., Thomson, S., Buck, E., Russo, S., Petti, F., Sujka-Kwok, I., Eyzaguirre, A., Rosenfeld-Franklin, M., Gibson, N.W., Miglarese, M., et al. (2008). Bypassing cellular EGF receptor dependence through epithelial-to-mesenchymal-like transitions. Clin. Exp. Metastasis. 25, 685–693.
Brandt, B.H., Roetger, A., Dittmar, T., Nikolai, G., Seeling, M., Merschjann, A., Nofer, J.R., Dehmer-Moller, G., Junker, R., Assmann, G., et al. (1999). c-erbB-2/EGFR as dominant heterodimerization partners determine a motogenic phenotype in human breast cancer cells. FASEB J. 13, 1939–1949.
Cardoso, A.P., Pinto, M.L., Pinto, A.T., Oliveira, M.I., Pinto, M.T., Goncalves, R., Relvas, J.B., Figueiredo, C., Seruca, R., Mantovani, A., et al. (2013). Macrophages stimulate gastric and colorectal cancer invasion through EGFR Y, c-Src, Erk1/2 and Akt phosphorylation and small GTPase activity. Oncogene [Epub ahead of print] doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.154
Citri, A., and Yarden, Y. (2006). EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7, 505–516.
De Luca, A., Carotenuto, A., Rachiglio, A., Gallo, M., Maiello, M.R., Aldinucci, D., Pinto, A., and Normanno, N. (2008). The role of the EGFR signaling in tumor microenvironment. J. Cell. Physiol. 214, 559–567.
Dittmar, T., Husemann, A., Schewe, Y., Nofer, J.R., Niggemann, B., Zanker, K.S., and Brandt, B.H. (2002). Induction of cancer cell migration by epidermal growth factor is initiated by specific phosphorylation of tyrosine 1248 of c-erbB-2 receptor via EGFR. FASEB J. 16, 1823–1825.
Du, W.W., Yang, B.B., Shatseva, T.A., Yang, B.L., Deng, Z., Shan, S.W., Lee, D.Y., Seth, A., and Yee, A.J. (2010). Versican G3 promotes mouse mammary tumor cell growth, migration, and metastasis by influencing EGF receptor signaling. PLoS One 5, e13828.
Eccles, S.A. (2001). The role of c-erbB-2/HER2/neu in breast cancer progression and metastasis. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 6, 393–406.
Fidler, I.J. (2003). The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat. Rev. Cancer 3, 453–458.
Fukunaga, E., Inoue, Y., Komiya, S., Horiguchi, K., Goto, K., Saitoh, M., Miyazawa, K., Koinuma, D., Hanyu, A., and Imamura, T. (2008). Smurf2 induces ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Smurf1 to prevent migration of breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 35660–35667.
Giltnane, J.M., Moeder, C.B., Camp, R.L., and Rimm, D.L. (2009). Quantitative multiplexed analysis of ErbB family coexpression for primary breast cancer prognosis in a large retrospective cohort. Cancer 115, 2400–2409.
Gril, B., Palmieri, D., Bronder, J.L., Herring, J.M., Vega-Valle, E., Feigenbaum, L., Liewehr, D.J., Steinberg, S.M., Merino, M.J., Rubin, S.D., et al. (2008). Effect of lapatinib on the outgrowth of metastatic breast cancer cells to the brain. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 100, 1092–1103.
Han, J., Li, L., Hu, J., Yu, L., Zheng, Y., Guo, J., Zheng, X., Yi, P., and Zhou, Y. (2010). Epidermal growth factor stimulates human trophoblast cell migration through Rho A and Rho C activation. Endocrinology 151, 1732–1742.
Hynes, N.E., and Lane, H.A. (2005). ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 5, 341–354.
Jemal, A., Siegel, R., Ward, E., Hao, Y., Xu, J., Murray, T., and Thun, M.J. (2008). Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J. Clin. 58, 71–96.
Jin, Y.H., Jeon, E.J., Li, Q.L., Lee, Y.H., Choi, J.K., Kim, W.J., Lee, K.Y., and Bae, S.C. (2004). Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates p300-dependent RUNX3 acetylation, which inhibits ubiquitination-mediated degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 29409–29417.
Jun, J.H., Yoon, W.J., Seo, S.B., Woo, K.M., Kim, G.S., Ryoo, H.M., and Baek, J.H. (2010). BMP2-activated Erk/MAP kinase stabilizes Runx2 by increasing p300 levels and histone acetyltransferase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 36410–36419.
Klapper, L.N., Kirschbaum, M.H., Sela, M., and Yarden, Y. (2000). Biochemical and clinical implications of the ErbB/HER signaling network of growth factor receptors. Adv. Cancer Res. 77, 25–79.
Kusama, T., Mukai, M., Endo, H., Ishikawa, O., Tatsuta, M., Nakamura, H., and Inoue, M. (2006). Inactivation of Rho GTPases by p190 RhoGAP reduces human pancreatic cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer Sci. 97, 848–853.
Kwei, K.A., Shain, A.H., Bair, R., Montgomery, K., Karikari, C.A., van de Rijn, M., Hidalgo, M., Maitra, A., Bashyam, M.D., and Pollack, J.R. (2011). SMURF1 amplification promotes invasiveness in pancreatic cancer. PLoS One 6, e23924.
Lee, H.L., Yi, T., Baek, K., Kwon, A., Hwang, H.R., Qadir, A.S., Park, H.J., Woo, K.M., Ryoo, H.M., Kim, G.S., et al. (2013). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha enhances the transcription of Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor 1 in an activating protein-1- and Runx2-dependent manner. J. Cell. Physiol. 228, 1076–1086.
Lo, H.W., Hsu, S.C., and Hung, M.C. (2006). EGFR signaling pathway in breast cancers: from traditional signal transduction to direct nuclear translocalization. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 95, 211–218.
MacDonald, I.C., Groom, A.C., and Chambers, A.F. (2002). Cancer spread and micrometastasis development: quantitative approaches for in vivo models. Bioessays 24, 885–893.
Miettinen, P.J., Ebner, R., Lopez, A.R., and Derynck, R. (1994). TGF-beta induced transdifferentiation of mammary epithelial cells to mesenchymal cells: involvement of type I receptors. J. Cell Biol. 127, 2021–2036.
Molli, P.R., Adam, L., and Kumar, R. (2008). Therapeutic IMC-C225 antibody inhibits breast cancer cell invasiveness via Vav2-depen-dent activation of RhoA GTPase. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 6161–6170.
Muller, T., Bain, G., Wang, X., and Papkoff, J. (2002). Regulation of epithelial cell migration and tumor formation by beta-catenin signaling. Exp. Cell. Res. 280, 119–133.
Nannuru, K.C., and Singh, R.K. (2010). Tumor-stromal interactions in bone metastasis. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 8, 105–113.
Nie, F., Yang, J., Wen, S., An, Y.L., Ding, J., Ju, S.H., Zhao, Z., Chen, H.J., Peng, X.G., Wong, S.T., et al. (2012). Involvement of epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression in the promotion of breast cancer brain metastasis. Cancer 118, 5198–5209.
Olayioye, M.A., Neve, R.M., Lane, H.A., and Hynes, N.E. (2000). The ErbB signaling network: receptor heterodimerization in development and cancer. EMBO J. 19, 3159–3167.
Ozdamar, B., Bose, R., Barrios-Rodiles, M., Wang, H.R., Zhang, Y., and Wrana, J.L. (2005). Regulation of the polarity protein Par6 by TGFbeta receptors controls epithelial cell plasticity. Science 307, 1603–1609.
Price, J.T., Wilson, H.M., and Haites, N.E. (1996). Epidermal growth factor (EGF) increases the in vitro invasion, motility and adhesion interactions of the primary renal carcinoma cell line, A704. Eur. J. Cancer 32A, 1977–1982.
Raftopoulou, M., and Hall, A. (2004). Cell migration: Rho GTPases lead the way. Dev. Biol. 265, 23–32.
Ridley, A.J., Schwartz, M.A., Burridge, K., Firtel, R.A., Ginsberg, M.H., Borisy, G., Parsons, J.T., and Horwitz, A.R. (2003). Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science 302, 1704–1709.
Sahai, E., Garcia-Medina, R., Pouyssegur, J., and Vial, E. (2007). Smurf1 regulates tumor cell plasticity and motility through degradation of RhoA leading to localized inhibition of contractility. J. Cell Biol. 176, 35–42.
Sanchez, N.S., and Barnett, J.V. (2012). TGFbeta and BMP-2 regulate epicardial cell invasion via TGFbetaR3 activation of the Par6/Smurf1/RhoA pathway. Cell. Signal. 24, 539–548.
Shibata, T., Kawano, T., Nagayasu, H., Okumura, K., Arisue, M., Hamada, J., Takeichi, N., and Hosokawa, M. (1996). Enhancing effects of epidermal growth factor on human squamous cell carcinoma motility and matrix degradation but not growth. Tumour Biol. 17, 168–175.
Solomayer, E.F., Diel, I.J., Meyberg, G.C., Gollan, C., and Bastert, G. (2000). Metastatic breast cancer: clinical course, prognosis and therapy related to the first site of metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 59, 271–278.
Suzuki, A., Shibata, T., Shimada, Y., Murakami, Y., Horii, A., Shiratori, K., Hirohashi, S., Inazawa, J., and Imoto, I. (2008). Identification of SMURF1 as a possible target for 7q21.3–22.1 amplification detected in a pancreatic cancer cell line by in-house array-based comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer Sci. 99, 986–994.
Townsend, T.A., Wrana, J.L., Davis, G.E., and Barnett, J.V. (2008). Transforming growth factor-beta-stimulated endocardial cell transformation is dependent on Par6c regulation of RhoA. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 13834–13841.
Vaidya, R.J., Ray, R.M., and Johnson, L.R. (2005). MEK1 restores migration of polyamine-depleted cells by retention and activation of Rac1 in the cytoplasm. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 288, C350–359.
Valles, A.M., Boyer, B., Badet, J., Tucker, G.C., Barritault, D., and Thiery, J.P. (1990). Acidic fibroblast growth factor is a modulator of epithelial plasticity in a rat bladder carcinoma cell line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 1124–1128.
Wang, H.R., Zhang, Y., Ozdamar, B., Ogunjimi, A.A., Alexandrova, E., Thomsen, G.H., and Wrana, J.L. (2003). Regulation of cell polarity and protrusion formation by targeting RhoA for degradation. Science 302, 1775–1779.
Worthylake, R.A., and Burridge, K. (2003). RhoA and ROCK promote migration by limiting membrane protrusions. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 13578–13584.
Yang, S., and Kim, H.M. (2012). The RhoA-ROCK-PTEN pathway as a molecular switch for anchorage dependent cell behavior. Biomaterials 33, 2902–2915.
Yang, X., Zhu, M.J., Sreejayan, N., Ren, J., and Du, M. (2005). Angiotensin II promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration through release of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor and activation of EGF-receptor pathway. Mol. Cells 20, 263–270.
Zhu, H., Kavsak, P., Abdollah, S., Wrana, J.L., and Thomsen, G.H. (1999). A SMAD ubiquitin ligase targets the BMP pathway and affects embryonic pattern formation. Nature 400, 687–693.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, A., Lee, HL., Woo, K.M. et al. SMURF1 Plays a role in EGF-induced breast cancer cell migration and invasion. Mol Cells 36, 548–555 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-0233-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-0233-4