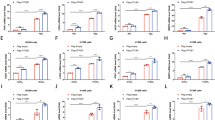
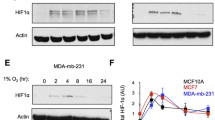
Abstract
Under hypoxic conditions, cells activate a transcriptional response mainly driven by hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs). HIF-1α stabilization and activity are known to be regulated by thioredoxin 1 (Txn1), but how the thioredoxin system regulates the hypoxic response is unknown. By examining the effects of Txn1 overexpression on HIF-1α function in HeLa, HT-29, MCF-7 and EMT6 cell lines, we found that this oxidoreductase did not stabilize HIF-1α, yet could increase its activity. These effects were dependent on the redox function of Txn1. However, Txn1 deficiency did not affect HIF-1α hypoxic-stabilization and activity, and overexpression of thioredoxin reductase 1 (TR1), the natural Txn1 reductase, had no influence on HIF-1α activity. Moreover, overexpression of Txn1 in TR1 deficient HeLa and EMT6 cells was still able to increase HIF-1α hypoxic activity. These results indicate that Txn1 is not essential for HIF-1α hypoxic stabilization or activity, that its overexpression can increase HIF-1α hypoxic activity, and that this effect is observed regardless of TR1 status. Thus, regulation of HIF-1α by the thioredoxin system depends on the specific levels of this system’s major components.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfranca, A., Gutierrez, M.D., Vara, A., Aragones, J., Vidal, F., and Landazuri, M.O. (2002). c-Jun and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 functionally cooperate in hypoxia-induced gene transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 12–22.
Alvarez-Tejado, M., Alfranca, A., Aragones, J., Vara, A., Landazuri, M.O., and del Peso, L. (2002). Lack of evidence for the involvement of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in the activation of hypoxia inducible factors by low oxygen tension. J. Biol. Chem. 28, 13508–13517.
Aragones, J., Jones, D.R., Martin, S., San Juan, M.A., Alfranca, A., Vidal, F., Vara, A., Merida, I., and Landazuri, M.O. (2001). Evidence for the involvement of diacylglycerol kinase in the activation of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1 by low oxygen tension. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 10548–10555.
Bruick, R.K., and McKnight, S.L. (2001). A conserved family of prolyl-4-hydroxylases that modify HIF. Science 294, 1337–1340.
Carrero, P., Okamoto, K., Coumailleau, P., O’Brien, S., Tanaka, H., and Poellinger, L. (2000). Redox-regulated recruitment of the transcriptional coactivators CREB-binding protein and SRC-1 to hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 402–415.
Chandel, N.S., Maltepe, E., Goldwasser, E., Mathieu, C.E., Simon, M.C., and Schumacker, P.T. (1998). Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species trigger hypoxia-induced transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 11715–11720.
Chua, Y.L., Dufour, E., Dassa, E.P., Rustin, P., Jacobs, H.T., Taylor, C.T., and Hagen, T. (2010). Stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein in hypoxia occurs independently of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 31277–31284.
Conrad, P.W., Freeman, T.L., Beitner-Johnson, D., and Millhorn, D. E. (1999a). EPAS1 trans-activation during hypoxia requires p42/p44 MAPK. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 33709–33713.
Conrad, P.W., Rust, R.T., Han, J., Millhorn, D.E., and Beitner-Johnson, D. (1999b). Selective activation of p38alpha and p38 gamma by hypoxia. Role in regulation of cyclin d1 by hypoxia in pc12 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 23570–23576.
Cormier-Regard, S., Nguyen, S.V., and Claycomb, W.C. (1998). Adrenomedullin gene expression is developmentally regulated and induced by hypoxia in rat ventricular cardiac myocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 17787–17792.
Ema, M., Hirota, K., Mimura, J., Abe, H., Yodoi, J., Sogawa, K., Poellinger, L., and Fujii-Kuriyama, Y. (1999). Molecular mechanisms of transcription activation by HLF and HIF1alpha in response to hypoxia: their stabilization and redox signal-induced interaction with CBP/p300. EMBO J. 18, 1905–1914.
Epstein, A.C., Gleadle, J.M., McNeill, L.A., Hewitson, K.S., O’Rourke, J., Mole, D.R., Mukherji, M., Metzen, E., Wilson, M.I., Dhanda, A., et al. (2001). C. elegans EGL-9 and mammalian homologs define a family of dioxygenases that regulate HIF by prolyl hydroxylation. Cell 107, 43–54.
Forsythe, J.A., Jiang, B.H., Iyer, N.V., Agani, F., Leung, S.W., Koos, R.D., and Semenza, G.L. (1996). Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 4604–4613.
Garayoa, M., Martinez, A., Lee, S., Pio, R., An, W.G., Neckers, L., Trepel, J., Montuenga, L.M., Ryan, H., Johnson, R., et al. (2000). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) up-regulates adrenomedullin expression in human tumor cell lines during oxygen deprivation: a possible promotion mechanism of carcinogenesis. Mol. Endocrinol. 14, 848–862.
Gimenez-Roqueplo, A.P., Favier, J., Rustin, P., Mourad, J.J., Plouin, P.F., Corvol, P., Rotig, A., and Jeunemaitre, X. (2001). The R22X mutation of the SDHD gene in hereditary paraganglioma abolishes the enzymatic activity of complex II in the mitochondrial respiratory chain and activates the hypoxia pathway. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 69, 1186–1197.
Hirota, K., and Semenza, G.L. (2001). Rac1 activity is required for the activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 21166–21172.
Hoffman, D.L., Salter, J.D., and Brookes, P.S. (2007). Response of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation to steady-state oxygen tension: implications for hypoxic cell signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 292, H101–108.
Huang, L.E., Arany, Z., Livingston, D.M., and Bunn, H.F. (1996). Activation of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor depends primarily upon redox-sensitive stabilization of its alpha subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 32253–32259.
Ivan, M., Kondo, K., Yang, H., Kim, W., Valiando, J., Ohh, M., Salic, A., Asara, J.M., Lane, W.S., and Kaelin, W.G., Jr. (2001). HIFalpha targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing. Science 292, 464–468.
Jaakkola, P., Mole, D.R., Tian, Y.M., Wilson, M.I., Gielbert, J., Gaskell, S.J., Kriegsheim, A., Hebestreit, H.F., Mukherji, M., Schofield, C.J., et al. (2001). Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science 292, 468–472.
Lando, D., Peet, D.J., Gorman, J.J., Whelan, D.A., White, M.F., and Bruick, R.K. (2002a). FIH-1 is an asparaginyl hydroxylase enzyme that regulates the transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor. Genes Dev. 16, 1466–1471.
Lando, D., Peet, D.J., Whelan, D.A., Gorman, J.J., and Whitelaw, M.L. (2002b). Asparagine hydroxylation of the HIF transactivation domain a hypoxic switch. Science 295, 858–861.
Mazure, N.M., Chen, E.Y., Laderoute, K.R., and Giaccia, A.J. (1997). Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor by hypoxia is modulated by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway in Ha-ras- transformed cells through a hypoxia inducible factor-1 transcriptional element. Blood 90, 3322–3331.
Meyer, M., Schreck, R., and Baeuerle, P.A. (1993). H2O2 and antioxidants have opposite effects on activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 in intact cells: AP-1 as secondary antioxidant-responsive factor. EMBO J. 12, 2005–2015.
Naranjo-Suarez, S., Carlson, B.A., Tsuji, P.A., Yoo, M.H., Gladyshev, V.N., and Hatfield, D.L. (2012). HIF-independent regulation of thioredoxin reductase 1 contributes to the high levels of reactive oxygen species induced by hypoxia. PLoS One 7, e30470.
Richard, D.E., Berra, E., Gothie, E., Roux, D., and Pouyssegur, J. (1999). p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases phosphorylate hypoxia- inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and enhance the transcriptional activity of HIF-1. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 32631–32637.
Schenk, H., Klein, M., Erdbrugger, W., Droge, W., and Schulze-Osthoff, K. (1994). Distinct effects of thioredoxin and antioxidants on the activation of transcription factors NF-kappa B and AP-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 1672–1676.
Selak, M.A., Armour, S.M., MacKenzie, E.D., Boulahbel, H., Watson, D.G., Mansfield, K.D., Pan, Y., Simon, M.C., Thompson, C.B., and Gottlieb, E. (2005). Succinate links TCA cycle dysfunction to oncogenesis by inhibiting HIF-alpha prolyl hydroxylase. Cancer Cell 7, 77–85.
Semenza, G.L., and Wang, G.L. (1992). A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12, 5447–5454.
Srinivas, V., Leshchinsky, I., Sang, N., King, M.P., Minchenko, A., and Caro, J. (2001). Oxygen sensing and HIF-1 activation does not require an active mitochondria respiratory chain electron-transfer pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 21995–21998.
Tobe, R., Yoo, M.H., Fradejas, N., Carlson, B.A., Calvo, S., Gladyshev, V.N., and Hatfield, D.L. (2012). Thioredoxin reductase 1 deficiency enhances selenite toxicity in cancer cells via a thioredoxin-independent mechanism. Biochem. J. 445, 423–430.
Turanov, A.A., Kehr, S., Marino, S.M., Yoo, M.H., Carlson, B.A., Hatfield, D.L., and Gladyshev, V.N. (2010). Mammalian thioredoxin reductase 1: roles in redox homoeostasis and characterization of cellular targets. Biochem. J. 430, 285–293.
Vaux, E.C., Metzen, E., Yeates, K.M., and Ratcliffe, P.J. (2001). Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor is preserved in the absence of a functioning mitochondrial respiratory chain. Blood 98, 296–302.
Welsh, S.J., Bellamy, W.T., Briehl, M.M., and Powis, G. (2002). The redox protein thioredoxin-1 (Trx-1) increases hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha protein expression: Trx-1 overexpression results in increased vascular endothelial growth factor production and enhanced tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 62, 5089–5095.
Wenger, R.H., Stiehl, D.P., and Camenisch, G. (2005). Integration of oxygen signaling at the consensus HRE. Sci. STKE 2005, re12.
Yoo, M.H., Xu, X.M., Carlson, B.A., Gladyshev, V.N., and Hatfield, D.L. (2006). Thioredoxin reductase 1 deficiency reverses tumor phenotype and tumorigenicity of lung carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 13005–13008.
Zhao, S., Lin, Y., Xu, W., Jiang, W., Zha, Z., Wang, P., Yu, W., Li, Z., Gong, L., Peng, Y., et al. (2009). Glioma-derived mutations in IDH1 dominantly inhibit IDH1 catalytic activity and induce HIF-1alpha. Science 324, 261–265.
Zhong, H., Chiles, K., Feldser, D., Laughner, E., Hanrahan, C., Georgescu, M.M., Simons, J.W., and Semenza, G.L. (2000). Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression by the epidermal growth factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP pathway in human prostate cancer cells: implications for tumor angiogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Res. 60, 1541–1545.
Zhou, J., Damdimopoulos, A.E., Spyrou, G., and Brune, B. (2007). Thioredoxin 1 and thioredoxin 2 have opposed regulatory functions on hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 7482–7490.
Zundel, W., Schindler, C., Hass-Kogan, D., Koong, A., Kaper, F., Chen, E., Gottschalk, A.R., Ryan, H.E., Johnson, R.S., Jefferson, A.B., et al. (2000). Loss of PTEN facilitates HIF-1 mediated gene expression. Genes Dev. 14, 391–396.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Naranjo-Suarez, S., Carlson, B.A., Tobe, R. et al. Regulation of HIF-1α activity by overexpression of thioredoxin is independent of thioredoxin reductase status. Mol Cells 36, 151–157 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-0121-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-0121-y