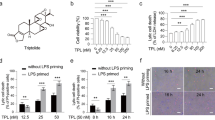
Abstract
Sepsis, a systemic inflammatory response syndrome, remains a potentially lethal condition. (S)-1-α-Naphthylmethyl-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline (CKD712) is noted as a drug candidate for sepsis. Many studies have demonstrated its significant anti-inflammatory effects. Here we first examined whether CKD712 inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced arachidonic acid (AA) release in the RAW 264.7 mouse monocyte cell line, and subsequently, its inhibitory mechanisms. CKD712 reversed LPS-associated morphological changes in the RAW 264.7 cells, and inhibited LPS-induced release of AA in a concentrationdependent manner. The inhibition was apparently due to the diminished expression of a cytosolic form of phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) by CKD712, resulting from reduced NF-κB activation. Furthermore, CKD712 inhibited the activation of ERK1/2 and SAP/JNK, but not of p38 MAPK. CKD712 had no effect on the activity or phosphorylation of cPLA2 and on calcium influx. Our results collectively suggest that CKD712 inhibits LPS-induced AA release through the inhibition of a MAPKs/NF-κB pathway leading to reduced cPLA2 expression in RAW 264.7 cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barancik, M., Bohacova, V., Kvackajova, J., Hudecova, S., Krizanova, O., and Breier, A. (2001). SB203580, a specific inhibitor of p38-MAPK pathway, is a new reversal agent of P-glycoproteinmediated multidrug resistance. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 14, 29–36.
Baron, R.M., Baron, M.J., and Perrella, M.A. (2006). Pathobiology of sepsis: are we still asking the same questions? Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 34, 129–134.
Bennett, B.L., Sasaki, D.T., Murray, B.W., O’Leary, E.C., Sakata, S.T., Xu, W., Leisten, J.C., Motiwala, A., Pierce, S., Satoh, Y., et al. (2001). SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun Nterminal kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 13681–13686.
Casas, J., Meana, C., Esquinas, E., Valdearcos, M., Pindado, J., Balsinde, J., and Balboa, M.A. (2009). Requirement of JNKmediated phosphorylation for translocation of group IVA phospholipase A2 to phagosomes in human macrophages. J. Immunol. 183, 2767–2774.
Clark, J.D., Schievella, A.R., Nalefski, E.A., and Lin, L.L. (1995). Cytosolic phospholipase A2. J. Lipid. Mediat. Cell Signal. 12, 83–117.
Dieter, P., Kolada, A., Kamionka, S., Schadow, A., and Kaszkin, M. (2002). Lipopolysaccharide-induced release of arachidonic acid and prostaglandins in liver macrophages: regulation by Group IV cytosolic phospholipase A2, but not by Group V and Group IIA secretory phospholipase A2. Cell Signal. 14, 199–204.
Gilroy, D.W., Newson, J., Sawmynaden, P., Willoughby, D.A., and Croxtall, J.D. (2004). A novel role for phospholipase A2 isoforms in the checkpoint control of acute inflammation. FASEB J. 18, 489–498.
Glover, S., de Carvalho, M.S., Bayburt, T., Jonas, M., Chi, E., Leslie, C.C., and Gelb, M.H. (1995). Translocation of the 85-kDa phospholipase A2 from cytosol to the nuclear envelope in rat basophilic leukemia cells stimulated with calcium ionophore or IgE/antigen. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 15359–15367.
Kang, Y.J., Lee, Y.S., Lee, G.W., Lee, D.H., Ryu, J.C., Yun-Choi, H.S., and Chang, K.C. (1999). Inhibition of activation of nuclear factor kappaB is responsible for inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by higenamine, an active component of aconite root. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 291, 314–320.
Kim, D.K., and Bonventre, J.V. (1993). Purification of a 100 kDa phospholipase A2 from spleen, lung and kidney: antiserum raised to pig spleen phospholipase A2 recognizes a similar form in bovine lung, kidney and platelets, and immunoprecipitates phospholipase A2 activity. Biochem. J. 294, 261–270.
Kim, Y.S., Kim, G.Y., Kim, J.H., You, H.J., Park, Y.M., Lee, H.K., Yu, H.C., Chung, S.M., Jin, Z.W., Ko, H.M., et al. (2006). Glutamine inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 activation and protects against endotoxin shock in mouse. Shock 25, 290–294.
Kumar, V., Abbas, A.K., Fausto, N., and Mitchell, R. (2007). Robbins Basic Pathology. 8th ed., (Saunders Elsevier).
Lamour, N.F., Subramanian, P., Wijesinghe, D.S., Stahelin, R.V., Bonventre, J.V., and Chalfant, C.E. (2009). Ceramide 1-phosphate is required for the translocation of group IVA cytosolic phospholipase A2 and prostaglandin synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 26897–26907.
Lee, C.W., Lin, C.C., Lee, I.T., Lee, H.C., and Yang, C.M. (2011). Activation and induction of cytosolic phospholipase a(2) by TNFalpha mediated through Nox2, MAPKs, NF-kappa B, and p300 in human tracheal smooth muscle cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 226, 2103–2114.
Leoncini, G., Bruzzese, D., and Signorello, M.G. (2006). Activation of p38 MAPKinase/cPLA2 pathway in homocysteine-treated platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 4, 209–216.
Leslie, C.C. (1997). Properties and regulation of cytosolic phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 16709–16712.
Levy, R., Dana, R., Hazan, I., Levy, I., Weber, G., Smoliakov, R., Pesach, I., Riesenberg, K., and Schlaeffer, F. (2000). Elevated cytosolic phospholipase A(2) expression and activity in human neutrophils during sepsis. Blood 95, 660–665.
Levy, M.M., Fink, M.P., Marshall, J.C., Abraham, E., Angus, D., Cook, D., Cohen, J., Opal, S.M., Vincent, J.L., and Ramsay, G. (2003). 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS international sepsis definitions conference. Crit. Care Med. 31, 1250–1256.
Lin, L.L., Wartmann, M., Lin, A.Y., Knopf, J.L., Seth, A., and Davis, R.J. (1993). cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell 72, 269–278.
Luo, S.F., Lin, W.N., Yang, C.M., Lee, C.W., Liao, C.H., Leu, Y.L., and Hsiao, L.D. (2006). Induction of cytosolic phospholipase A2 by lipopolysaccharide in canine tracheal smooth muscle cells: involvement of MAPKs and NF-kappaB pathways. Cell Signal. 18, 1201–1211.
Magrioti, V., and Kokotos, G. (2009). Phospholipase A2 inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 20, 1–18.
McGuirk, S.P., Griselli, M., Stumper, O.F., Rumball, E.M., Miller, P., Dhillon, R., de Giovanni, J.V., Wright, J.G., Barron, D.J., and Brawn, W.J. (2006). Staged surgical management of hypoplastic left heart syndrome: a single institution 12 year experience. Heart 92, 364–370.
Nagase, T., Uozumi, N., Ishii, S., Kume, K., Izumi, T., Ouchi, Y., and Shimizu, T. (2000). Acute lung injury by sepsis and acid aspiration: a key role for cytosolic phospholipase A2. Nat. Immunol. 1, 42–46.
Nagase, T., Uozumi, N., Aoki-Nagase, T., Terawaki, K., Ishii, S., Tomita, T., Yamamoto, H., Hashizume, K., Ouchi, Y., and Shimizu, T. (2003). A potent inhibitor of cytosolic phospholipase A2, arachidonyl trifluoromethyl ketone, attenuates LPS-induced lung injury in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 284, L720–726.
Oh, Y.J., Youn, J.H., Min, H.J., Kim, D.H., Lee, S.S., Choi, I.H., and Shin, J.S. (2011). CKD712, (S)-1-(alpha-naphthylmethyl)-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline, inhibits the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated secretion of HMGB1 by inhibiting PI3K and classical protein kinase C. Int. Immunopharmacol. 11, 1160–1165.
Park, J.E., Kang, Y.J., Park, M.K., Lee, Y.S., Kim, H.J., Seo, H.G., Lee, J.H., Hye Sook, Y.C., Shin, J.S., Lee, H.W., et al. (2006). Enantiomers of higenamine inhibit LPS-induced iNOS in a macrophage cell line and improve the survival of mice with experimental endotoxemia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 6, 226–233.
Park, J.H., Hwang, I.C., Ha, N., Lee, S., Kim, J.M., Lee, S.S., Yu, H., Lim, I.T., You, J.A., and Kim, D.H. (2011). Effects of the antisepsis drug, (S)-1-(alpha-naphthylmethyl)-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline (CKD-712), on mortality, inflammation, and organ injuries in rodent sepsis models. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 485–494.
Pyo, M.K., Kim, J.M., Jin, J.L., Chang, K.C., Lee, D.H., and Yun-Choi, H.S. (2007). Effects of higenamine and its 1-naphthyl analogs, YS-49 and YS-51, on platelet TXA2 synthesis and aggregation. Thromb. Res. 120, 81–86.
Riendeau, D., Guay, J., Weech, P.K., Laliberte, F., Yergey, J., Li, C., Desmarais, S., Perrier, H., Liu, S., Nicoll-Griffith, D., et al. (1994). Arachidonyl trifluoromethyl ketone, a potent inhibitor of 85-kDa phospholipase A2, blocks production of arachidonate and 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid by calcium ionophore-challenged platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 15619–15624.
Roshak, A., Sathe, G., and Marshall, L.A. (1994). Suppression of monocyte 85-kDa phospholipase A2 by antisense and effects on endotoxin-induced prostaglandin biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 25999–26005.
Saxena, R.K., Vallyathan, V., and Lewis, D.M. (2003). Evidence for lipopolysaccharide-induced differentiation of RAW264.7 murine macrophage cell line into dendritic like cells. J. Biosci. 28, 129–134.
Su, H., McClarty, G., Dong, F., Hatch, G.M., Pan, Z.K., and Zhong, G. (2004). Activation of Raf/MEK/ERK/cPLA2 signaling pathway is essential for chlamydial acquisition of host glycerophospholipids. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 9409–9416.
Tsoyi, K., Kim, H.J., Shin, J.S., Kim, D.H., Cho, H.J., Lee, S.S., Ahn, S.K., Yun-Choi, H.S., Lee, J.H., Seo, H.G., et al. (2008). HO-1 and JAK-2/STAT-1 signals are involved in preferential inhibition of iNOS over COX-2 gene expression by newly synthesized tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid, CKD712, in cells activated with lipopolysacchride. Cell Signal. 20, 1839–1847.
Tsoyi, K., Kim, W.S., Kim, Y.M., Kim, H.J., Seo, H.G., Lee, J.H., Yun-Choi, H.S., and Chang, K.C. (2009). Upregulation of PTEN by CKD712, a synthetic tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid, selectively inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced VCAM-1 but not ICAM-1 expression in human endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 207, 412–419.
Uozumi, N., Kita, Y., and Shimizu, T. (2008). Modulation of lipid and protein mediators of inflammation by cytosolic phospholipase A2alpha during experimental sepsis. J. Immunol. 181, 3558–3566.
Van Putten, V., Refaat, Z., Dessev, C., Blaine, S., Wick, M., Butterfield, L., Han, S.Y., Heasley, L.E., and Nemenoff, R.A. (2001). Induction of cytosolic phospholipase A2 by oncogenic Ras is mediated through the JNK and ERK pathways in rat epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 1226–1232.
Wang, X., Xue, H., Xu, Q., Zhang, K., Hao, X., Wang, L., and Yan, G. (2008). p38 kinase/cytosolic phospholipase A2/cyclooxygenase-2 pathway: a new signaling cascade for lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-1beta and interleukin-6 release in differentiated U937 cells. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 86, 61–67.
Xin, X., Yang, N., and Faber, J.E. (1999). Platelet-derived growth factor inhibits alpha1D-adrenergic receptor expression in vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro and ex vivo. Mol. Pharmacol. 56, 1143–1151.
Yang, C.M., Lin, M.I., Hsieh, H.L., Sun, C.C., Ma, Y.H., and Hsiao, L.D. (2005). Bradykinin-induced p42/p44 MAPK phosphorylation and cell proliferation via Src, EGF receptors, and PI3-K/Akt in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Cell Physiol. 203, 538–546.
Zhi, L., Ang, A.D., Zhang, H., Moore, P.K., and Bhatia, M. (2007) Hydrogen sulfide induces the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines in human monocyte cell line U937 via the ERK-NFkappaB pathway. J. Leukoc. Biol. 81, 1322–1332.
Zhou, S.J., and Du, G.Y. (2003). Effects of higenamine on the cardio-circulatory system. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 28, 910–913.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J.M., Choi, Y.H., Kim, S.K. et al. (S)-tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid inhibits LPS-induced arachidonic acid release through downregulation of cPLA2 expression. Mol Cells 36, 400–409 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-0078-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-0078-x