Abstract
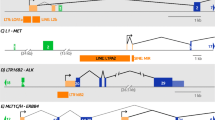
Retroviral integration provides us with a powerful tool to realize prolonged gene expressions that are often critical to gene therapy. However, the perturbation of gene regulations in host cells by viral genome integration can lead to detrimental effects, yielding cancer. The oncogenic potential of retroviruses is linked to the preference of retroviruses to integrate into genomic regions that are enriched in gene regulatory elements. To better navigate the double-edged sword of retroviral integration we need to understand how retroviruses select their favored genomic loci during infections. In this study I showed that in addition to host proteins that tether retroviral pre-integration complexes to specific genomic regions, the epigenetic architecture of host genome might strongly affect retroviral integration patterns. Specifically, retroviruses showed their characteristic integration preference in differentiated somatic cells. In contrast, retroviral infections of hES cells, which are known to display decondensed chromatin, produced random-like integration patterns lacking of strong preference for regulatory-element-rich genomic regions. Better identification of the cellular and viral factors that determine retroviral integration patterns will facilitate the design of retroviral vectors for safer use in gene therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang, Y.S., Gaspar-Maia, A., Lemischka, I.R., and Bernstein, E. (2011). Stem cells and reprogramming: breaking the epigenetic barrier? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 32, 394–401.
Appelt, J.U., Giordano, F.A., Ecker, M., Roeder, I., Grund, N., Hotz-Wagenblatt, A., Opelz, G., Zeller, W.J., Allgayer, H., Fruehauf, S., et al. (2009). QuickMap: a public tool for large-scale gene therapy vector insertion site mapping and analysis. Gene Ther. 16, 885–893.
Bartholomae, C.C., Arens, A., Balaggan, K.S., Yanez-Munoz, R.J., Montini, E., Howe, S.J., Paruzynski, A., Korn, B., Appelt, J.U., Macneil, A., et al. (2011). Lentiviral vector integration profiles differ in rodent postmitotic tissues. Mol. Ther. 19, 703–710.
Biasco, L., Ambrosi, A., Pellin, D., Bartholomae, C., Brigida, I., Roncarolo, M.G., Di Serio, C., von Kalle, C., Schmidt, M., and Aiuti, A. (2011). Integration profile of retroviral vector in gene therapy treated patients is cell-specific according to gene expression and chromatin conformation of target cell. EMBO Mol. Med. 3, 89–101.
Cattoglio, C., Facchini, G., Sartori, D., Antonelli, A., Miccio, A., Cassani, B., Schmidt, M., von Kalle, C., Howe, S., Thrasher, A.J., et al. (2007). Hot spots of retroviral integration in human CD34+ hematopoietic cells. Blood 110, 1770–1778.
Cattoglio, C., Pellin, D., Rizzi, E., Maruggi, G., Corti, G., Miselli, F., Sartori, D., Guffanti, A., Di Serio, C., Ambrosi, A., et al. (2010). High-definition mapping of retroviral integration sites identifies active regulatory elements in human multipotent hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 116, 5507–5517.
Dull, T., Zufferey, R., Kelly, M., Mandel, R.J., Nguyen, M., Trono, D., and Naldini, L. (1998). A third-generation lentivirus vector with a conditional packaging system. J. Virol. 72, 8463–8471.
Efroni, S., Duttagupta, R., Cheng, J., Dehghani, H., Hoeppner, D.J., Dash, C., Bazett-Jones, D.P., Le Grice, S., McKay, R.D., Buetow, K.H., et al. (2008). Global transcription in pluripotent embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2, 437–447.
Engelman, A., and Cherepanov, P. (2008). The lentiviral integrase binding protein LEDGF/p75 and HIV-1 replication. PLoS Pathog. 4, e1000046.
Felice, B., Cattoglio, C., Cittaro, D., Testa, A., Miccio, A., Ferrari, G., Luzi, L., Recchia, A., and Mavilio, F. (2009). Transcription factor binding sites are genetic determinants of retroviral integration in the human genome. PLoS One 4, e4571.
Fisher, C.L., and Fisher, A.G. (2011). Chromatin states in pluripotent, differentiated, and reprogrammed cells. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 21, 140–146.
Hacein-Bey-Abina, S., Von Kalle, C., Schmidt, M., McCormack, M.P., Wulffraat, N., Leboulch, P., Lim, A., Osborne, C.S., Pawliuk, R., Morillon, E., et al. (2003). LMO2-associated clonal T cell proliferation in two patients after gene therapy for SCID-X1. Science 302, 415–419.
Hematti, P., Hong, B.K., Ferguson, C., Adler, R., Hanawa, H., Sellers, S., Holt, I.E., Eckfeldt, C.E., Sharma, Y., Schmidt, M., et al. (2004). Distinct genomic integration of MLV and SIV vectors in primate hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. PLoS Biol. 2, e423.
Huang da, W., Sherman, B.T., and Lempicki, R.A. (2009a). Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 1–13.
Huang da, W., Sherman, B.T., and Lempicki, R.A. (2009b). Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 4, 44–57.
Joffe, B., Leonhardt, H., and Solovei, I. (2010). Differentiation and large scale spatial organization of the genome. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 20, 562–569.
Jorgensen, H.F., Azuara, V., Amoils, S., Spivakov, M., Terry, A., Nesterova, T., Cobb, B.S., Ramsahoye, B., Merkenschlager, M., and Fisher, A.G. (2007). The impact of chromatin modifiers on the timing of locus replication in mouse embryonic stem cells. Genome Biol. 8, R169.
Kalpana, G.V., Marmon, S., Wang, W., Crabtree, G.R., and Goff, S.P. (1994). Binding and stimulation of HIV-1 integrase by a human homolog of yeast transcription factor SNF5. Science 266, 2002–2006.
Kiem, H.P., Ironside, C., Beard, B.C., and Trobridge, G.D. (2010). A retroviral vector common integration site between leupaxin and zinc finger protein 91 (ZFP91) observed in baboon hematopoietic repopulating cells. Exp. Hematol. 38, 819–22, 822.e1–3.
Kim, S., Kim, N., Dong, B., Boren, D., Lee, S.A., Das Gupta, J., Gaughan, C., Klein, E.A., Lee, C., Silverman, R.H., et al. (2008). Integration site preference of xenotropic murine leukemia virusrelated virus, a new human retrovirus associated with prostate cancer. J. Virol. 82, 9964–9977.
Lewinski, M.K., Yamashita, M., Emerman, M., Ciuffi, A., Marshall, H., Crawford, G., Collins, F., Shinn, P., Leipzig, J., Hannenhalli, S., et al. (2006). Retroviral DNA integration: viral and cellular determinants of target-site selection. PLoS Pathog. 2, e60.
Li, Y., Powell, S., Brunette, E., Lebkowski, J., and Mandalam, R. (2005). Expansion of human embryonic stem cells in defined serum-free medium devoid of animal-derived products. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 91, 688–698.
Lim, K.I., Klimczak, R., Yu, J.H., and Schaffer, D.V. (2010). Specific insertions of zinc finger domains into Gag-Pol yield engineered retroviral vectors with selective integration properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 12475–12480.
Lois, C., Hong, E.J., Pease, S., Brown, E.J., and Baltimore, D. (2002). Germline transmission and tissue-specific expression of transgenes delivered by lentiviral vectors. Science 295, 868–872.
Mattout, A., and Meshorer, E. (2010). Chromatin plasticity and genome organization in pluripotent embryonic stem cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 22, 334–341.
Mitchell, R.S., Beitzel, B.F., Schroder, A.R., Shinn, P., Chen, H., Berry, C.C., Ecker, J.R., and Bushman, F.D. (2004). Retroviral DNA integration: ASLV, HIV, and MLV show distinct target site preferences. PLoS Biol. 2, E234.
Orkin, S.H., and Hochedlinger, K. (2011). Chromatin connections to pluripotency and cellular reprogramming. Cell 145, 835–850.
Schroder, A.R., Shinn, P., Chen, H., Berry, C., Ecker, J.R., and Bushman, F. (2002). HIV-1 integration in the human genome favors active genes and local hotspots. Cell 110, 521–529.
Wu, X., Li, Y., Crise, B., and Burgess, S.M. (2003). Transcription start regions in the human genome are favored targets for MLV integration. Science 300, 1749–1751.
Zhang, Y.W., Denham, J., and Thies, R.S. (2006). Oligodendrocyte progenitor cells derived from human embryonic stem cells express neurotrophic factors. Stem Cells Dev. 15, 943–952.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, Ki. Retroviral infection of hES cells produces random-like integration patterns. Mol Cells 33, 525–531 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-012-0038-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-012-0038-x