Abstract
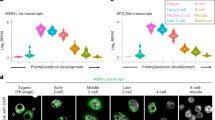
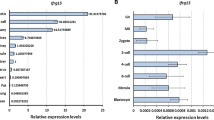
The retromer complex is a heteropentameric protein unit associated with retrograde transport of cargo proteins from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. Functional silencing study of the Vps26a gene indicated the important role of the retromer complex during early developmental stages in the mouse. However, individual expression patterns and quantitative analysis of individual members of the retromer complex during the early developmental stages has not been investigated. In this study, we conducted quantitative expression analysis of six retromer complex genes (Vps26a, Vps26b, Vps29, Vps35, Snx1, and Snx2) and one related receptor gene (Ci-mpr) during the eleven embryonic stages with normal MEF (mouse embryonic fibroblast) and Vps26a−/− MEF cells. Remarkably, except for Vps26a (maternal expression pattern), all tested genes showed maternal-zygotic expression patterns. And five genes (Vps26b, Vps29, Vps35, Snx2, and Ci-mpr) showed a pattern of decreased expression in Vps26a−/− MEF cells by comparative analysis between normal MEF and Vps26a−/− MEF cells. However, the Snx1 gene showed a pattern of increased expression in Vps26a−/− MEF cells. From our results, we could assume that retromer complexrelated genes have important roles during oocyte development. However, in the preimplantation stage, they did not have significant roles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amati, F., Biancolella, M., Farcomeni, A., Giallonardi, S., Bueno, S., Minella, D., Vecchione, L., Chillemi, G., Desideri, A., and Novelli, G. (2007). Dynamic changes in gene expression profiles of 22q11 and related orthologous genes during mouse development. Gene 391, 91–102.
Arighi, C.N., Hartnell, L.M., Aguilar, R.C., Haft, C.R., and Bonifacino, J.S. (2004). Role of the mammalian retromer in sorting of the cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor. J. Cell Biol. 165, 123–133.
Bachhawat, A.K., Suhan, J., and Jones, E.W. (1994). The yeast homolog of H <beta> 58, a mouse gene essential for embryogenesis, performs a role in the delivery of proteins to the vacuole. Genes Dev. 8, 1379–1387.
Belenkaya, T.Y., Wu, Y., Tang, X., Zhou, B., Cheng, L., Sharma, Y.V., Yan, D., Selva, E.M., and Lin, X. (2008). The retromer complex influences Wnt secretion by recycling wntless from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. Dev. Cell 14, 120–131.
Bonifacino, J.S., and Hurley, J.H. (2008). Retromer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 20, 427–436.
Chen, D., Xiao, H., Zhang, K., Wang, B., Gao, Z., Jian, Y., Qi, X., Sun, J., Miao, L., and Yang, C. (2010). Retromer is required for apoptotic cell clearance by phagocytic receptor recycling. Science 327, 1261–1264.
Collins, B.M. (2008). The structure and function of the retromer protein complex. Traffic 9, 1811–1822.
Collins, B.M., Norwood, S.J., Kerr, M.C., Mahony, D., Seaman, M.N., Teasdale, R.D., and Owen, D.J. (2008). Structure of Vps26B and mapping of its interaction with the retromer protein complex. Traffic 9, 366–379.
Hamatani, T., Carter, M.G., Sharov, A.A., and Ko, M.S. (2004). Dynamics of global gene expression changes during mouse preimplantation development. Dev. Cell 6, 117–131.
Hierro, A., Rojas, A.L., Rojas, R., Murthy, N., Effantin, G., Kajava, A.V., Steven, A.C., Bonifacino, J.S., and Hurley, J.H. (2007). Functional architecture of the retromer cargo-recognition complex. Nature 449, 1063–1067.
Kerr, M.C., Bennetts, J.S., Simpson, F., Thomas, E.C., Flegg, C., Gleeson, P.A., Wicking, C., and Teasdale, R.D. (2005). A novel mammalian retromer component, Vps26B. Traffic 6, 991–1001.
Kurten, R.C., Cadena, D.L., and Gill, G.N. (1996). Enhanced degradation of EGF receptors by a sorting nexin, SNX1. Science 272, 1008–1010.
Lee, J.J., Radice, G., Perkins, C.P., and Costantini, F. (1992). Identification and characterization of a novel, evolutionarily conserved gene disrupted by the murine H beta 58 embryonic lethal transgene insertion. Development 115, 277–288.
Mamo, S., Gal, A.B., Bodo, S., and Dinnyes, A. (2007). Quantitative evaluation and selection of reference genes in mouse oocytes and embryos cultured in vivo and in vitro. BMC Dev. Biol. 7, 14.
Muhammad, A., Flores, I., Zhang, H., Yu, R., Staniszewski, A., Planel, E., Herman, M., Ho, L., Kreber, R., Honig, L.S., et al. (2008). Retromer deficiency observed in Alzheimer’s disease causes hippocampal dysfunction, neurodegeneration, and Abeta accumulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 7327–7332.
Nisar, S., Kelly, E., Cullen, P.J., and Mundell, S.J. (2010). Regulation of P2Y1 receptor traffic by sorting Nexin 1 is retromer independent. Traffic 11, 508–519.
Port, F., Kuster, M., Herr, P., Furger, E., Banziger, C., Hausmann, G., and Basler, K. (2008). Wingless secretion promotes and requires retromer-dependent cycling of Wntless. Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 178–185.
Radice, G., Lee, J.J., and Costantini, F. (1991). H beta 58, an insertional mutation affecting early postimplantation development of the mouse embryo. Development 111, 801–811.
Rojas, R., Kametaka, S., Haft, C.R., and Bonifacino, J.S. (2007). Interchangeable but essential functions of SNX1 and SNX2 in the association of retromer with endosomes and the trafficking of mannose 6-phosphate receptors. Mol. Cell Biol. 27, 1112–1124.
Rozen, S., and Skaletsky, H. (2000). Primer3 on the www for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol. Biol. 132, 365–386.
Schwarz, D.G., Griffin, C.T., Schneider, E.A., Yee, D., and Magnuson, T. (2002). Genetic analysis of sorting nexins 1 and 2 reveals a redundant and essential function in mice. Mol. Biol. Cell 13, 3588–3600.
Seaman, M.N. (2004). Cargo-selective endosomal sorting for retrieval to the Golgi requires retromer. J. Cell Biol. 165, 111–122.
Seaman, M.N. (2005). Recycle your receptors with retromer. Trends Cell Biol. 15, 68–75.
Seaman, M.N. (2007). Identification of a novel conserved sorting motif required for retromer-mediated endosome-to-TGN retrieval. J. Cell Sci. 120, 2378–2389.
Seaman, M.N., McCaffery, J.M., and Emr, S.D. (1998). A membrane coat complex essential for endosome-to-Golgi retrograde transport in yeast. J. Cell Biol. 142, 665–681.
Shi, H., Rojas, R., Bonifacino, J.S., and Hurley, J.H. (2006). The retromer subunit Vps26 has an arrestin fold and binds Vps35 through its C-terminal domain. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 540–548.
Small, S.A. (2008). Retromer sorting: a pathogenic pathway in lateonset Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 65, 323–328.
Small, S.A., Kent, K., Pierce, A., Leung, C., Kang, M.S., Okada, H., Honig, L., Vonsattel, J.P., and Kim, T.W. (2005). Model-guided microarray implicates the retromer complex in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 58, 909–919.
Vandesompele, J., De Preter, K., Pattyn, F., Poppe, B., Van Roy, N., De Paepe, A., and Speleman, F. (2002). Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 3, RESEARCH0034.
Verges, M., Luton, F., Gruber, C., Tiemann, F., Reinders, L.G., Huang, L., Burlingame, A.L., Haft, C.R., and Mostov, K.E. (2004). The mammalian retromer regulates transcytosis of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. Nat. Cell Biol. 6, 763–769.
Wang, Z.Q., Fung, M.R., Barlow, D.P., and Wagner, E.F. (1994). Regulation of embryonic growth and lysosomal targeting by the imprinted Igf2/Mpr gene. Nature 372, 464–467.
Wang, Y., Zhou, Y., Szabo, K., Haft, C.R., and Trejo, J. (2002). Down-regulation of protease-activated receptor-1 is regulated by sorting nexin 1. Mol. Biol. Cell 13, 1965–1976.
Wang, T.H., Chang, C.L., Wu, H.M., Chiu, Y.M., Chen, C.K., and Wang, H.S. (2006). Insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II), IGFbinding protein-3 (IGFBP-3), and IGFBP-4 in follicular fluid are associated with oocyte maturation and embryo development. Fertil. Steril. 86, 1392–1401.
Worby, C.A., and Dixon, J.E. (2002). Sorting out the cellular functions of sorting nexins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 919–931.
Zeng, F., Baldwin, D.A., and Schultz, R.M. (2004). Transcript profiling during preimplantation mouse development. Dev. Biol. 272, 483–496.
Zhao, X., Nothwehr, S., Lara-Lemus, R., Zhang, B.Y., Peter, H., and Arvan, P. (2007). Dominant-negative behavior of mammalian Vps35 in yeast requires a conserved PRLYL motif involved in retromer assembly. Traffic 8, 1829–1840.
Zhong, Q., Watson, M.J., Lazar, C.S., Hounslow, A.M., Waltho, J.P., and Gill, G.N. (2005). Determinants of the endosomal localization of sorting nexin 1. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 2049–2057.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, SJ., Huh, JW., Kim, YH. et al. Quantitative analysis of retromer complex-related genes during embryo development in the mouse. Mol Cells 31, 431–436 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-0272-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-0272-7