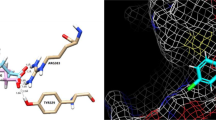
Abstract
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 (HIF-1) plays an important role as a transcription factor under hypoxia. It activates numerous genes including those involved in angiogenesis, glucose metabolisms, cell proliferation and cell survival. The HIF-1α subunit is regulated by 2-oxoglutarate (OG)- and Fe(II)-dependent hydroxylases, including Factor Inhibiting HIF-1 (FIH-1). FIH-1 hydroxylates Asn803 of HIF-1α and blocks its interaction with co-activating molecules. Quinol family compounds such as 5-chloro-7-iodo-8-hydroxyquinoline (Clioquinol) have been shown to inhibit the hydroxylation activity of FIH-1. Here we determined the complex crystal structures of FIH-1: Clioquinol and FIH-1: 8-Hydroxyquinoline. Clioquinol and 8-Hydroxyquinoline bind to the active site of FIH-1 by coordinating the Fe(II) ion, thereby inhibiting the binding of a co-substrate, 2OG. Contrary to other known FIH-1 inhibitors that have negative charges, Clioquinol and 8-hydroxyquinoline are neutral in charge and can provide a template for improved inhibitor design that can selectively inhibit FIH-1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arany, Z., Huang, L., Eckner, R., Bhattacharya, S., Jiang, C., Goldberg, M., Bunn, H., and Livingston, D. (1996). An essential role for p300/CBP in the cellular response to hypoxia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 12969.
Berra, E., Benizri, E., Ginouves, A., Volmat, V., Roux, D., and Pouyssegur, J. (2003) HIF prolyl-hydroxylase 2 is the key oxygen sensor setting low steady-state levels of HIF-1alpha in normoxia. EMBO J. 22, 4082.
Bush, A., and Masters, C. (2001). Clioquinol’s return. Science 292, 2251–2252.
Choi, S., Choi, K., Park, Y., Cho, H., Yang, E., and Park, H. (2006). Clioquinol, a Cu (II)/Zn (II) chelator, inhibits both ubiquitination and asparagine hydroxylation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 {alpha}, leading to expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and erythropoietin in normoxic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 34056.
Dann, C.E., 3rd, Bruick, R.K., and Deisenhofer, J. (2002). Structure of factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor 1: An asparaginyl hydroxylase involved in the hypoxic response pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 15351–15356.
Elkins, J.M., Hewitson, K.S., McNeill, L.A., Seibel, J.F., Schlemminger, I., Pugh, C.W., Ratcliffe, P.J., and Schofield, C.J. (2003). Structure of factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) reveals mechanism of oxidative modification of HIF-1 alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 1802–1806.
Emsley, P., and Cowtan, K. (2004). Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. Section D: Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2126–2132.
Hewitson, K.S., McNeill, L.A., Riordan, M.V., Tian, Y.M., Bullock, A.N., Welford, R.W., Elkins, J.M., Oldham, N.J., Bhattacharya, S., Gleadle, J.M., et al. (2002). Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) asparagine hydroxylase is identical to factor inhibiting HIF (FIH) and is related to the cupin structural family. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 26351–26355.
Hewitson, K.S., McNeill, L.A., and Schofield, C.J. (2004). Modulating the hypoxia-inducible factor signaling pathway: applications from cardiovascular disease to cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 10, 821–833.
Hewitson, K.S., Lienard, B.M., McDonough, M.A., Clifton, I.J., Butler, D., Soares, A.S., Oldham, N.J., McNeill, L.A., and Schofield, C.J. (2007). Structural and mechanistic studies on the inhibition of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factor hydroxylases by tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 3293–3301.
Holm, L., and Sander, C. (1995). Dali: a network tool for protein structure comparison. Trends Biochem. Sci. 20, 478–480.
Kung, A., Zabludoff, S., France, D., Freedman, S., Tanner, E., Vieira, A., Cornell-Kennon, S., Lee, J., Wang, B., and Wang, J. (2004). Small molecule blockade of transcriptional coactivation of the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway. Cancer Cell 6, 33–43.
Lando, D., Peet, D.J., Gorman, J.J., Whelan, D.A., Whitelaw, M.L., and Bruick, R.K. (2002). FIH-1 is an asparaginyl hydroxylase enzyme that regulates the transcriptional activity of hypoxiainducible factor. Genes Dev. 16, 1466–1471.
Lee, C., Kim, S., Jeong, D., Lee, S., and Ryu, S. (2003). Structure of human FIH-1 reveals a unique active site pocket and interaction sites for HIF-1 and von Hippel-Lindau. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 7558–7563.
McDonough, M.A., McNeill, L.A., Tilliet, M., Papamicael, C.A., Chen, Q.Y., Banerji, B., Hewitson, K.S., and Schofield, C.J. (2005). Selective inhibition of factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 7680–7681.
Murshudov, G.N., Vagin, A.A., and Dodson, E.J. (1997). Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 53, 240–255.
Nguyen, T., Hamby, A., and Massa, S.M. (2005). Clioquinol downregulates mutant huntingtin expression in vitro and mitigates pathology in a Huntington’s disease mouse model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 11840–11845.
Raman, B., Ban, T., Yamaguchi, K., Sakai, M., Kawai, T., Naiki, H., and Goto, Y. (2005). Metal ion-dependent effects of clioquinol on the fibril growth of an amyloid ta peptide. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 16157.
Ritchie, C., Bush, A., Mackinnon, A., Macfarlane, S., Mastwyk, M., MacGregor, L., Kiers, L., Cherny, R., Li, Q., and Tammer, A. (2003). Metal-protein attenuation with iodochlorhydroxyquin (clioquinol) targeting abeta amyloid deposition and toxicity in Alzheimer disease A pilot phase 2 clinical trial. Vol. 60, (Am. Med. Assoc.), pp. 1685–1691.
Schofield, C., and Ratcliffe, P. (2004). Oxygen sensing by HIF hydroxylases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 343–354.
Schofield, C., and Zhang, Z. (1999). Structural and mechanistic studies on 2-oxoglutarate-dependent oxygenases and related enzymes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 9, 722–731.
Tabira, T. (2001). Clioquinol’s return: cautions from Japan. Science 292, 2251.
Tateishi, J. (2000). Subacute myelo-optico-neuropathy: clioquinol intoxication in humans and animals. Neuropathology 20, 20–24.
Vagin, A., and Teplyakov, A. (2000). An approach to multi-copy search in molecular replacement. Acta Crystallogr. Section D: Biol. Crystallogr. 56, 1622–1624.
Wang, G., Jiang, B., Rue, E., and Semenza, G. (1995). Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 is a Basic-Helix-Loop-Helix-PAS Heterodimer Regulated by Cellular O SUB 2/SUB Tension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 5510–5514.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0104-1
About this article
Cite this article
Moon, H., Han, S., Park, H. et al. Crystal structures of human FIH-1 in complex with quinol family inhibitors. Mol Cells 29, 471–474 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0058-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0058-3