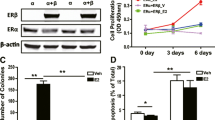
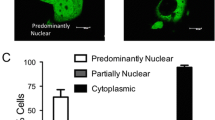
Abstract
Estrogen receptor α (ERα) mediates the mitogenic effects of estrogen. ERα signaling regulates the normal growth and differentiation of mammary tissue, but uncontrolled ERα activation increases the risk to breast cancer. Estrogen binding induces ligand-dependent ERα activation, thereby facilitating ERα dimerization, promoter binding and coactivator recruitment. ERα can also be activated in a ligand-independent manner by many signaling pathways, including protein kinase A (PKA) signaling. However, in several ERα-positive breast cancer cells, PKA inhibits estrogen-dependent cell growth. FoxH1 represses the transcriptional activities of estrogen receptors and androgen receptors (AR). Interestingly, FoxH1 has been found to inhibit the PKA-induced and ligand-induced activation of AR. In the present study, we examined the effects of PKA activation on the ability of FoxH1 to represses ERα transcriptional activity. We found that PKA increases the protein stability of FoxH1, and that FoxH1 inhibits PKA-induced and estradiol-induced activation of an estrogen response element (ERE). Furthermore, in MCF7 cells, FoxH1 knockdown increased the PKA-induced and estradiol-induced activation of the ERE. These results suggest that PKA can negatively regulate ERα, at least in part, through FoxH1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Dhaheri, M.H., and Rowan, B.G. (2007). Protein kinase A exhibits selective modulation of estradiol-dependent transcription in breast cancer cells that is associated with decreased ligand binding, altered estrogen receptor α promoter interaction, and changes in receptor phosphorylation. Mol. Endocrinol. 21, 439–456.
Arnold, S.F., Obourn, J.D., Jaffe, H., and Notides, A.C. (1995). Phosphorylation of the human estrogen receptor on tyrosine 537 in vivo and by src family tyrosine kinases in vitro. Mol. Endocrinol. 9, 24–33.
Chen, X., Weisberg, E., Fridmacher, V., Watanabe, M., Naco, G., and Whitman, M. (1997). Smad4 and FAST-1 in the assembly of activin-responsive factor. Nature 389, 85–89.
Chen, D., Pace, P.E., Coombes, R.C., and Ali, S. (1999). Phosphorylation of human estrogen receptor α by protein kinase A regulates dimerization. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 1002–1015.
Chen, G., Nomura, M., Morinaga, H., Matsubara, E., Okabe, T., Goto, K., Yanase, T., Zheng, H., Lu, J., and Nawata, H. (2005). Modulation of androgen receptor transactivation by FoxH1: A newly identified androgen receptor corepressor. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 36355–36363.
Cho, H., and Katzenellenbogen, B.S. (1993). Synergistic activation of estrogen receptor-mediated transcription by estradiol and protein kinase activators. Mol. Endocrinol. 7, 441–452.
Cui, Y., Zhang, M., Pestell, R., Curran, E.M., Welshons, W.V., and Fuqua, S.A. (2004). Phosphorylation of estrogen receptor α blocks its acetylation and regulates estrogen sensitivity. Cancer Res. 64, 9199–9208.
Feng, W., Webb, P., Nguyen, P., Liu, X., Li, J., Karin, M., and Kushner, P.J. (2001). Potentiation of estrogen receptor activation function 1 (AF-1) by Src/JNK through a serine 118-independent pathway. Mol. Endocrinol. 15, 32–45.
Kang, K., Lee, S.B., Jung, S.H., Cha, K.H., Park, W.D., Sohn, Y.C., and Nho, C.W. (2009). Tectoridin, a poor ligand of estrogen receptor alpha, exerts its estrogenic effects via an ERK-dependent pathway. Mol. Cells 27, 351–357.
Kato, S., Endoh, H., Masuhiro, Y., Kitamoto, T., Uchiyama, S., Sasaki, H., Masushige, S., Gotoh, Y., Nishida, E., Kawashima, H., et al. (1995). Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science 270, 1491–1494.
Kofron, M., Puck, H., Standley, H., Wylie, C., Old, R., Whitman, M., and Heasman, J. (2004). New roles for FoxH1 in patterning the early embryo. Development 131, 5065–5078.
Lannigan, D.A. (2003). Estrogen receptor phosphorylation. Steroids 68, 1–9.
Lee, H., and Bai, W. (2002). Regulation of estrogen receptor nuclear export by ligand-induced and p38-mediated receptor phosphorylation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 5835–5845.
Loven, M.A., Wood, J.R., and Nardulli, A.M. (2001). Interaction of estrogen receptors α and β with estrogen response elements. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 181, 151–163.
Massagué, J., and Gomis, R.R. (2006). The logic of TGFβ signaling. FEBS Lett. 580, 2811–2820.
McKenna, N.J., Lanz, R.B., and O’Malley, B.W. (1999). Nuclear receptor coregulators: cellular and molecular biology. Endocrine Rev. 20, 321–344.
Michalides, R., Griekspoor, A., Balkenende, A., Verwoerd, D., Janssen, L., Jalink, K., Floore, A., Velds, A., van’t Veer, L., and Neefjes, J. (2004). Tamoxifen resistance by a conformational arrest of the estrogen receptor α after PKA activation in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 5, 597–605.
Nilsson, S., Makela, S., Treuter, E., Tujague, M., Thomsen, J., Andersson, G., Enmark, E., Pettersson, K., Warner, M., and Gustafsson, J.A. (2001). Mechanisms of estrogen action. Physiol. Rev. 81, 1535–1565.
Pike, M.C., Spicer, D.V., Dahmoush, L., and Press, M.F. (1993). Estrogens, progestogens, normal breast cell proliferation, and breast cancer risk. Epidemiol. Rev. 15, 17–35.
Roessler, E., Ouspenskaia, M.V., Karkera, J.D., Velez, J.I., Kantipong, A., Lacbawan, F., Bowers, P., Belmont, J.W., Towbin, J.A., Goldmuntz, E., et al. (2008). Reduced NODAL signaling strength via mutation of several pathway members including FOXH1 is linked to human heart defects and holoprosencephaly. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 83, 18–29.
Rogatsky, I., Trowbridge, J.M., and Garabedian, M.J. (1999). Potentiation of human estrogen receptor α transcriptional activation through phosphorylation of serines 104 and 106 by the cyclin ACDK2 complex. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 22296–22302.
Schier, A.F. (2003). Nodal signaling in vertebrate development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 19, 589–621.
Sun, M., Paciga, J.E., Feldman, R.I., Yuan, Z., Coppola, D., Lu, Y.Y., Shelley, S.A., Nicosia, S.V., and Cheng, J.Q. (2001). Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH Kinase (PI3K)/AKT2, activated in breast cancer, regulates and is induced by estrogen receptor α (ERα) via interaction between ERα and PI3K. Cancer Res. 61, 5985–5991.
Watanabe, M., and Whitman, M. (1999). FAST-1 is a key maternal effector of mesoderm inducers in the early Xenopus embryo. Development 126, 5621–5634.
Whitman, M. (2001). Nodal signaling in early vertebrate embryos: themes and variations. Dev. Cell 1, 605–617.
Xu, J., and Li, Q. (2003). Review of the in vivo functions of the p160 steroid receptor coactivator family. Mol. Endocrinol. 17, 1681–1692.
Zhou, S., Zawel, L., Lengauer, C., Kinzler, K.W., and Vogelstein, B. (1998). Characterization of human FAST-1, a TGF β and activin signal transducer. Mol. Cell 2, 121–127.
Zwart, W., Griekspoor, A., Berno, V., Lakeman, K., Jalink, K., Mancini, M., Neefjes, J., and Michalides, R. (2007). PKA-induced resistance to tamoxifen is associated with an altered orientation of ERα towards co-activator SRC-1. EMBO J. 26, 3534–3544.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Yum, J., Jeong, H.M., Kim, S. et al. PKA-Mediated stabilization of FoxH1 negatively regulates ERα activity. Mol Cells 28, 67–71 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0099-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0099-7