Abstract
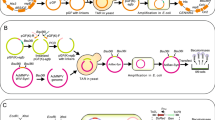
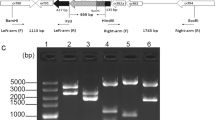
The goal of this study was to create a novel baculovirus expression system that does not require recombinant virus purification steps. Transfection of insect cells with transfer vectors containing barnase under control of the Cotesia plutellae bracovirus (CpBV) promoters ORF3004 or ORF3005 reduced cell growth. Co-transfection with bApGOZA DNA yielded no recombinant viruses and non-recombinant backgrounds. To further investigate the detrimental effects of barnase on insect cells, two recombinant bacmids harboring the barnase gene under control of the CpBV promoters, namely bAcFast-3004ProBarnase and bAcFast-3005ProBarnase, were constructed. While no viral replication was observed when only the recombinant bacmids were transfected, recombinant viruses were generated when the bacmids were co-transfected with the transfer vector, pAcUWPolh, through substitution of the barnase gene with the native polyhedrin gene by homologous recombination. Moreover, no non-recombinant backgrounds were detected from unpurified recombinant stocks using PCR analysis. These results indicate that CpBV promoters can be used to improve baculovirus expression vectors by means of lethal gene expression under the control of these promoters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Airenne, K.J., Peltomaa, E., Hytonen, V.P., Laitinen, O.H., and Yla-Herttuala, S. (2003). Improved generation of recombinant baculovirus genomes in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, e10.
Beckage, N.E. (1993). Games parasites play: the dynamic roles of peptides and proteins in the host-parasite interaction. In Parasites and Pathogens of insects, Vol. 1, Parasites, N.E. Beckage, S.N. Thompson, and B. A. Federici, eds. (New York, USA: Academic Press), pp. 25–58.
Beckage, N.E., Templeton, T.J., Nielsen, B.D., Cook, D.I., and Stoltz, D.B. (1987). Parasitism-induced hemolymph polypeptides in Manduca sexta (L.) larvae parasitized by the braconid wasp Cotesia congregata (Say). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 17, 439–455.
Choi, J.Y., Woo, S.D., Je, Y.H., and Kang, S.K. (1999). Development of a novel expression vector system using Spodoptera exigua nucleopolyhedrovirus. Mol. Cells 9, 504–509.
Choi, J.Y., Woo, S.D., Lee, H.K., Hong, H.K., Je, Y.H., Park, J.H., Song, J.Y., An, S.H., and Kang, S.K. (2000). High-level expression of canine parvovirus VP2 using Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus vector. Arch. Virol. 145, 171–177.
Choi, J.Y., Roh, J.Y., Kang, J.N., Shim, H.J., Woo, S.D., Jin, B.R., Li, M.S., and Je, Y.H. (2005). Genomic segments cloning and analysis of Cotesia plutellae polydnavirus using plasmid capture system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 332, 487–493.
Choi, J.Y., Kwon, S.-J., Roh, J.Y., Yang, T.-J., Li, M.S., Park, B.-S., Kim, Y., Woo, S.-D., Jin, B.R., and Je, Y.H. (2009). Analysis of promoter activity of selected Cotesia plutellae bracovirus genes. J. Gen. Virol. 90, 1262–1269.
Drezen, J.M., Provost, B., Espagne, E., Cattolico, L., Dupuy, C., Poirie, M., Periquet, G., and Huguet, E. (2003). Polydnavirus genome: integrated vs. free virus. J. Insect Physiol. 49, 407–417.
Fleming, J.A. (1992). Polydnaviruses: mutualists and pathogens. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 37, 401–425.
Hartley, R.W. (1989). Barnase and barstar: two small proteins to fold and fit together. Trends Biochem. Sci. 14, 450–454.
Hartley, R.W., and Smeaton, J.R. (1973). On the reaction between the extracellular ribonuclease of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (barnase) and its intracellular inhibitor (barstar). J. Biol. Chem. 248, 5624–5626.
Harwood, S.H., and Beckage, N.E. (1994). Purification and characterization of an early-expressed polydnavirus-induced protein from the hemolymph of Manduca sexta larvae parasitized by Cotesia congregate. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 24, 685–698.
Hu, Y.C. (2005). Baculovirus as a highly efficient expression vector in insect and mammalian cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 26, 405–416.
Je, Y.H., Chang, J.H., Choi, J.Y., Roh, J.Y., Jin, B.R., O’Reilly, D.R., and Kang, S.K. (2001)a. A defective viral genome maintained in Escherichia coli for the generation of baculovirus expression vectors. Biotechnol. Lett. 23, 575–582.
Je, Y.H., Chang, J.H., Roh, J.Y., and Jin, B.R. (2001)b. Generation of baculovirus expression vector using defective Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome maintained in Escherichia coli for Occ+ virus production. Int. J. Indust. Entomol. 2, 155–160.
Kitts, P.A., and Possee, R.D. (1993). A method for producing recombinant baculovirus expression vectors at high frequency. BioTechniques 14, 810–817.
Leder, L., Freuler, F., Forstner, M., and Mayr, L.M. (2007). New methods for efficient protein production in drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 10, 193–202.
Luckow, V.A., Lee, S.C., Barry, G.F., and Olins, P.O. (1993). Efficient generation of infectious recombinant baculoviruses by sitespecific transposon-mediated insertion of foreign genes into a baculovirus genome propagated in Escherichia coli. J. Virol. 67, 4566–4579.
O’Reilly, D.R., Miller, L.K., and Luckow, V.A. (1992). Baculovirus Expression Vectors: A Laboratory Manual (New York, USA: Oxford University Press).
Peakman, T.C., Harris, R.A., and Gewert, D.R. (1992). Highly efficient generation of recombinant baculoviruses by enzymatically medicated site-specific in vitro recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 20, 495–500.
Possee, R.D., Hitchman, R.B., Richards, K.S., Mann, S.G., Siaterli, E., Nixon, C.P., Irving, H., Assenberg, R., Alderton, D., Owens, R.J., et al. (2008). Generation of baculovirus vectors for the high-throughput production of proteins in insect cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 101, 1115–1122.
Qin, Q., Liu, Y.L., Zhu, Y., Li, S.Y., and Qi, Y.P. (2005). Construction of a transposon-mediated baculovirus vector Hanpvid and a new cell line for expressing barnase. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 38, 41–48.
Schlaeppi, J.M., Henke, M., Mahnke, M., Hartmann, S., Schmitz, R., Pouliquen, Y., Kerins, B., Weber, E., Kolbinger, F., and Kocher, H.P. (2006). A semi-automated large-scale process for the production of recombinant tagged proteins in the Baculovirus expression system. Protein Expr. Purif. 50, 185–195.
Stoltz, D.B. (1993). Polydnavirus life cycle. In Parasites and Pathogens of insects, Vol. 1, Parasites, N.E. Beckage, S.N. Thompson, and B.A. Federici, eds. (New York, USA: Academic Press), pp. 167–187.
Summers, M.D., and Dib-Hajj, S.D. (1995). Polydnavirus-facilitated endoparasite protection against host immune defenses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 29–36.
Turnbull, M.W., and Webb, B.A. (2002). Perspectives on polydnavirus origins and evolution. Adv. Virus Res. 58, 203–254.
Whitfield, J.B. (2002). Estimating the age of the polydnavirus/braconid wasp symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 7508–7513.
Yamanaka, A., Hayakawa, Y., Noda, H., Nakashima, N., and Watanabe, H. (1996). Characterization of polydnavirus-encoded mRNA in parasitized armyworm larvae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 26, 529–536.
Yao, L.G., Liu, Z.C., Zhang, X.M., Kan, Y.C., and Zhou, J.J. (2007). A highly efficient method for the generation of a recombinant Bombyx mori nuclear-polyhedrosis-virus Bacmid and largescale expression of foreign proteins in silkworm (B. mori) larvae. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 48, 45–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J.Y., Kim, YS., Wang, Y. et al. Improved baculovirus vectors expressing barnase using promoters from Cotesia plutellae bracovirus. Mol Cells 28, 19–24 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0096-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0096-x