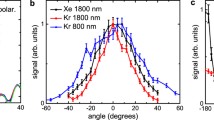
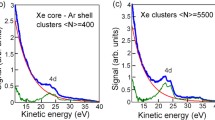
Abstract.
Carbon and metal clusters are excited by strong femtosecond laser pulses with up to 1016 W/cm2, yielding ionized clusters and highly charged atomic ions. For small carbon clusters and fullerenes the abundance of charged species correlates with the laser power, while for metal clusters the ionization efficiency is additionally strongly affected by the chosen laser pulse width which may result in an enhanced up–charging of the metal particle. In the case of platinum atomic charge states up to z=20 are detected at a pulse duration of about 600 fs. This observation is in accordance with a model based on a multi–plasmon excitation process.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 September 1998 / Received in final form: 14 January 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schumacher, M., Teuber, S., Köller, L. et al. Clusters in strong laser fields: Comparison between carbon, platinum, and lead clusters. Eur. Phys. J. D 9, 411–414 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100530050468
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100530050468