Abstract:
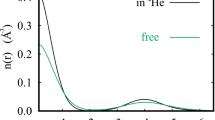
We have measured, using the TOSCA spectrometer at ISIS, the inelastic incoherent neutron scattering spectrum of liquid and solid para-hydrogen along the T = 19.3 K isotherm. From the high-energy region of the spectrum, where the Impulse Approximation for the Centre of Mass motion applies, we have been able to extract the mean translational kinetic energy, which, as expected, turns out rather different from the classical value and density dependent. We find that the density behaviours in the liquid and the solid phase are slightly different. This confirms a similar feature already observed in liquid and solid helium at T = 6.1 K [M. Celli, M. Zoppi, J. Mayers, Phys. Rev. B 58, 242 (1998)]. The spectra from the solid phase have been also analysed in the low-energy region and allowed us to derive the Debye-Waller factor of solid para-hydrogen as a function of density. The comparison with the available experimental data in the literature is rather good and confirms the excellent performances of TOSCA in the spectroscopic analysis of the condensed phases of para-hydrogen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 8 February 2001 and Received in final form 24 April 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zoppi, M., Colognesi, D. & Celli, M. Density dependence of mean kinetic energy in liquid and solid hydrogen at 19.3 K. Eur. Phys. J. B 23, 171–178 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510170065
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510170065