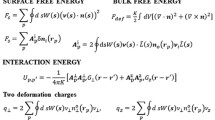Abstract:
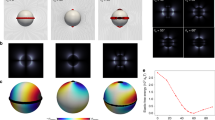
The role of surface energy in the behavior of colloidal particles in liquid crystalline phases is investigated. When the surface energy dominates, a hedgehog defect is formed and, according to an electrostatic analogy, the distortions around the particles exhibit a dipolar character. By contrast, for weaker anchoring, the configuration becomes quadrupolar as evidenced by the structure of latex clusters in lyotropic systems and the observation of defects reminiscent of Saturn rings in thermotropic systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 21 June 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mondain-Monval, O., Dedieu, J., Gulik-Krzywicki, T. et al. Weak surface energy in nematic dispersions: Saturn ring defects and quadrupolar interactions. Eur. Phys. J. B 12, 167–170 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050992
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050992