Abstract
Background
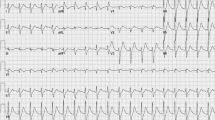
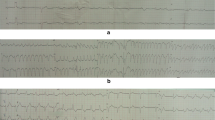
Lithium toxicity has been associated with electrocardiographic abnormalities, such as QT interval prolongation.
Case report
An unresponsive patient with a history of alcohol abuse and recently diagnosed bipolar disorder was brought to the emergency department. An elevated lithium level of 4.7 mmol/L was found. The corrected QT interval was significantly prolonged at 727 ms. The patient was dialyzed and recovered fully.
Discussion
This case illustrates the importance of a systematic evaluation of all patients who may have been exposed to a toxic ingestion.
Zusammenfassung
Hintergrund
Lithiumvergiftungen können Veränderungen im EKG, wie eine Verlängerung des QT-Intervalls, hervorrufen.
Fallbericht
Eine Patientin mit Alkoholabhängigkeit und vor kurzem diagnostizierter bipolarer Störung wurde nicht ansprechbar eingeliefert. Eine erhöhte Lithium-Konzentration von 4,7 mmol/L wurde festgestellt. Es zeigte sich eine QTc-Verlängerung auf 727 ms. Die Patientin wurde dialysiert und erreichte eine vollständige Genesung.
Diskussion
Dieser Fall illustriert die Wichtigkeit einer systematischen Evaluierung aller Patienten, bei denen eine Vergiftung möglich erscheint.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bealer SL, Little JG (2013) Seizures following hippocampal kindling induce QT interval prolongation and increased susceptibility to arrhythmias in rats. Epilepsy Res 105:216–219
Becker TK, Yeung SJ (2010) Drug-induced QT interval prolongation in cancer patients. Oncol Rev 4:223–232
Can A, Schulze TG, Gould TD (2014) Molecular actions and clinical pharmacogenetics of lithium therapy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 123:3–16
Eyer F, Pfab R, Felgenhauer N et al (2006) Lithium poisoning: pharmacokinetics and clearance during different therapeutic measures. J Clin Psychopharmacol 26:325–330
Howland RH (2007) Lithium: underappreciated and underused? J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv 45:13–17
Jacob AI, Hope RR (1979) Prolongation of the Q-T interval in lithium toxicity. J Electrocardiol 12:117–119
La Rocca R, Foschi A, Preston NM et al (2012) QT interval prolongation and bradycardia in lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Int J Cardiol 162:e1–e2
Mamiya K, Sadanaga T, Sekita A et al (2005) Lithium concentration correlates with QTc in patients with psychosis. J Electrocardiol 38:148–151
Mateer JR, Clark MR (1982) Lithium toxicity with rarely reported ECG manifestations. Ann Emerg Med 11:208–211
Mowry JB, Spyker DA, Cantilena LR Jr et al (2013) 2012 annual report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 30th annual report. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 51:949–1229
Offerman SR, Alsop JA, Lee J et al (2010) Hospitalized lithium overdose cases reported to the California Poison Control System. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 48:443–448
Waring WS (2006) Management of lithium toxicity. Toxicol Rev 25:221–230
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest. This submission did not receive any external financial support.
Additional information
Redaktion
Prof. Dr. M. Fischer, Göppingen
Prof. Dr. K.-G. Kanz, München
Prof. Dr. W. Schreiber, Wien
Prof. Dr. F. Walcher, Magdeburg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, T., Hariri, H. A case of lithium toxicity with significant QT interval prolongation. Notfall Rettungsmed 18, 227–230 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10049-015-0008-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10049-015-0008-x