Abstract
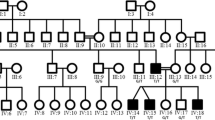
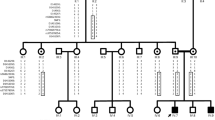
Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) neuropathy is one of the most common hereditary disorders of the human peripheral nervous system. The CMT syndrome includes weakness and atrophy of distal muscles, high arched feet (pes cavus), depressed or absent deep tendon reflexes, and mild sensory loss. Dominant intermediate CMT (DI-CMT) neuropathy is a form of CMT with intermediate median motor nerve conduction velocities. We previously localized the DI-CMT locus to a 16.8-cM region on chromosome 19p12-p13.2. Extended haplotype analysis and clinical assessment of additional family members and a report of a second family linked to this locus has enabled us to narrow the candidate region to a 6-cM interval flanked by D19S558 and D19S432. Selection of positional candidate genes for screening was performed on the basis of neural expression and microarray analysis of Schwann cell differentiation in vivo. Seven candidate genes have been investigated. These include six genes localized in the original linkage interval and one in the newly refined region. They are excluded as a cause for DI-CMT neuropathy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dyck PJ, Lambert EH (1968) Lower motor and primary sensory neuron diseases with peroneal muscular atrophy. II. Neurologic, genetic and electrophysiologic findings in various neuronal degenerations. Arch Neurol 18:619–625
Harding AE, Thomas PK (1980) The clinical features of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy types I and II. Brain 103:259–280
Berger P, Young P, Suter U (2002) Molecular cell biology of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Neurogenetics 4:1-15
Meuleman J, Timmerman V, Nelis E, De Jonghe P (2000) Molecular genetics of inherited peripheral neuropathies: who are the actors? Acta Neurol Belg 100:171–180
Davis CJ, Bradley WG, Madrid R (1978) The peroneal muscular atrophy syndrome: clinical, genetic, electrophysiological and nerve biopsy studies. I. Clinical, genetic and electrophysiological findings and classification. J Genet Hum 26:311–349
Rossi A, Paradiso C, Cioni R, Rizzuto N, Guazzi G (1985) Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: study of a large kinship with an intermediate form. J Neurol 232:91–98
Salisachs P (1974) Wide spectrum of motor conduction velocity in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. An anatomico-physiological interpretation. J Neurol Sci 23:25–31
Villanova M, Timmerman V, De Jonghe P, Malandrini A, Rizzuto N, Van Broeckhoven C, Guazzi G, Rossi A (1998) Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: an intermediate form. Neuromuscul Disord 8:392–384
Malandrini A, Ceuterick C, Villanov M, Gambelli S, Berti G, Rossi A, Guazzi GC (2001) Ultrastructural findings in the peripheral nerve in a family with the intermediate form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 33:59–63
Kennerson ML, Zhu D, Gardner RJ, Storey E, Merory J, Robertson SP, Nicholson GA (2001) Dominant intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy maps to chromosome 19p12-p13.2. Am J Hum Genet 69:883–888
Verhoeven K, De Jonghe P, Coen K, Verpoorten N, Auer-Grumbach M, Kwon JM, FitzPatrick D, Schmedding E, De Vriendt E, Jacobs A, Van Gerwen V, Wagner K, Hartung HP, Timmerman V (2003) Mutations in the small GTP-ase late endosomal protein RAB7 cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2B neuropathy. Am J Hum Genet (in press)
Speer M, Graham F, Bonner E, Collier K, Stajich JE, Gaskell P, Perricak-Vance M, Vance J (2002) Reduction in the minimum candidate interval in the dominant-intermediate form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy to D19S586-D19S432. Neurogenetics 4:83–85
Lupski JR, Oca-Luna RM de, Slaugenhaupt S, Pentao L, Guzzetta V, Trask BJ, Saucedo-Cardenas O, Barker DF, Killian JM, Garcia CA, et al (1991) DNA duplication associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Cell 66:219–232
Patel PI, Roa BB, Welcher AA, Schoener-Scott R, Trask BJ, Pentao L, Snipes GJ, Garcia CA, Francke U, Shooter EM, et al (1992) The gene for the peripheral myelin protein PMP-22 is a candidate for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Nat Genet 1:159–165
Hayasaka K, Takada G, Ionasescu VV (1993) Mutation of the myelin P0 gene in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 1B. Hum Mol Genet 2:1369–1372
Warner LE, Mancias P, Butler IJ, McDonald CM, Keppen L, Koob KG, Lupski JR (1998) Mutations in the early growth response 2 (EGR2) gene are associated with hereditary myelinopathies. Nat Genet 18:382–384
Zhao C, Takita J, Tanaka Y, Setou M, Nakagawa T, Takeda S, Yang HW, Terada S, Nakata T, Takei Y, Saito M, Tsuji S, Hayashi Y, Hirokawa N (2001) Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2A caused by mutation in a microtubule motor KIF1Bbeta. Cell 105:587–597
Mersiyanova IV, Perepelov AV, Polyakov AV, Sitnikov VF, Dadali EL, Oparin RB, Petrin AN, Evgrafov OV (2000) A new variant of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2 is probably the result of a mutation in the neurofilament-light gene. Am J Hum Genet 67:37–46
Jordanova A, De Jonghe P, Boerkoel CF, Takashima H, De Vriendt E, Ceuterick C, Martin JJ, Butler IJ, Mancias P, Papasozomenos SC, Terespolsky D, Potocki L, Brown CW, Shy M, Rita DA, Tournev I, Kremensky I, Lupski JR, Timmerman V (2003) Mutations in the neurofilament light chain gene (NEFL) cause early onset severe Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Brain 126:590–597
Verhoeven K, Villanova M, Rossi A, Malandrini A, De Jonghe P, Timmerman V (2001) Localization of the gene for the intermediate form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth to chromosome 10q24.1-q25.1. Am J Hum Genet 69:889–894
Street VA, Bennett CL, Goldy JD, Shirk AJ, Kleopa KA, Tempel BL, Lipe HP, Scherer SS, Bird TD, Chance PF (2003) Mutation of a putative protein degradation gene LITAF/SIMPLE in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease 1C. Neurology 60:22–26
Ophoff RA, Terwindt GM, Vergouwe MN, Eijk R van, Mohrenweiser H, Litt M, Hofker MH, Haan J, Ferrari MD, Frants RR (1996) A 3-Mb region for the familial hemiplegic migraine locus on 19p13.1-p13.2: exclusion of PRKCSH as a candidate gene. Dutch Migraine Genetic Research Group. Eur J Hum Genet 4:321–328
Shimizu N, Ohta M, Fujiwara C, Sagara J, Mochizuki N, Oda T, Utiyama H (1991) Expression of a novel immediate early gene during 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced macrophagic differentiation of HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem 266:12157–12161
Houzelstein D, Bullock SL, Lynch DE, Grigorieva EF, Wilson VA, Beddington RS (2002) Growth and early postimplantation defects in mice deficient for the bromodomain-containing protein Brd4. Mol Cell Biol 22:3794–3802
Wilton SD, Lim L, Dorosz SD, Gunn HC, Eyre HJ, Callen DF, Laing NG (1996) Assignment of the human alpha-tropomyosin gene TPM4 to band 19p13.1 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet 72:294–296
Litt M, LaMorticella D, Bond CT, Adelman JP (1999) Gene structure and chromosome mapping of the human small-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel SK1 gene (KCNN1). Cytogenet Cell Genet 86:70–73
Elson GC, Coignac AB de, Aubry JP, Delneste Y, Magistrelli G, Holzwarth J, Bonnefoy JY, Gauchat JF (1999) BSMAP, a novel protein expressed specifically in the brain whose gene is localized on chromosome 19p12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 264:55–62
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the families who participated in this study. This work is supported by a grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, D., Kennerson, M., Merory, J. et al. Refined localization of dominant intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy and exclusion of seven known candidate genes in the region. Neurogenetics 4, 179–183 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-003-0147-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-003-0147-y