Abstract
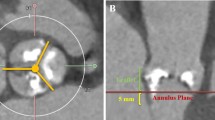
Rapid deployment valve has expanded surgical indication for high-risk patients with aortic stenosis despite its accommodated risk for conduction disorder (CD). The purpose of this study was to evaluate the degree of oversizing in association with postoperative CD. During June 2019 to September 2021, 25 patients underwent aortic valve replacement with Edwards INTUITY. Device size selection was evaluated intraoperatively using provided sizers. Oversizing was evaluated retrospectively by measuring the difference of the dimension of the annulus and left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) compared to the dimensions of the device used by preoperative-computed tomography. Although there was no incidence of pacemaker implantation, seven patients (28.0%) experienced CD after surgery. There was no difference in device area and annulus area (CD: − 37 ± 22.7 mm2 vs. no CD: − 56 ± 63.6 mm2, p = 0.47), and device circumference and annulus circumference (CD: − 4.4 ± 2.77 mm vs. no CD: − 6.9 ± 5.60 mm, p = 0.26) in patients with and without CD. However, there was a significant difference in area of the device skirt and sub-annular area at the LVOT (CD: 114 ± 28.4 mm2 vs. no CD: − 8 ± 80.0 mm2, p < 0.001), and circumference of device skirt and the LVOT (CD: 3.9 ± 2.08 mm vs. no CD: − 4.6 ± 5.24 mm, p < 0.001) between the two groups. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that an area difference of 77.7 mm2 and circumference difference of 0.91 mm at LVOT were associated with postoperative CD with specificities of 0.83, 0.78 and sensitivity of 1.0, 1.0, respectively. Preoperative measurement of the LVOT may be useful in evaluating the risk of postoperative CD in patients receiving rapid deployment valve.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auffret V, Puri R, Urena M, Chamandi C, Rodriguez-Gabella T, Philippon F, et al. Conduction disturbances after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: current status and future perspectives. Circulation. 2017;136:1049–69.
Mogilansky C, Balan R, Deutsch C, Czesla M, Massoudy P. New postoperative conduction abnormalities after the implantation of a rapid-deployment aortic valve prosthesis. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2019;28:581–6.
Andreas M, Coti I, Rosenhek R, Shabanian S, Mahr S, Uyanik-Uenal K, et al. Intermediate-term outcome of 500 consecutive rapid-deployment surgical aortic valve procedures. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019;55:527–33.
Wahlers TCW, Andreas M, Rahmanian P, Candolfi P, Zemanova B, Giot C, et al. Outcomes of a rapid deployment aortic valve versus its conventional counterpart: a propensity-matched analysis. Innovations (Philadelphia, Pa). 2018;13:177–83.
Dizon JM, Nazif TM, Hess PL, Biviano A, Garan H, Douglas PS, et al. Chronic pacing and adverse outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Heart. 2015;101:1665–71.
Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American society of echocardiography and the European association of cardiovascular imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015;28:1-39.e14.
Otto CM, Nishimura RA, Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Erwin JP 3rd, Gentile F, et al. 2020 ACC/AHA guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association joint committee on clinical practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77:e25–197.
Smith D. Bioprosthetic valve durability: TAVR versus SAVR using different definitions of valve deterioration. Int J Cardiol. 2018;268:176–8.
Bourguignon T, Bouquiaux-Stablo AL, Candolfi P, Mirza A, Loardi C, May MA, et al. Very long-term outcomes of the Carpentier-Edwards Perimount valve in aortic position. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015;99:831–7.
Hwang YM, Kim J, Lee JH, Kim M, Hwang J, Kim JB, et al. Conduction disturbance after isolated surgical aortic valve replacement in degenerative aortic stenosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:1556-65.e1.
Romano MA, Koeckert M, Mumtaz MA, Slachman FN, Patel HJ, Chitwood WR Jr, et al. Permanent pacemaker implantation after rapid deployment aortic valve replacement. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018;106:685–90.
Herry M, Laghlam D, Touboul O, Nguyen LS, Estagnasié P, Brusset A, et al. Pacemaker implantation after aortic valve replacement: rapid-deployment Intuity® compared to conventional bioprostheses. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020;58:335–42.
D’Onofrio A, Tessari C, Bagozzi L, Migliore F, Filippini C, Cibin G, et al. Conduction disorders after aortic valve replacement with rapid-deployment bioprostheses: early occurrence and one-year evolution. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2020;9:396–407.
Sohn SH, Kim KH, Kang Y, Kim JS, Choi JW. Recovery from conduction abnormalities after aortic valve replacement using edwards intuity. Ann Thorac Surg. 2021;112:1356–62.
Lee JJ, Goldschlager N, Mahadevan VS. Atrioventricular and intraventricular block after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2018;52:315–22.
Nazif TM, Dizon JM, Hahn RT, Xu K, Babaliaros V, Douglas PS, et al. Predictors and clinical outcomes of permanent pacemaker implantation after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: the PARTNER (Placement of AoRtic TraNscathetER Valves) trial and registry. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:60–9.
Aktug Ö, Dohmen G, Brehmer K, Koos R, Altiok E, Deserno V, et al. Incidence and predictors of left bundle branch block after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Int J Cardiol. 2012;160:26–30.
Katsanos S, van Rosendael P, Kamperidis V, van der Kley F, Joyce E, Debonnaire P, et al. Insights into new-onset rhythm conduction disorders detected by multi-detector row computed tomography after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Am J Cardiol. 2014;114:1556–61.
Bernardi FL, Ribeiro HB, Carvalho LA, Sarmento-Leite R, Mangione JA, Lemos PA, et al. Direct transcatheter heart valve implantation versus implantation with balloon predilatation: insights from the brazilian transcatheter aortic valve replacement registry. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;9:e003605.
Ferrara J, Deharo P, Resseguier N, Porto A, Jaussaud N, Morera P, et al. Rapid deployment versus trans-catheter aortic valve replacement in intermediate-risk patients: a propensity score analysis. J Card Surg. 2021;36:2004–12.
Useini D, Beluli B, Christ H, Schlömicher M, Ewais E, Haldenwang P, et al. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement using the SAPIEN 3 valve versus surgical aortic valve replacement using the rapid deployment INTUITY valve: midterm outcomes. J Card Surg. 2021;36:610–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection were performed by DH, TY, SK, and TF. Anaylsis were performed by DH, MNM, and TY. The first draft of the manuscript was written by DH, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Revision, review, and editing was performed by DH, MNM, NK and AY, All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hori, D., Yamamoto, T., Kusadokoro, S. et al. Evaluation of oversizing in association with conduction disorder after implantation of a rapid deployment valve. J Artif Organs 25, 238–244 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-021-01301-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-021-01301-4