Abstract
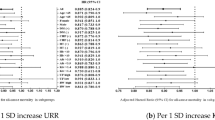
Clinical guidelines for hemodialysis therapy have been described in an evidence-based manner with most evidence from randomized control trials or retrospective studies in which all generations of the hemodialysis patients were enrolled. Therefore, the question still remains whether these guidelines can be applied to increasing older patients. This study is an observational study, including 735 patients who received maintenance hemodialysis in April 2006. At baseline, the participants’ age was 62.1 ± 12.8 years (mean ± SD). Hemodialysis duration was 103.7 ± 89.3 months. In a 5-year observation period (actual follow-up period: 1551 ± 499 days), 175 patients died. Prognostic factors were investigated by multivariate analysis with Cox proportional hazard model. Next, we stratified the patients according to their age. 363 patients were included in the middle-aged patient’s category between 40 and 64 years, and 314 were involved in the older patient’s category between 65 and 84 years old. As a subanalysis, significant predictors of 5-year survival were examined in the age-stratified cohort. Then, Kt/V, serum β2-microglobulin and calcium concentration were significant predictors in our entire cohort, as well as body mass index, neutrophil count, and serum sodium concentration even after adjustment for age, gender, diabetic status and hemodialysis duration. However, Kt/V, serum β2-microglobulin and calcium concentration controlled by hemodialysis prescriptions were independent risk factors especially in older patients, not in middle-aged patients. In conclusion, hemodialysis prescriptions for lowering uremic toxins and managing mineral-bone disorder are important to decrease the risk of death even in older hemodialysis patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamagata K, Yagisawa T, Nakai S, Nakayama M, Imai E, Hattori M, Iseki K, Akiba T. Prevalence and incidence of chronic kidney disease stage G5 in Japan. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2015;19:54–64.
Nakai S, Hanafusa N, Masakane I, Taniguchi M, Hamano T, Shoji T, Hasegawa T, Itami N, Yamagata K, Shinoda T, Kazama JJ, Watanabe Y, Shigematsu T, Marubayashi S, Morita O, Wada A, Hashimoto S, Suzuki K, Nakamoto H, Kimata N, Wakai K, Fujii N, Ogata S, Tsuchida K, Nishi H, Iseki K, Tsubakihara Y. An overview of regular dialysis treatment in Japan (as of 31 December 2012). Ther Apher Dial. 2014;18:535–602.
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Cano NJ, Budde K, Chazot C, Kovesdy CP, Mak RH, Mehrotra R, Raj DS, Sehgal AR, Stenvinkel P, Ikizler TA. Diets and enteral supplements for improving outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;7:369 – 84.
Ikizler TA, Cano NJ, Franch H, Fouque D, Himmelfarb J, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kuhlmann MK, Stenvinkel P, TerWee P, Teta D, Wang AY, Wanner C, International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. Prevention and treatment of protein energy wasting in chronic kidney disease patients: a consensus statement by the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. Kidney Int. 2013;84:1096 – 107.
Desai AA, Nissenson A, Chertow GM, Farid M, Singh I, Van Oijen MG, Esrailian E, Solomon MD, Spiegel BM. The relationship between laboratory-based outcome measures and mortality in end-stage renal disease: a systemic review. Hemodial Int. 2009;13:347 – 59.
Cheung AK, Rocco MV, Yan G, Leypoldt JK, Levin NW, Greene T, Agodoa L, Bailey J, Beck GJ, Clark W, Levey AS, Ornt DB, Schulman G, Schwab S, Teehan B, Eknoyan G. Serum beta-2 microglobulin levels predict mortality in dialysis patients: results of the HEMO study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:546 – 55.
Okuno S, Ishimura E, Kohno K, Fujino-Katoh Y, Maeno Y, Yamakawa T, Inaba M, Nishizawa Y. Serum beta2-microglobulin level is a significant predictor of mortality in maintenance haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:571–7.
Block GA. Therapeutic interventions for chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorders: focus on mortality. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2011;20:376 – 81.
Watanabe Y, Kawanishi H, Suzuki K, Nakai S, Tsuchida K, Tabei K, Akiba T, Masakane I, Takemoto Y, Tomo T, Itami N, Komatsu Y, Hattori M, Mineshima M, Yamashita A, Saito A, Naito H, Hirakata H, Minakuchi J. “Maintenance Hemodialysis: Hemodialysis Prescriptions” Guideline Working Group, Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy. Japanese society for dialysis therapy clinical guideline for “Maintenance hemodialysis: hemodialysis prescriptions”. Ther Apher Dial. 2015;19(Suppl 1):67–92.
Fukagawa M, Yokoyama K, Koiwa F, Taniguchi M, Shoji T, Kazama JJ, Komaba H, Ando R, Kakuta T, Fujii H, Nakayama M, Shibagaki Y, Fukumoto S, Fujii N, Hattori M, Ashida A, Iseki K, Shigematsu T, Tsukamoto Y, Tsubakihara Y, Tomo T, Hirakata H, Akizawa T, CKD-MBD Guideline Working Group; Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy. Clinical practice guideline for the management of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder. Ther Apher Dial. 2013;17:247–88.
Ramakrishnan K, Braunhofer P, Newsome B, Lubeck D, Wang S, Deuson J, Claxton AJ. The economic impact of improving phosphate binder therapy adherence and attainment of guideline phosphorus goals in hemodialysis patients: a Medicare cost-offset model. Adv Ther. 2014;31:1272–86.
Cheung AK, Levin NW, Greene T, Agodoa L, Bailey J, Beck G, Clark W, Levey AS, Leypoldt JK, Ornt DB, Rocco MV, Schulman G, Schwab S, Teehan B, Eknoyan G. Effects of high-flux hemodialysis on clinical outcomes: results of the HEMO study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:3251–63.
Shinzato T, Nakai S, Fujita Y, Takai I, Morita H, Nakane K, Maeda K. Determination of Kt/V and protein catabolic rate using pre- and postdialysis blood urea nitrogen concentrations. Nephron. 1994;67:280 – 90.
Shigematsu T, Akizawa T, Uchida E, Tsukamoto Y, Iwasaki M, Koshikawa S, KRN1493 Study Group. Long-term cinacalcet HCl treatment improved bone metabolism in Japanese hemodialysis patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism. Am J Nephrol. 2009;29:230–6.
Kakiya R, Shoji T, Tsujimoto Y, Tatsumi N, Hatsuda S, Shinohara K, Kimoto E, Tahara H, Koyama H, Emoto M, Ishimura E, Miki T, Tabata T, Nishizawa Y. Body fat mass and lean mass as predictors of survival in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2006;70:549–56.
Shoji T, Shinohara K, Kimoto E, Emoto M, Tahara H, Koyama H, Inaba M, Fukumoto S, Ishimura E, Miki T, Tabata T, Nishizawa Y. Lower risk for cardiovascular mortality in oral 1alpha-hydroxy vitamin D3 users in a haemodialysis population. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19:179 – 84.
Barron E, Lara J, White M, Mathers JC. Blood-borne biomarkers of mortality risk: systematic review of cohort studies. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0127550.
Szczech LA, Reddan DN, Klassen PS, Coladonato J, Chua B, Lowrie EG, Lazarus JM, Owen WF Jr. Interactions between dialysis-related volume exposures, nutritional surrogates and mortality among ESRD patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003;18:1585–91.
Dekker MJ, Marcelli D, Canaud B, Konings CJ, Leunissen KM, Levin NW, Carioni P, Maheshwari V, Raimann JG, van der Sande FM, Usvyat LA, Kotanko P, Kooman JP. Unraveling the relationship between mortality, hyponatremia, inflammation and malnutrition in hemodialysis patients: results from the international MONDO initiative. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2016;70:779–84.
Jamal SA, Vandermeer B, Raggi P, Mendelssohn DC, Chatterley T, Dorgan M, Lok CE, Fitchett D, Tsuyuki RT. Effect of calcium-based versus non-calcium-based phosphate binders on mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2013;382:1268–77.
Argyropoulos CP, Chen SS, Ng YH, Roumelioti ME, Shaffi K, Singh PP, Tzamaloukas AH. Rediscovering beta-2 microglobulin as a biomarker across the spectrum of kidney diseases. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017;4:73.
Nakagawa N, Matsuki M, Yao N, Hirayama T, Ishida H, Kikuchi K, Hasebe N. Impact of metabolic disturbances and malnutrition-inflammation on 6-year mortality in Japanese patients undergoing hemodialysis. Ther Apher Dial. 2014;19:30–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank Daisuke Hirose and Hiroyuki Michiwaki for collecting data (Kawashima Hospital), and Michael Hann (Naval Medical Center San Diego) for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Kojiro Nagai and Motokazu Matsuura are equally contributed.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagai, K., Matsuura, M., Tsuchida, K. et al. Prognostic factors for mortality in middle-aged and older hemodialysis patients: a 5-year observational study. J Artif Organs 21, 94–101 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-017-0993-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-017-0993-2