Abstract
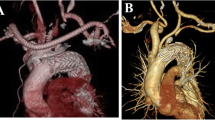
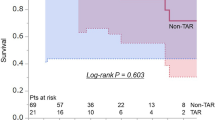
Thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) combined with supra-aortic debranching is a promising approach for distal aortic arch disease, especially in high-risk patients. Most debranching TEVAR procedures for distal arch pathologies can now be performed by using extra-thoracic bypass and endovascular repair, without intra-thoracic manipulation needing sternotomy or thoracotomy. To compare the early outcomes of extra-thoracic debranching TEVAR with those of conventional arch replacement, we retrospectively reviewed data from 20 high-risk patients with distal aortic arch disease who underwent extra-thoracic debranching TEVAR and 16 patients who underwent total arch replacement from March 2009 to November 2011. Patient demographics, operative data, and outcomes in each group were evaluated and compared. The mean follow-up period was 22.4 ± 12.7 months. In the extra-thoracic debranching TEVAR group, primary technical success was achieved in all cases. One patient (5 %) died of low cardiac output syndrome within 30 days after surgery. Two patients had perioperative morbidities (10 %); both had a stroke during the procedure. No endoleak or graft migration was observed, and all bypass grafts remained patent. No patient had paraplegia, a new aortic event, or surgical site infection. In conclusion, the early outcomes of extra-thoracic debranching TEVAR in high-risk patients with distal aortic arch disease were satisfactory and encouraging, compared with conventional arch replacement. Extra-thoracic debranching TEVAR has the advantage of less invasiveness and no possibility of sternal infection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishimaru S. Endografting of the aortic arch. J Endovasc Ther. 2004;11:1162–71.
Szeto WY, Bavaria JE, Bowen FW, Woo EY, Fairman RM, Pochettino A. The hybrid total arch repair: brachiocephalic bypass and concomitant endovascular aortic arch stent graft placement. J Card Surg. 2007;22:97–102.
Criado FJ. A percutaneous technique for preservation of arch branch patency during thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR): retrograde catheterization and stenting. J Endovasc Ther. 2007;14:54–8.
Cires G, Noll RE, Albuquerque FC, Tonnessen BH, Sternbergh WC. Endovascular debranching of the aortic arch during thoracic endograft repair. J Vasc Surg. 2011;53:1485–91.
Yoshida RA, Kolvenbach R, Yoshida WB, Wassijew S, Schwierz E, Lin F. Total endovascular debranching of the aortic arch. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;42:627–30.
Manning BJ, Ivancev K, Harris PL. In situ fenestration in the aortic arch. J Vasc Surg. 2010;52:491–4.
Kawaguchi S, Yokoi Y, Shimazaki T, Koide K, Matsumoto M, Shigematsu H. Thoracic endovascular aneurysm repair in Japan: experience with fenestrated stent grafts in the treatment of distal arch aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2008;48:24S–9S.
Greenberg RK, Qureshi M. Fenestrated and branched devices in the pipeline. J Vasc Surg. 2010;52:15S–21S.
Ohata T, Miyamoto Y, Mitsuno M, Yamamura M, Tanaka H, Ryomoto M. Modified sandwich technique for acute aortic dissection. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2007;15:261–3.
Tamura N, Komiya T, Sakaguchi G, Kobayashi T. ‘Turn-up’ anastomotic technique for acute aortic dissection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2007;31:548–9.
Kato M, Kuratani T. The history and current status of thoracic endovascular aneurysm repair in Japan. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2008;49:503–10.
Bavaria J, Milewski RK, Baker J, Moeller P, Szeto W, Pochettino A. Classic hybrid evolving approach to distal arch aneurysms: toward the zone zero solution. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;140:S77–80.
Antoniou GA, El Sakka K, Hamady M, Wolfe JH. Hybrid treatment of complex aortic arch disease with supra-aortic debranching and endovascular stent graft repair. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2010;39:683–90.
Kuwano H, Amano J, Yokomise H. Thoracic and cardiovascular surgery in Japan during 2010: annual report by The Japanese Association for Thoracic Surgery. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012;60:680–708.
Benedetto U, Melina G, Angeloni E, Codispoti M, Sinatra R. Current results of open total arch replacement versus hybrid thoracic endovascular aortic repair for aortic arch aneurysm: a meta-analysis of comparative studies. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013;145:305–6.
Ohrlander T, Sonesson B, Ivancev K, Resch T, Dias N, Malina M. The chimney graft: a technique for preserving or rescuing aortic branch vessels in stent-graft sealing zones. J Endovasc Ther. 2008;15:427–32.
Lotfi S, Clough RE, Ali T, Salter R, Young CP, Bell R, Modarai B, Taylor P. Hybrid repair of complex thoracic aortic arch pathology: long-term outcomes of extra-anatomic bypass grafting of the supra-aortic trunk. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013;36:46–55.
Vallejo N, Rodriguez-Lopez JA, Heidari P, Wheatley G, Caparrelli D, Ramaiah V, Diethrich EB. Hybrid repair of thoracic aortic lesions for zone 0 and 1 in high-risk patients. J Vasc Surg. 2012;55:318–25.
Ferrero E, Ferri M, Viazzo A, Robaldo A, Zingarelli E, Sansone F, Casabona R, Nessi F. Is total debranching a safe procedure for extensive aortic-arch disease? A single experience of 27 cases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012;41:177–82.
Canaud L, Hireche K, Berthet JP, Branchereau P, Marty-Ané C, Alric P. Endovascular repair of aortic arch lesions in high-risk patients or after previous aortic surgery: midterm results. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;140:52–8.
Murashita T, Matsuda H, Domae K, Iba Y, Tanaka H, Sasaki H, Ogino H. Less invasive surgical treatment for aortic arch aneurysms in high-risk patients: a comparative study of hybrid thoracic endovascular aortic repair and conventional total arch replacement. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012;143:1007–13.
Conflict of interest
All the authors have declared no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, K., Ohata, T., Ueda, H. et al. Early outcomes of extra-thoracic debranching thoracic endovascular aortic repair for distal aortic arch disease. J Artif Organs 17, 236–242 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-014-0774-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-014-0774-0