Abstract
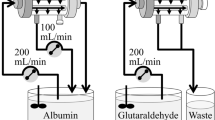
The dialyzer housing structure should be designed in such a way that high dialysis performance is achieved. To achieve high dialysis performance, the flow of the dialysis fluid and blood should be uniform, without channeling and dead spaces. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of fiber packing density on the flow of dialysis fluid and blood, and on the dialysis performance of a hollow-fiber dialyzer at defined flow rates for blood (Q B = 200 mL/min), dialysis fluid (Q D = 500 mL/min), and filtrate (Q F = 0 mL/min). We measured Q D, Q B, and solute clearance for 3 test dialyzers with dialyzer housing different diameters. To evaluate the flow of dialysis fluid and blood, we measured the residence time of the dialysis fluid and blood in the test dialyzers by use of the pulse–response method. We also measured the clearances of urea, creatinine, vitamin B12, and lysozyme to evaluate the dialysis performance of the test dialyzers. At packing densities ranging from 48 to 67%, higher packing densities and lower housing diameters of the dialyzer resulted in higher dialysis performance because the dialysis fluid and blood entered the hollow-fiber bundle smoothly and, hence, increased contact area between the dialysis fluid and the blood led to better dialysis performance.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirano A, Yamamoto K, Matsuda M, Ogawa T, Yakushiji T, Miyasaka T, Sakai K. Evaluation of dialyzer housing structure and hollow-fiber dialysis membranes to achieve high dialysis performance. Ther Aphaer Dial. 2011;15:66–74.
Kim JC, Kim JH, Kim H-C, Kang E, Ronco C, Kim HC. Analysis of blood and dialysis-fluid flow in a hemodialyzer by perfusion computed tomography. WC2009, IFMBE Proceedings 2009; 25/VII; 831–834.
Ronco C, Brendolan A, Crepaldi C, Rodighiero M, Scabardi M. Blood and dialysis-fluid flow distributions in hollow-fiber hemodialyzers analyzed by computerized helical scanning technique. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:S53–61.
Hoenich NA, Kerr DNS. Engineering design of hemodialysis. J Biomed Eng. 1983;5:55–8.
Fukuda M, Miyazaki M, Uezumi S, Yoshida M. Design and assessment of the new APS dialyzer. J Artif Organs. 2006;9:192–8.
Fijimura T, Uchi Y, Fukuda M, Miyazaki M, Uezumi S, Hiyoshi T. Development of a dialyzer with enhanced internal filtration to increase the clearance of low molecular weight proteins. J Artif Organs. 2004;7:149–54.
Sato Y, Mineshima M, Ishimori I, Kaneko I, Akiba T, Terasawa S. Effect of hollow fiber length on solute removal and quantification of internal filtration rate by Doppler ultrasound. Int J Artif Organs. 2003;26:129–34.
Leypoldt JK, Cheung AK, Chirananthavat T, Gilson JF, Kamerath CD, Deeter RB. Hollow fiber shape alters solute clearances in high flux hemodialyzers. ASAIO J. 2003;49:81–7.
Yang M-C, Lin C-C. Influence of design of the hemodialyzer inlet chamber on red blood damage during hemodialysis. ASAIO J. 2001;47:92–6.
Lu J, Lu W. Blood flow velocity and ultra-filtration velocity measured by CT imaging system inside a densely bundled hollow fiber dialyzer. Intern J Heat Mass Transf. 2010;53:1844–50.
Yamashita AC, Fujita R, Tomisawa N, Jinbo Y, Yamamura M. Effect of packing density of hollow fibers on solute removal performances of dialyzers. Hemodial Int. 2009;13:S2–7.
Yamamoto K, Matsuda M, Hirano A, Takizawa N, Iwashima S, Yakushiji T, Fukuda M, Miyasaka T, Sakai K. Computational evaluation of dialysis fluid flow in dialyzers with variously designed housings. J Artif Organs. 2009;33:481–6.
Poh CK, Hardy PA, Liao Z, Huang Z, Gao Dl. Effect of flow baffles on the dialysate flow distribution of hollow-fiber hemodialyzers a nonintrusive experimental study using MRI. J Biomech Eng. 2003;125:481–9.
Osuga T, Obata T, Ikehara H. Detection of small degree of nonuniformity in dialysate flow in hollow-fiber dialyzer using proton magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2004;22:417–20.
Takesawa S, Terasawa M, Sakagami M, Kobayashi T, Hidai H, Sakai K. Nondestructive evaluation by X-ray computed tomography of dialysate flow patterns in capillary dialyzers. ASAIO J. 1988;34:794–9.
Sakai Y, Wada S, Matsumoto H, Suyama T, Ohno O, Anno I. Nondestructive evaluation of blood flow in a dialyzer using X-ray computed tomography. Artif Organs. 2003;3:197–204.
Yamamoto K, Matsukawa H, Yakushiji T, Fukuda M, Hiroshi T, Sakai K. Technical evaluation of dialysis-fluid flow in a newly designed dialyzer. ASAIO J. 2007;53:36–40.
Levenspiel O. Non-ideal flow. In: Chemical reaction engineering. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley; 1972. p. 253–325.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Asahi Kasei Kuraray Medical Co., Ltd for providing hand-made dialyzers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirano, A., Kida, S., Yamamoto, Ki. et al. Experimental evaluation of flow and dialysis performance of hollow-fiber dialyzers with different packing densities. J Artif Organs 15, 168–175 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-011-0620-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-011-0620-6