Abstract
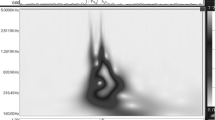
Bileaflet mechanical heart valves, which exhibit hemodynamic performance fairly similar to that of native valves, can be investigated by the analysis of their closing sounds. Signal spectra calculated from the closing sounds are characterized by specific features that are suitable for the functional evaluation of the valves. Five commercial bileaflet mechanical heart valves were studied under different conditions that were simulated in vitro using a Sheffield pulse duplicator for the aortic position. The closing sounds were acquired by means of a phonocardiographic apparatus, analyzed by a specifically implemented algorithm, and were statistically compared. This article was aimed at classifying the investigated valves on the basis of their signal spectra: different profiles were identified, depending on the working conditions; moreover, closing sound reproducibility and intensity allowed the ranking of valve performances with respect to the “noise” produced by valve closure. In particular, results demonstrated which valves were characterized by the lowest noise (i.e., the Medtronic Advantage and St. Jude Regent valves) and which were characterized by the highest reproducibility (OnX, Medtronic Advantage, and St. Jude Regent valves) under the examined experimental conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fallon AM, Marzec UM, Hansonb SR, Yoganathanc AP. Thrombin formation in vitro in response to shear-induced activation of platelets. Thromb Res 2007;121:397–406
Blome-Eberwein SA, Mrowinski D, Hofmeister J, Hetzer R. Impact of mechanical heart valve prosthesis sound on patients’ quality of life. Ann Thorac Surg 1 1996;61(2):594–602
Donnerstein RL. An in vivo analysis of ultrasonic signals created by closing bileaflet mechanical heart valves. In: Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 1996. Bridging disciplines for biomedicine. Proceedings of the 18th Annual International Conference of the IEEE, vol 3. Washington, DC: IEEE, 1996;1343–1344
Bagno A, Anzil F, Tarzia V, Pengo V, Ruggeri A, Gerosa G. Application of wavelet analysis to the phonocardiographic signal of mechanical heart valve closing sounds. Int J Artif Organs 2009;32:166–172
Sugiki H, Shiiya N, Murashita T, Yasuda K. Bileaflet mechanical valve sound analysis using a continuous wavelet transform. J Artif Organs 2006;9:42–49
Sugiki H, Shiiya N, Murashita T, Kunihara T, Matsuzaki K, Kubota T, Matsui Y, Sugiki K. Wavelet analysis of bileaflet mechanical valve sounds. J Artif Organs 2007;10(1):16–21
Sugiki H, Murashita T, Shiiya N, Matsui Y, Sugiki K. Wavelet analysis of valve closing sound detects malfunction of bileaflet mechanical valve. J Artif Organs 2008;11(1):29–37
Bagno A, Anzil F, Buselli R, Tarzia V, Pengo V, Gerosa G. Is the analysis over the time domain or over the frequency domain significant for the detection of bileaflet mechanical heart valve dysfunction? Ann Thorac Surg 2009;87:986–987
Bottio T, Caprili L, Casarotto D, Gerosa G. Small aortic annulus: the hydrodynamic performances of five commercially available bileaflet mechanical valves. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2004;128:457–462
Bagno A, Buselli R, Anzil F, Tarzia V, Pengo V, Ruggeri A, Bottio T, Gerosa G. In vitro characterization of bileaflet mechanical heart valves closing sound. 35th Annual Computers in Cardiology Conference, September 14–17, 2008, Bologna, Italy
Razzolini R, Gerosa G, Leoni L, Casarotto D, Chioin R, Dalla Volta S. Transaortic gradient is pressure-dependent in a pulsatile model of the circulation. J Heart Valve Dis 1999;8:279–283
Sheffield Pulse Duplicator Instruction Manual, The University of Sheffield, Department of Medical Physics and Clinical Engineering, Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Sheffield, UK
King MJ, Corden J, David T, Fisher J. A three-dimensional, timedependent analysis of flow through a bileaflet mechanical heart valve: comparison of experimental and numerical results. J Biomech 1996;29(5):609–618
King MJ, David T, Fisher J. Three-dimensional study of the effect of two leaflet opening angles on the time-dependent flow through a bileaflet mechanical heart valve. Med Eng Phys 1997;19:235–241
Fritzsche D, Eitz T, Laczkovics A, Liebold A, Knaut M, Matschke K, Sagie A, Mehlhorn U, Horstkotte D, Koerfer R. Early detection of mechanical valve dysfunction using a new home monitoring device. Ann Thorac Surg 2007;83:542–548
Welch PD. The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra: a method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms. IEEE Trans Audio Electroacoust 1967;AU-15:70–73
Nuttall AH. Some windows with very good sidelobe behavior. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process 1981;29:84–91
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bagno, A., Anzil, F., Buselli, R. et al. Bileaflet mechanical heart valve closing sounds: in vitro classification by phonocardiographic analysis. J Artif Organs 12, 172–181 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-009-0470-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-009-0470-7