Abstract
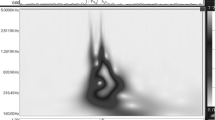
We investigated shunt murmurs based on wavelet transform analysis as a new method for assessing vascular access function. In the present study, in patients with venous stenosis near an arteriovenous fistula (A-V fistula), a sensor was placed at different positions around the stenosis and shunt murmur signals obtained using a measurement system were subjected to time–frequency analysis based on wavelet transforms. The shunt murmurs obtained from the stenotic region closely represented some features of murmurs that are often referred to as “high-pitch” murmurs in the clinical setting. In contrast, shunt murmurs obtained about 5 cm downstream of the stenotic region closely represented some features of murmurs that are often referred to as “low-pitch” murmurs in the clinical setting. Furthermore, with the aim of extending the lifespan of arteriovenous grafts (A-V grafts) by detecting and treating stenotic lesions before the A-V graft becomes occluded, we evaluated the possibility of utilizing the present shunt murmur analysis for monitoring stenosis in such A-V grafts. When shunt murmurs from patients with A-V grafts were analyzed, the results suggested that the blood flow through the venous anastomosis of the graft was the most turbulent. This present method whereby blood flow in an A-V fistula is assessed based on the frequency distribution on a time–frequency plane by wavelet transform analysis is advantageous because findings are not markedly affected by sensor attachment. Furthermore, because the sensor is attached using an adhesive collar, measurements can be taken over a short period of time before each dialysis session.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V Wong R Ward J Taylor S Selvakumar TV How A Bakran (1996) ArticleTitleFactors associated with early failure of arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis access Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 12 207–213 Occurrence Handle8760984 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymA2cjptlE%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1078-5884(96)80108-0
SL Lin CH Huang HS Chen WA Hsu CJ Yen TS Yen (1998) ArticleTitleEffects of age and diabetes on blood flow rate and primary outcome of newly created hemodialysis arteriovenous fistulas Am J Nephrol 18 96–100 Occurrence Handle9569949 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c3jtFClug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1159/000013315
InstitutionalAuthorNameNational Kidney Foundation (1997) ArticleTitleDOQI clinical practice guidelines for vascular access Am J Kidney Dis 30 IssueIDsuppl 3 s150–s191
S Glanz B Bashist DH Gordon K Butt R Adamsons (1982) ArticleTitleAngiography of upper extremity access fistulas for dialysis Radiology 143 45–52 Occurrence Handle6461026 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi2C2M7oslE%3D
M Malovrh (1998) ArticleTitleNon-invasive evaluation of vessels by duplex sonography prior to construction of arteriovenous fistulas for hemodialysis Nephrol Dial Transplant 13 125–129 Occurrence Handle9481727 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7kt1OhtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1093/ndt/13.1.125
GB Zibari MS Rohr MD Landreneau RM Bridges GA DeVault FH Petty KJ Costley ST Brown JC McDonald (1988) ArticleTitleComplications from permanent hemodialysis vascular access Surgery 104 681–686 Occurrence Handle3175866 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaD3MbnvVA%3D
GA Beathard (1998) ArticleTitleEndovascular management of thrombosed dialysis access grafts Am J Kidney Dis 32 172–175 Occurrence Handle9669441 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czjt1Wjtg%3D%3D
A Besarab KL Sullivan RP Ross MJ Moritz (1995) ArticleTitleUtility of intra-access pressure monitoring in detecting and correcting venous outlet stenoses prior to thrombosis Kidney Int 47 1364–1373 Occurrence Handle7637266 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqA28vislA%3D
CS Hayek WR Thompson C Tuchinda RA Wojcik JS Lombardo (2003) ArticleTitleWavelet processing of systolic murmurs to assist with clinical diagnosis of heart disease Biomed Instrum Technol 37 IssueID4 263–270 Occurrence Handle12923978
I Daubechies (1990) ArticleTitleThe wavelet transform, time-frequency localization and signal analysis IEEE Trans Inf Theory IT-36 961–1005 Occurrence Handle10.1109/18.57199
S Sakakibara (1995) Wavelet beginner's guide Tokyo Denki University Press Tokyo
SB Palder RL Kirkman AD Whittemore RM Hakim JM Lazarus NL Tilney (1985) ArticleTitleVascular access for hemodialysis: patency rates and results of revision Ann Surg 202 235–239 Occurrence Handle4015229 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiqB2M%2FmslE%3D
ZS Jackson H Ishibashi AI Gotlieb BL Langille (2001) ArticleTitleEffects of anastomotic angle on vascular tissue responses at end-to-side arterial grafts J Vasc Surg 34 300–307 Occurrence Handle11496283 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MvltVeksA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1067/mva.2001.115815
TR Kohler TR Kirkman LW Kraiss BK Zierler AW Clowes (1991) ArticleTitleIncreased blood flow inhibits neointima hyperplasia in endothelialized vascular grafts Circ Res 69 1557–1565 Occurrence Handle1954675 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2D28zlvVM%3D
DP Giddens CK Zarins S Glagov (1993) ArticleTitleThe role of fluid mechanics in the localization and detection of atherosclerosis J Biomech Eng 115 588–594 Occurrence Handle8302046 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuC3szmsFw%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, T., Tsuji, K., Kawashima, N. et al. Evaluation of blood access dysfunction based on a wavelet transform analysis of shunt murmurs. J Artif Organs 9, 97–104 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-005-0327-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-005-0327-7