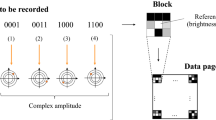
Abstract
In practical applications of holographic data storage (HDS), which offers both high capacity and high transfer rates, reduction of the error rate is a major issue. In this study, we have applied a convolutional neural network (CNN)-based demodulation scheme for constant-weight codes to HDS and have demonstrated that the error rate can be reduced by approximately one order of magnitude when compared with that of the conventional ranking method. We have also evaluated the HDS error characteristics, which were not clarified fully in previous studies. The results of this evaluation showed that symbols with certain specific shapes are prone to errors. This study is expected to provide useful knowledge for use in practical applications of HDS.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Psaltis, D., Burr, G.: Holographic data storage. Computer 31(2), 52 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1109/2.652917
Glass, A., Cardillo, M., Coufal, H.J., Psaltis, D., Sincerbox, G.T.: Holographic Data Storage. Springer, Berlin (2000)
Curtis, K., Dhar, L., Hill, A., Wilson, W., Ayres, M. (eds.): Holographic Data Storage: From Theory to Practical Systems. Wiley, New Jersey (2010)
Curtis, K., Dhar, L., Hoskins, A., Ayres, M., Fotheringham, E.: in Holographic Data Storage: From Theory to Practical Systems, 8th edn., pp. 151–183. Wiley, New Jersey (2010)
Nishimoto, K., Naito, F., Yamamoto, M.: Soft-decision viterbi decoding for 2/4 modulation code in holographic memory. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45(5R), 4102 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.45.4102
Kim, N.Y., Lee, J., Lee, J.: Rate 5/9 two-dimensional pseudobalanced code for holographic data storage systems. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45(2B), 1293 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.45.1293
Malki, O., Knittel, J., Przygodda, F., Trautner, H., Richter, H.: Two-dimensional modulation for holographic data storage systems. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 47(7S1), 5993 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.47.5993
Okumura, T., Hayashi, T., Akiyama, J., Maeda, S., Murakami, Y., Takahashi, A.: Two-dimensional partial response maximum likelihood with constant-weight constraint for holographic data storage. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 47(7S1), 5971 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.47.5971
Yoshida, S., Takahata, Y., Horiuchi, S., Yamamoto, M.: Spatial run-length limited code for reduction of hologram size in holographic data storage. Opt. Commun. 358, 103 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2015.08.088
Chou, W.C., Neifeld, M.A.: Soft-decision array decoding for volume holographic memory systems. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 18(1), 185 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAA.18.000185
Pishro-Nik, H., Rahnavard, N., Ha, J., Fekri, F., Adibi, A.: Low-density parity-check codes for volume holographic memory systems. Appl. Opt. 42(5), 861 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.42.000861
Yoon, P., Chung, B., Kim, H., Park, J., Park, G.: Low-density parity-check code for holographic data storage system with balanced modulation code. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 47(7S1), 5981 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.47.5981
Keskinoz, M., Kumar, B.V.K.V.: Application of linear minimum mean-squared-error equalization for volume holographic data storage. Appl. Opt. 38(20), 4387 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.38.004387
Choi, A.S., Baek, W.S.: Equalization for digital holographic data storage. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 40(3S), 1737 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.40.1737
Nabavi, S., Kumar, B.V.K.V.: Application of linear and nonlinear equalization methods for holographic data storage. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45(2B), 1079 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.45.1079
Kim, J., Lee, J.: Partial response maximum likelihood detections using two-dimensional soft output viterbi algorithm with two-dimensional equalizer for holographic data storage. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 48(3S1), 03A033 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.48.03A033
Koo, K., Kim, S.Y., Kim, S.W.: Modified two-dimensional soft output viterbi algorithm with two-dimensional partial response target for holographic data storage. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 51(8S2), 08JB03 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.51.08JB03
Kim, K., Kim, S.H., Koo, G., Seo, M.S., Kim, S.W.: Decision feedback equalizer for holographic data storage. Appl. Opt. 57(15), 4056 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.57.004056
Shimobaba, T., Kuwata, N., Homma, M., Takahashi, T., Nagahama, Y., Sano, M., Hasegawa, S., Hirayama, R., Kakue, T., Shiraki, A., Takada, N., Ito, T.: Convolutional neural network-based data page classification for holographic memory. Appl. Opt. 56(26), 7327 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.56.007327
Katano, Y., Muroi, T., Kinoshita, N., Ishii, N., Hayashi, N.: Data demodulation using convolutional neural networks for holographic data storage. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 57(9S1), 09SC01 (2018). https://doi.org/10.7567/JJAP.57.09SC01
Lecun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., Haffner, P.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86(11), 2278 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1109/5.726791
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Salakhutdinov, R.: Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 15(56), 1929 (2014)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A Method for stochastic optimization. In: Proceedings of international conference on learning representations (ICLR), pp. 1–15 (2015)
Barbastathis, G., Levene, M., Psaltis, D.: Shift multiplexing with spherical reference waves. Appl. Opt. 35(14), 2403 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.35.002403
Yoshida, S., Matsubara, T., Kurata, H., Horiuchi, S., Yamamoto, M.: Multi-dimensional shift multiplexing technique with spherical reference waves. IEICE Trans. Electron. E–96C(12), 1520 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1587/transele.E96.C.1520
Yoshida, S., Kurata, H., Ozawa, S., Okubo, K., Horiuchi, S., Ushiyama, Z., Yamamoto, M., Koga, S., Tanaka, A.: High-density holographic data storage using three-dimensional shift multiplexing with spherical reference wave. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 52(9S2), 09LD07 (2013). https://doi.org/10.7567/JJAP.52.09LD07
Ushiyama, Z., Kurata, H., Tsukamoto, Y., Yoshida, S., Yamamoto, M.: Shift-peristrophic multiplexing for high density holographic data storage. Appl. Sci. 4(2), 148 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3390/app4020148
Yoshida, S., Takahata, Y., Horiuchi, S., Yamamoto, M.: Diffraction model of peristrophic multiplexing with spherical reference wave. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 32(2), 224 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAA.32.000224
Nobukawa, T., Nomura, T.: Shift multiplexing with a spherical wave in holographic data storage based on a computer-generated hologram. Appl. Opt. 56(13), F31 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.56.000F31
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurokawa, S., Yoshida, S. Demodulation scheme for constant-weight codes using convolutional neural network in holographic data storage. Opt Rev 29, 375–381 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-022-00744-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-022-00744-1