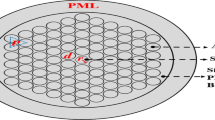
Abstract
In this study, an automobile wheel type photonic crystal fiber (PCF) has been designed to investigate the effect of the background material on analyte sensing. The designed PCF has a circular hollow core with eight slot-type air holes in cladding. The analysis is performed in the range of 0.5–1.5 THz, and different background materials are chosen during the simulation, for example, fused silica, BK7 glass, Zeonex, and SF2 glass. The sensing performance and light propagation properties are investigated to find out the suitable background material of the designed PCF. At 1 THz, the maximum sensitivity is achieved using fused silica as a background material, while BK7 glass, Zeonex, and SF2 glass show slightly lower relative sensitivity than fused silica. The obtained relative sensitivity is 92.0% of fused silica, 91.2% for BK7 glass, 90.1% for Zeonex, and 88.1% for SF2 glass. In this study, SF2 glass shows the lowest sensitivity, highest effective material loss, and highest confinement loss compares to fused silica, BK7 glass, and Zeonex. In contrast, fused silica shows the highest relative sensitivity, lowest effective material loss, and lowest confinement loss.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Timofeyenko, Y.G., Rosentreter, J.J., Mayo, S.: Piezoelectric quartz crystal microbalance sensor for trace aqueous cyanide ion determination. Anal. Chem. 79, 251–255 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1021/AC060890M
Wu, J., Wang, L., Wang, Q., Zou, L., Ye, B.: The novel voltammetric method for determination of hesperetin based on a sensitive electrochemical sensor. Talanta 150, 61–70 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TALANTA.2015.12.026
EkhlasurRahaman, M., Bellal Hossain, M., Shekhar Mondal, H., Saha, R., Mahbub Hossain, M., Shamim Ahsan, M.: Highly sensitive photonic crystal fiber liquid sensor in terahertz frequency range. Mater. Today Proc. 43, 3815–3820 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATPR.2020.11.413
Iqbal, F., Biswas, S., Bulbul, A.A.M., Rahaman, H., Hossain, M.B., Rahaman, M.E., Awal, M.A.: Alcohol sensing and classification using PCF-based sensor. Sens. Bio-Sensing Res. 30, 100384 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SBSR.2020.100384
Jiaqiang, X., Yuping, C., Daoyong, C., Jianian, S.: Hydrothermal synthesis and gas sensing characters of ZnO nanorods. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 113, 526–531 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2005.03.097
Shkotova, L.V., Soldatkin, A.P., Gonchar, M.V., Schuhmann, W., Dzyadevych, S.V.: Amperometric biosensor for ethanol detection based on alcohol oxidase immobilised within electrochemically deposited Resydrol film. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 26, 411–414 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEC.2005.10.031
Hossain, M.B., Podder, E.: Design and investigation of PCF-based blood components sensor in terahertz regime. Appl. Phys. A. 125, 861 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3164-x
Rahaman, M.E., Jibon, R.H., Ahsan, M.S., Ahmed, F., Sohn, I.-B.: Glucose level measurement using photonic crystal fiber–based plasmonic sensor. Plasmon. 2021(1), 1–11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11468-021-01497-4
Rahaman, M.E., Jibon, R.H., Hossain, M.B., Mondal, H.S., Bulbul, A.A.M., Saha, A., Hassan, M.M.: Sensing Toxic Carbonyl Compounds in Cigarette Smoke by Photonic Crystal Fiber. 2020 11th Int. Conf. Comput. Commun. Netw. Technol. ICCCNT 2020. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCNT49239.2020.9225607
Hossain, M.B., Podder, E., Bulbul, A.A.-M., Mondal, H.S.: Bane chemicals detection through photonic crystal fiber in THz regime. Opt. Fiber Technol. 54, 102102 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yofte.2019.102102
Asaduzzaman, S., Ahmed, K., Bhuiyan, T., Farah, T.: Hybrid photonic crystal fiber in chemical sensing. Springerplus 5, 1–11 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/S40064-016-2415-Y
Ahmed, K., Morshed, M.: Design and numerical analysis of microstructured-core octagonal photonic crystal fiber for sensing applications. Sens. Bio-Sensing Res. 7, 1–6 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SBSR.2015.10.005
Arik, E., Koral, C., Altan, H., Esentürk, O.: A new method for alcohol content determination of fuel oils by terahertz spectroscopy. Int. Conf. Infrared, Millimeter, Terahertz Waves, IRMMW-THz. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/IRMMW-THZ.2013.6665885
Paul, B.K., Ahmed, K., Vigneswaran, D., Sen, S., Islam, M.S.: Quasi photonic crystal fiber for chemical sensing purpose in the terahertz regime: design and analysis. Opt. Quantum Electron 51, 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11082-019-1956-Z
Ademgil, H., Haxha, S.: PCF based sensor with high sensitivity, high birefringence and low confinement losses for liquid analyte sensing applications. Sensors 15, 31833–31842 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/s151229891
Asaduzzaman, S., Ahmed, K.: Microarray-core based circular photonic crystal fiber for high chemical sensing capacity with low confinement loss. Opt. Appl. 47, 41–49 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5277/OA170104
Podder, E., Hossain, M.B., Al-Mamun Bulbul, A., Shekhar Mondal, H.: Ethanol Detection Through Photonic Crystal Fiber. In: Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence, Springer, Singapore, pp 175–182 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7564-4_15
Arif, M.F.H., Biddut, M.J.H.: A new structure of photonic crystal fiber with high sensitivity, high nonlinearity, high birefringence and low confinement loss for liquid analyte sensing applications. Sens. Bio-Sensing Res. 12, 8–14 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SBSR.2016.11.003
Sultana, J., Islam, M.S., Ahmed, K., Dinovitser, A., Ng, B.W.-H., Abbott, D.: Terahertz detection of alcohol using a photonic crystal fiber sensor. Appl. Opt. 57, 2426 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.57.002426
Ahmed, K., Ahmed, F., Roy, S., Paul, B.K., Aktar, M.N.: Refractive index based blood components sensing in terahertz spectrum. IEEE Sens. J (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2019.2895166
Islam, M.S., Sultana, J., Dinovitser, A., Ahmed, K., Islam, M.R., Faisal, M., Ng, B.W.H., Abbott, D.: A novel Zeonex based photonic sensor for alcohol detection in beverages. 2nd IEEE Int. Conf. Telecommun. Photonics, ICTP 2017. 2017-Decem, 114–118 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTP.2017.8285905
Abdullah-Al-Shafi, M., Sen, S.: Design and analysis of a chemical sensing octagonal photonic crystal fiber (O-PCF) based optical sensor with high relative sensitivity for terahertz (THz) regime. Sens. Bio-Sensing Res. 29, 100372 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SBSR.2020.100372
Islam, M.S., Sultana, J., Ahmed, K., Islam, M.R., Dinovitser, A., Ng, B.W.-H., Abbott, D.: A novel approach for spectroscopic chemical identification using photonic crystal fiber in the Terahertz Regime. IEEE Sens. J. 18, 575–582 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2017.2775642
Islam, M.S., Sultana, J., Dinovitser, A., Ahmed, K., Ng, B.W.H., Abbott, D.: Sensing of toxic chemicals using polarized photonic crystal fiber in the terahertz regime. Opt. Commun. 426, 341–347 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2018.05.030
Ahmed, K., Islam, M.I., Paul, B.K., Islam, M.S., Sen, S., Chowdhury, S., Uddin, M.S., Asaduzzaman, S., Bahar, A.N.: Effect of photonic crystal fiber background materials in sensing and communication applications. Mater. Discov. 7, 8–14 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.md.2017.05.002
Islam, M.S., Sultana, J., Cordeiro, C.M.B., Cruz, A.L.S., DInovitser, A., Ng, B.W.H., Abbott, D.: Broadband Characterization of Glass and Polymer Materials Using THz-TDS. Int. Conf. Infrared, Millimeter, Terahertz Waves, IRMMW-THz. 2019-September, (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/IRMMW-THZ.2019.8874013
Islam, M.S., Cordeiro, C.M.B., Nine, M.J., Sultana, J., Cruz, A.L.S., DInovitser, A., Ng, B.W.H., Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H., Losic, D., Abbott, D.: Experimental Study on Glass and Polymers: Determining the Optimal Material for Potential Use in Terahertz Technology. IEEE Access. 8, 97204–97214 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2996278
Naftaly, M., Miles, R.E.: Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy for material characterization. Proc. IEEE. 95, 1658–1665 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2007.898835
Cruz, A.L.S., Cordeiro, C.M.B., Abbott, D., Sultana, J., Franco, M.A.R., Islam, M.S.: Terahertz optical fibers [Invited]. Opt. Express 28(11), 16089–16117 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.389999
Cruz, C.H.B., Cordeiro, C.M.B., Barretto, E.C.S., Chesini, G., Franco, M.A.R., Large, M.C.J., Lwin, R.: Microstructured-core optical fibre for evanescent sensing applications. Opt. Express 14(26), 13056–13066 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.14.013056
Zhang, L., Ren, G.J., Yao, J.Q.: A new photonic crystal fiber gas sensor based on evanescent wave in terahertz wave band: design and simulation. Optoelectron. Lett. 9, 438–440 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-013-3157-5
Shi, C., Wang, D.N., Ho, H.L., Ruan, S.C., Jin, W., Hoo, Y.L.: Design and modeling of a photonic crystal fiber gas sensor. Appl. Opt 42(18), 3509–3515 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.42.003509
Paul, B.K., Ahmed, K., Vigneswaran, D., Ahmed, F., Roy, S., Abbott, D.: Quasi-photonic crystal fiber-based spectroscopic chemical sensor in the terahertz spectrum: design and analysis. IEEE Sens. J. 18, 9948–9954 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2018.2872892
Saitoh, K., Koshiba, M.: Leakage loss and group velocity dispersion in air-core photonic bandgap fibers. Opt. Express 11(23), 3100–3109 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.11.003100
Islam, M.S., Faisal, M., Razzak, S.M.A.: Extremely low loss porous-core photonic crystal fiber with ultra-flat dispersion in terahertz regime. JOSA B 34(8), 1747–1754 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.34.001747
Hasan, M.M., Sen, S., Rana, M.J., Paul, B.K., Habib, M.A., Daiyan, G.M., Ahmed, K.: Heptagonal photonic crystal fiber based chemical sensor in THz regime. 2019 Jt. 8th Int. Conf. Informatics, Electron. Vision, ICIEV 2019 3rd Int. Conf. Imaging, Vis. Pattern Recognition, icIVPR 2019 with Int. Conf. Act. Behav. Comput. ABC 2019. 40–44 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIEV.2019.8858555
Yakasai, I., Abas, P.E., Kaijage, S.F., Caesarendra, W., Begum, F.: Proposal for a quad-elliptical photonic crystal fiber for Terahertz Wave guidance and sensing chemical warfare liquids. Photonics 6, 78 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/PHOTONICS6030078
Kanmani, R., Ahmed, K., Roy, S., Ahmed, F., Kumar Paul, B., Mani Rajan, M.S.: The performance of hosting and core materials for slotted core Q-PCF in terahertz spectrum. Optik 194, 163084 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJLEO.2019.163084
Bise, R.T., Trevor, D.J.: Sol-gel derived microstructured fiber: Fabrication and characterization. Conf. Opt. Fiber Commun. Tech. Dig. Ser. 3, 269–271 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/OFC.2005.192772
Petrovich, M.N., Brakel, A. van, Poletti, F., Mukasa, K., Austin, E., Finazzi, V., Petropoulos, P., O’Driscoll, E., Watson, M., DelMonte, T., Monro, T.M., Dakin, J.P., Richardson, D.J.: Microstructured fibres for sensing applications. 6005, 78–92 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.631617
Broeng, J., Mogilevstev, D., Barkou, S.E., Bjarklev, A.: Photonic crystal fibers: a new class of optical waveguides. Opt. Fiber Technol. 5, 305–330 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1006/OFTE.1998.0279
Ghazanfari, A., Li, W., Leu, M.C., Hilmas, G.E.: A novel freeform extrusion fabrication process for producing solid ceramic components with uniform layered radiation drying. Addit. Manuf. 15, 102–112 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2017.04.001
Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H., Schuppich, J., Dowler, A., Lima-Marques, L., Monro, T.M.: 3D-printed extrusion dies: a versatile approach to optical material processing. Opt. Mater. Express. 4, 1494 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1364/ome.4.001494
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahaman, M.E., Hossain, M.B. & Mondal, H.S. Effect of background materials in photonic crystal fiber sensor. Opt Rev 29, 1–6 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-021-00712-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-021-00712-1