Abstract
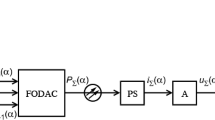
A precise and fast method for controlling the reference-beam angle of an angular-multiplexed holographic data storage system (HDSS)—to achieve larger capacity and faster data-transfer rate—is proposed. The reference beam is first controlled by a galvanometer mirror (GM) with an “angular control signal (ACS)” applied to its zero-cross angle (which differs by a certain offset angle from the target angle). The offset angle is then eliminated by referring to the output from a rotary encoder inside the GM, and the optimum angle for the reference beam is obtained. Next, a servo beam is used for the ACS, and the ACS value is obtained as a differential signal between the beam intensities of the diffracted reference beam and the diffracted servo beam. The servo beam is orthogonally polarized in regard to the reference beam and has a slightly different incident angle. A reference-beam angular error lower than 3.3 mdeg was confirmed in simulations and experiments.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coufal, H.J., Psaltis, D., Sincerbox, G.T.: Holographic Data Storage, pp. 10–18. Springer, Berlin (2000)
van Heerden, P.J.: Theory of optical information storage in solids. Appl. Opt. 2, 393 (1963)
Hong, J.H., McMichael, I., Chang, T.Y., Christian, W., Paek, E.G.: Volume holographic memory systems: techniques and architectures. Opt. Eng. 34, 2193 (1995)
Mok, F.H.: Angle-multiplexed storage of 5000 holograms in lithium niobate. Opt. Lett. 18, 915 (1993)
Ashley, J., Bernal, M.-P., Burr, G.W., Coufal, H., Guenther, H., Hoffnagle, J.A., Jefferson, C.M., Marcus, B., Macfarlane, R.M., Shelby, R.M., Sincerbox, G.T.: Holographic data storage. IBM J. Res. Dev. 44, 341 (2000)
Anderson, K., Curtis, K.: Polytopic multiplexing. Opt. Lett. 29, 1402 (2004)
Horimai, H., Tan, X.: Advanced collinear holography. Opt. Rev. 12, 90 (2005)
Sato, M., Ogasawara, M., Ito, Y., Tanaka, S., Iida, T.: New coaxial interference method for consumer holographic memory. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 3850 (2007)
Tanaka, K., Hara, M., Tokuyama, K., Hirooka, K., Ishioka, K., Fukumoto, A., Watanabe, K.: Improved performance in coaxial holographic data recording. Opt. Express 15, 16196 (2007)
Shimura, T., Ichimura, S., Fujimura, R., Kuroda, K., Tan, X., Horimai, H.: Analysis of a collinear holographic storage system: introduction of pixel spread function. Opt. Lett. 31, 1208 (2006)
Shimada, K, Ishii, T., Ide, T., Hughes, S., Hoskins, A., Curtis, K.: High density recording using monocular architecture for 500GB consumer system. Tech. Dig. Optical Data Storage, TuC2 (2009).
Hosaka, M., Ishii, T., Tanaka, A., Koga, S., Hoshizawa, T.: 1 Tbit/inch2 recording in angular-multiplexing holographic memory with constant signal-to-scatter ratio schedule. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 52, 09LD01 (2013).
Hosaka, M., Ishii, T., Hoshizawa, T.: Region-divided adaptive equalization for holographic memory. Tech. Dig. Int. Symp. Opt. Mem. Opt. Data Storage, OMB6 (2011).
Ishii, T., Shimada, K., Hughes, S., Hoskins, A., Curtis, K.: Margin allocation for a 500GB holographic memory system using monocular architecture. Tech. Dig. Opt. Data Storage, PD1 (2009)
Nakamura, Y., Shimada, K., Ishii, T., Ishihara, H., Hosaka, M., Hoshizawa, T.: High-density recording method with RLL coding for holographic memory system. Tech. Dig. Int. Symp. Opt. Mem. Opt. Data Storage, OMB5 (2011)
Fujita, T., Horikoshi, H.: Focus sensing method using far-field diffracted waves and Its application to holographic data discs. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 48, 03A037 (2009)
Göröcs, Z., Sarkadi, T., Erdei, G., Koppa, P.: Hologram positioning servo for phase-encoded holographic data storage systems. Appl. Opt. 49, 611 (2010)
Song, H.-C., Kim, N., Kim, D.-H., Lim, S.-Y., Cho, J. H., Yang, H., Park, N.-C., Park, K.-S., Park, Y.-P.: Tracking servo method using reflective optical filter for holographic data storage system. Microsyst Technol, 1057 (2011)
Lee, C.W., Kwak, B.S., Chung, C.C., Tomizuka, M.: Design of the tracking controller for holographic digital data storage. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 15, 242 (2010)
Kim, S.-H., Kim, J.H., Lee, Y., Yang, H., Park, J.-Y., Park, K.-S., Park, Y.-P.: Tilt error measurement and compensation method for the holographic data storage system using disturbance observer. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 45, 2248 (2009)
Ayres, M., Hoskins, A., Smith, P.C., Kane, J.: Wobble alignment for angularly multiplexed holograms. Tech. Dig. Int. Symp. Opt. Mem. Opt. Data Storage, ThC01 (2008)
Kim, J.H., Yang, H., Kim, N., Jeong, W., Park, J.B.: Pattern analysis for tilt servo control in holographic data storage system. Microsyst Technol, 1677 (2012)
Usui, T., Ogawa, A., Okano, H., Watanabe, K., Kuroda, K., Tatsuta, S., Kubota, Y.: Temperature compensation servo algorithm for holographic data storage. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49, 08BKD04 (2010).
Kim, N., Junga, K., Kima, K., Yoona, P., Parka, J., Park, J.: A novel angle servo for holographic data storage system. Proc. SPIE 6620 Optical Data Storage 66201M (2007).
Curtis, K., Dhar, L., Hill, A., Wilson, W., Ayres, M.: Holographic Data Storage. Wiley, Chichester, p. 352 (2010)
Coufal, H.J., Psaltis, D., Sincerbox, G.T.: Holographic Data Storage, pp. 42–44. Springer, Berlin (2000)
Curtis, K., Dhar, L., Hill, A., Wilson, W., Ayres, M.: Holographic Data Storage. Wiley, Chichester, pp. 349–350 (2010)
Curtis, K., Dhar, L., Hill, A., Wilson, W., Ayres, M.: Holographic Data Storage. Wiley, Chichester, p. 53 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamazaki, K., Hosaka, M., Yamada, K. et al. Ultra-narrow interval angular control signal for holographic data storage system. Opt Rev 23, 848–858 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-016-0252-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-016-0252-4