Abstract
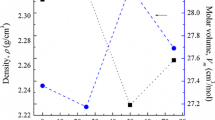
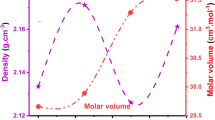
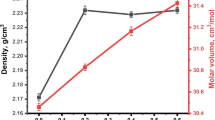
Reducing the glass phonon energy is an essential procedure to achieve high efficient radiative upconversion process. The degree of covalence of chemical bonds is responsible for the high oscillator strength of intracenter transitions in rare-earth ions. So, conversion covalent to ionic glass character is proposed as a structure-sensitive criterion that controls the phonon energy of the glasses. A series of oxyfluoro aluminum-borate host glasses used for upconversion application is prepared by the conventional melt-quenching technique. Through lithium oxide substitution by lithium fluoride, the ionic-covalent property of Li+ ion successes to regulate the band gap energies of the studied glasses. Furthermore, a new method to determine the glass phonon energy is offered.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Baki, M., El-Diasty, F.: Glasses for photonic technologies. Inter. J. Opt. Appl. 3, 125–137 (2013)
Rai, A., Rai, S.B., Mahato, K.K.: Frequency upconversion involving quartets of ions in a Pr3+/Eu3+ oxyfluoroborate glass. Chem. Phys. Lett. 414, 222–225 (2005)
Mahato, K.K., Rai, S.B.: Laser spectroscopic studies of Tb3+-doped oxyfluoroborate glass. Spectrochim. Acta A 56, 2333–2340 (2000)
Kumar, A., Rai, D.K., Rai, S.B.: Luminescence of Gd3+ ions doped in oxyfluoroborate glass. Solid State Commun. 117, 387–392 (2001)
Pisarska, J., Ryba-Romanowski, W., Dominiak-Dzik, G., Goryczka, T., Pisarski, W.A.: Nd-doped oxyfluoroborate glasses and glass-ceramics for NIR laser applications. J. Alloys Comp. 451, 223–225 (2008)
Bahadur, A., Dwivedi, Y., Rai, S.B.: Optical properties of cerium doped oxyfluoroborate glass. Spectrochim. Acta A: Mol. Biomol. Spect. 110, 400–403 (2013)
Mahato, K.K., Rai, A., Rai, S.B.: Optical properties of Dy3+ doped in oxyfluoroborate glass. Spectrochim. Acta A 61, 431–436 (2005)
Tver’yanovich, Y.S., Pastor, A.A.: Resonant optical nonlinearity in vitreous semiconductors. Glass Phys. Chem. 29, 328–329 (2003)
Mamedov, A.A., Noginov, M.A., Smirnov, V.A., Sokolov, V.V., Shcherbakov, I.A.: Application of sulfide glasses as active media of diode-pumped neodymium lasers. Fiz. Khim. Stekla 17, 446–450 (1991)
El-Diasty, F., Abdel-Baki, M., Abdel-Wahab, F. A.: Oxyfluoro aluminum-borate host glass: Interband gap study and estimation of radiative lifetime for luminescent dopant ions. Opt. Quant. Electron 48, (2016)
Mott, N.F., Davis, E.A.: Electronic Processes in Non-Crystalline Materials. Oxford Univ Press, Oxford (1979)
Tauc, J.: Amorphous and liquid semiconductors, p. 159. Plenum Press, London (1974)
Pye, L.D., Frechette, V.D., Kreidl, N.J.: Borate glasses: structure, properties and applications. Plenum, New York (1978)
Duffy, J.A.: Ultraviolet transparency of glass: a chemical approach in terms of band theory, polarisability and electronegativity. Phys. Chem. Glasses 42, 151–157 (2001)
Abdel-Baki, M., Abdel Wahab, F., El-Diasty, F.: One-photon band gap engineering of borate glass doped with ZnO for photonics applications. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 073506 (2012)
Holleman, A. F., Wiberg, E.:Inorganic Chemistry. Academic Press P, 135, (2001)
Rada, S., Pascuta, P., Culea, M., Pop, L., Culea, E.: Structural properties of the boro-bismuthate glasses containing gadolinium ions. Vib. Spectrosc. 48, 255–258 (2008)
Saddeek, Y.B., Shaaban, E.R., Moustafa, H.M.: Spectroscopic properties, electronic polarizability, and optical basicity of Bi2O3–Li2O–B2O3 glasses. Phys. B 403, 2399–2407 (2008)
Kamitsos, E.I., Karakassides, M.A., Chryssikos, G.D.: Vibrational spectra of magnesium sodium borate glasses: 2. Raman and mid-infrared investigation of network structure. J. Phys. Chem. 91, 1073–1079 (1987)
Pascuta, P., Borodi, G., Culea, E.: Structural investigation of bismuth borate glass ceramics containing gadolinium ions by X-ray diffraction and FTIR spectroscopy. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 20, 360–365 (2009)
Ali, K.A., El-Din Mostafa, A.G.: Study of the structure and some physical properties of sodium-boro-Pphosphate glasses containing antimony and iron oxides. Turk. J. Phys. 27, 225–233 (2003)
Varsamis, C.P.E., Kamitsos, E.I., Minami, T.: Structural investigation of superionic AgI-containing orthoborate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 345 and 346, 93–98 (2004)
Chakrabarti, R., Annapurna, K., Buddhudu, : Emission analysis of Eu3+ : CaO–La2O3–B2O3 glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 353, 1422–1426 (2007)
Denning, J.H., Boss, S.D.: The vibrational spectra and structures of some rare-earth borates. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 28, 1775–1785 (1972)
Ren, M., Lin, J.H., Dong, Y., Yang, L.Q., Su, M.Z., You, L.P.: Structure and phase transition of GdBO3. Chem. Mater. 11, 1576–1580 (1999)
Kamitsos, E.I., Karakassides, M.A., Patsis, A.P.: Spectroscopic study of carbonate retention in high-basicity borate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 111, 252–262 (1989)
Kamitsos, E.I., Karakassides, M.A.: Structural studies of binary and pseudobinary sodium borate glasses of high sodium content. Phys. Chem. Glasses 30, 19–26 (1989)
Kamitsos, E.I., Patsis, A.P., Karakassides, M.A., Chryssikos, G.D.: Infrared reflectance spectra of lithium borate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 126, 52–67 (1990)
Varsamis, C.P., Kamitsos, E.I., Chryssikos, G.D.: Structure of fast-ion-conducting AgI-doped borate glasses in bulk and thin film forms. Phys. Rev. B. 60, 3885–3898 (1999)
Winterstein-Beckmann, A., Möncke, D., Palles, D., Kamitsos, E.I., Wondraczek, L.: Structure–property correlations in highly modified Sr, Mn-borate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 376, 165–174 (2013)
Duffy, J.A.: The importance of π-bonding in glass chemistry: borate glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol. B 49, 317–325 (2008)
Varshneya, A.K.: Fundamentals of inorganic glasses. Academic Press Inc., New York (1994)
Upender, G., Ramesh, S., Prasada, M., Sathe, V.G., Mouli, V.C.: Optical band gap, glass transition temperature and structural studies of (100–2x)TeO2–xAg2O–xWO3 glass system. J. Alloys Comp. 504, 468–474 (2010)
Abdel-Baki, M., Abdel Wahab, F.A., Radi, A., El-Diasty, F.: Factors affecting optical dispersion in borate glass systems. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 68, 1457–1470 (2007)
Essick, J.M., Mather, R.T.: Characterization of a bulk semiconductor’s band gap via a near-absorption edge optical transmission experiment. Am. J. Phys. 61, 646–649 (1993)
Som, T., Karmakar, B.: Green and red fluorescence upconversion in neodymium-doped low phonon antimony glasses. J. Alloys Comp. 476, 383–389 (2009)
Som, T., Karmakar, B.: Infrared-to-red upconversion luminescence in samarium-doped antimony glasses. J. Lumine. 128, 1989–1996 (2008)
Miller, P.J., Cody, C.A.: Infrared and Raman investigation of vitreous antimony trioxide. Spectrochim. Acta A 38, 555–559 (1982)
Karmakar, B., Dwivedi, R.N.: FT-IRRS, UV–Vis–NIR absorption and green upconversion in Er3+ doped lead silicate glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 342, 132–139 (2004)
Sun, H., Xu, S., Dai, S., Wen, L., Zhang, J., Hu, L., Jiang, Z.: Efficient frequency upconversion emission in Er3+-doped novel strontium lead bismuth glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 351, 288–292 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Baki, M., El-Diasty, F. Oxyfluoroborate host glass for upconversion application: phonon energy calculation. Opt Rev 23, 284–289 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-016-0199-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-016-0199-5