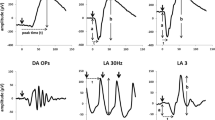
Abstract
The presence of cornea hysteresis (CH) in characterizing the intraocular pressure (IOP) of a human eye deteriorates the accuracy of IOP. To suppress CH, the pressure gauge of a tonometer must be located as close as possible to the cornea. However, this arrangement is unpractical because appropriate working distance to the cornea is required. In this paper, a time-delay calibrated (TDC) method is proposed to counteract the undesired effect of CH in characterizing the IOP. Employing this TDC method, the CH approaches to zero for most eyes measured.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forbes, M., Pico, G., Grolman, B.: A noncontact applanation tonometer. Description and clinical evaluation. Arch. Ophthalmol. 91, 134 (1974)
Kling, S., Bekesi, N., Dorronsoro, C., Pascual, D., Marcos, S.: Corneal viscoelastic properties from finite-element analysis of in vivo air-puff deformation. PLoS One 9, e104904 (2014)
Šilih, M.Š., Hawlina, M.: Influence of corneal thickness on comparative intraocular pressure measurements with Goldmann and non-contact tonometers in keratoconus. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 220, 843 (2003)
Li, J., Herndon, L.W., Asrani, S.G., Stinnett, S., Allingham, R.R.: Clinical comparison of the Proview eye pressure monitor with the Goldmann applanation tonometer and the Tonopen. Arch. Ophthalmol. 122, 1117 (2004)
Lleo, A., Marcos, A., Calatayud, M., Alonso, L., Rahhal, S.M., Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A.: The relationship between central corneal thickness and Goldmann applanation tonometry. Clin. Exp. Optom. 86, 104 (2003)
Gatinel, D., Chaabouni, S., Adam, P.A., Munck, J., Puech, M., Hoang-Xuan, T.: Corneal hysteresis, resistance factor, topography, and pachymetry after corneal lamellar flap. J. Refract. Surg. 23, 76 (2007)
Sathi Devi, A.V.: The ocular response analyzer. J. Curr. Glaucoma Pract. 3, 24 (2009)
Congdon, N.G., Broman, A.T., Bandeen-Roche, K., Grover, D., Quigley, H.A.: Central corneal thickness and corneal hysteresis associated with glaucoma damage. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 141, 868 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, KJ., Tsai, CL., Wang, W. et al. A time-delay calibrated method for cornea hysteresis and intraocular pressure measurement. Opt Rev 23, 340–345 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-015-0168-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-015-0168-4