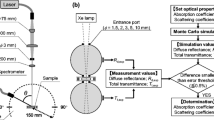
Abstract
The anisotropy factor g, one of the optical properties of biological tissues, has a strong influence on the calculation of the scattering coefficient μ s in inverse Monte Carlo (iMC) simulations. It has been reported that g has the wavelength and absorption dependence; however, few attempts have been made to calculate μ s using g values by taking the wavelength and absorption dependence into account. In this study, the angular distributions of scattered light for biological tissue phantoms containing hemoglobin as a light absorber were measured by a goniometric optical setup at strongly (405 nm) and weakly (664 nm) absorbing wavelengths to obtain g. Subsequently, the optical properties were calculated with the measured values of g by integrating sphere measurements and an iMC simulation, and compared with the results obtained with a conventional g value of 0.9. The μ s values with measured g were overestimated at the strongly absorbing wavelength, but underestimated at the weakly absorbing wavelength if 0.9 was used in the iMC simulation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greve, B., Raulin, C.: Professional errors caused by lasers and intense pulsed light technology in dermatology and aesthetic medicine: preventive strategies and case studies. Dermatol. Surg. 28(2), 156–161 (2002)
Haedersdal, M.: Side effects from the pulsed dye laser: the importance of skin pigmentation and skin redness. Acta Derm. Venereol. 78(6), 445–450 (1998)
Hammes, S., Karsai, S., Metelmann, H.-R., Pohl, L., Kaiser, K., Park, B.-H., Raulin, C.: Treatment errors resulting from use of lasers and IPL by medical laypersons: results of a nationwide survey. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 11(2), 149–156 (2013)
Nilsson, A.M.K., Sturesson, C., Liu, D.L., Andersson-Engels, S.: Changes in spectral shape of tissue optical properties in conjunction with laser-induced thermotherapy. Appl. Opt. 37(7), 1256–1267 (1998)
Yaroslavsky, A.N., Schulze, P.C., Yaroslavsky, I.V., Schober, R., Ulrich, F., Schwarzmaier, H.-J.: Optical properties of selected native and coagulated human brain tissues in vitro in the visible and near infrared spectral range. Phys. Med. Biol. 47(12), 2059–2073 (2002)
Simpson, C.R., Kohl, M., Essenpreis, M., Cope, M.: Near-infrared optical properties of ex vivo human skin and subcutaneous tissues measured using the Monte Carlo inversion technique. Phys. Med. Biol. 43(9), 2465–2478 (1998)
Ritz, J.P., Roggan, A., Isbert, C., Muller, G., Buhr, H.J., Germer, C.T.: Optical properties of native and coagulated porcine liver tissue between 400 and 2400 nm. Lasers Surg. Med. 29(3), 205–212 (2001)
Salomatina, E., Jiang, B., Novak, J., Yaroslavsky, A.N.: Optical properties of normal and cancerous human skin in the visible and near-infrared spectral range. J. Biomed. Opt. 11(6), 064026 (2006)
Friebel, M., Roggan, A., Muller, G.J., Meinke, M.C.: Determination of optical properties of human blood in the spectral range 250 to 1100 nm using Monte Carlo simulations with hematocrit-dependent effective scattering phase functions. J. Biomed. Opt. 11(3), 034021 (2006)
Terada, T., Nanjo, T., Honda, N., Ishii, K., Awazu, K.: Error analysis of tissue optical properties determined by double-integrating sphere system and inverse Monte Carlo method. In: Proceedings of SPIE, vol 7897, 78971W (2011)
Horibe, T., Ishii, K., Honda, N., Awazu, K.: Improvement of scattering coefficient estimation in inverse Monte Carlo calculation by considering wavelength dependence of refractive index and sample thickness. In: Proceedings of CLSM 2013, pp. 2–11 (2013)
Fukutomi, D., Ishii, K., Awazu, K.: Highly accurate scattering spectra of strongly absorbing samples obtained using an integrating sphere system by considering the angular distribution of diffusely reflected light. Lasers Med. Sci. 30(4), 1335–1340 (2015)
Hall, G., Jacques, S.L., Eliceiri, K.W., Campagnola, P.J.: Goniometric measurements of thick tissue using Monte Carlo simulations to obtain the single scattering anisotropy coefficient. Biomed. Opt. Express 3(11), 2707–2719 (2012)
Fernandez-Oliveras, A., Rubino, M., Perez, M.M.: Scattering anisotropy measurements in dental tissues and biomaterials. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid. Publ. 7, 12016 (2012)
Sardar, D.K., Mayo, M.L., Glickman, R.D.: Optical characterization of melanin. J. Biomed. Opt. 6(4), 404–411 (2001)
Forster, F.K., Kienle, A., Michels, R., Hibst, R.: Phase function measurements on nonspherical scatterers using a two-axis goniometer. J. Biomed. Opt. 11(2), 024018 (2006)
Saccomandi, P., Vogel, V., Bazrafshan, B., Maurer, J., Schena, E., Vogl, T.J., Silvestri, S., Mantele, W.: Estimation of anisotropy coefficient of swine pancreas, liver and muscle at 1064 nm based on goniometric technique. J. Biophotonics 8(5), 422–428 (2014)
Kodach, V.M., Faber, D.J., van Marle, J., van Leeuwen, T.G., Kalkman, J.: Determination of the scattering anisotropy with optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express 19(7), 6131–6140 (2011)
Kienle, A., Patterson, M.S., Ott, L., Steiner, R.: Determination of the scattering coefficient and the anisotropy factor from laser Doppler spectra of liquids including blood. Appl. Opt. 35(19), 3404–3412 (1996)
Wang, P., Li, Y., Chen, B.: Measurement of the anisotropy factor with azimuthal light backscattering. Optoelectron. Lett. 10(6), 470–472 (2014)
Zamora-Rojasa, E., Aernoutsb, B., Garrido-Varoa, A., Perez-Marina, D., Guerrero-Ginela, J.E., Saeysb, W.: Double integrating sphere measurements for estimating optical properties of pig subcutaneous adipose tissue. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 19, 218–226 (2013)
Tuchin, V.V.: Tissue Optics, 2nd edn, pp. 132–142. SPIE, Washington (2007)
Wang, L., Jacques, S.L., Zheng, L.: MCML-Monte Carlo modeling of light transport in multi-layered tissues. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 47(2), 131–146 (1995)
Oregon Medical Laser Center at Providence St. Vincent Medical Center, http://omlc.ogi.edu/software/mc/
Wen, X., Tuchin, V.V., Luo, Q., Zhu, D.: Controling the scattering of Intralipid by using optical clearing agents. Phys. Med. Biol. 54(22), 6917–6930 (2009)
Staveren, H.J., Moes, C.J.M., Marie, J., Prahl, S.A., Gemert, M.J.C.: Light scattering in lntralipid-10% in the wavelength range of 400–1100 nm. Appl. Opt. 30(31), 4507–4514 (1991)
Saidi, I.S., Jacques, S.L., Tittel, F.K.: Mie and Rayleigh modeling of visible-light scattering in neonatal skin. Appl. Opt. 34(31), 7410–7418 (1995)
Bashkatov, A.N., Genina, E.A., Kochubey, V.I., Tuchin, V.V.: Optical properties of human skin, subcutaneous and mucous tissues in the wavelength range from 400 to 2000 nm. J. Phys. D 38(15), 2543–2555 (2005)
Flock, S.T., Wilson, B.C., Patterson, M.S.: Total attenuation coefficients and scattering phase functions of tissues and phantom materials at 633 nm. J. Med. Phys. 14(5), 835–841 (1987)
Henyey, L.G., Greenstein, J.L.: Diffuse radiation in galaxy. Astrophys. J. 93, 70–83 (1941)
Tuchin, V.V.: Tissue Optics, 2nd edn, pp. 3–22. SPIE, Washington (2007)
Mourant, J.R., Boyer, J., Hielscher, A.H., Bigio, I.J.: Influence of the scattering phase function on light transport measurements in turbid media performed with small source–detector separations. Opt. Lett. 21(7), 546–548 (1996)
Yaroslavsky, A.N., Yaroslavsky, I.V., Goldbach, T., Schwarzmaier, H.-J.: Influence of the scattering phase function approximation on the optical properties of blood determined from the integrating sphere measurements. J. Biomed. Opt. 4(1), 47–53 (1999)
Kienle, A., Forster, F.K., Hibst, R.: Influence of the phase function on determination of the optical properties of biological tissue by spatially resolved reflectance. Opt. Lett. 26(20), 1571–1573 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukutomi, D., Ishii, K. & Awazu, K. Determination of the scattering coefficient of biological tissue considering the wavelength and absorption dependence of the anisotropy factor. Opt Rev 23, 291–298 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-015-0161-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-015-0161-y