Abstract
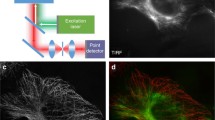
In stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy, the lateral resolution is in the range of tens of nanometers depending on the sample and the instrument. The axial resolution, however, is in standard systems limited by diffraction to about 500 nm. We present an approach to three-dimensional diffraction-unlimited resolution by observing the sample at two optical angles. The system is realized by using an atomic force microscope (AFM) chip as a microreflector to deflect the STED beams near the region-of-interest (ROI), thus allowing observations at an angle ∠. Consequently, the superior lateral resolution can be utilized to resolve details in the axial direction of the main optical axis of the microscope. Here, fluorescent nanoparticles 90 nm apart and biological structures 80 nm apart along axial direction were distinguished by utilizing an off-the-shelf, commercial STED microscope, coupled with an AFM and an AFM chip micro-reflector.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. W. Hell and J. Wichmann: Opt. Lett. 19 (1994) 780.
E. Betzig, G. H. Patterson, R. Sougrat, O. W. Lindwasser, S. Olenych, J. S. Bonifacino, M. W. Davidson, J. Lippincott-Schwartz, and H. F. Hess: Science 313 (2006) 1642.
M. J. Rust, M. Bates, and X. Zhuang: Nat. Methods 3 (2006) 793.
M. G. L. Gustafsson: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 (2005) 13081.
E. Rittweger, K. Y. Han, S. E. Irvine, C. Eggeling, and S. W. Hell: Nat. Photonics 3 (2009) 144.
V. Westphal, S. O. Rizzoli, M. A. Lauterbach, D. Kamin, R. Jahn, and S. W. Hell: Science 320 (2008) 246.
S. Hell and E. H. K. Stelzer: J. Opt. Soc. Am. 9 (1992) 2159.
P. E. Hänninen, S. W. Hell, J. Salo, E. Soini, and C. Cremer: Appl. Phys. Lett. 66 (1995) 1698.
A. H. Voie, D. H. Burns, and F. A. Spelman: J. Microsc. 170 (1993) 229.
J. Huisken, J. Swoger, F. Del Bene, J. Wittbrodt, and E. H. K. Stelzer: Science 305 (2004) 1007.
J. C. M. Gebhardt, D. M. Suter, R. Roy, Z. W. Zhao, A. R. Chapman, S. Basu, T. Maniatis, and X. S. Xie: Nat. Methods 10 (2013) 421.
E. H. K. Stelzer and S. Lindek: Opt. Commun. 111 (1994) 536.
S. Lindek, T. Stefany, and E. H. K. Stelzer: J. Microsc. 188 (1997) 280.
P. J. Shaw, D. A. Agard, Y. Hiraoka, and J. W. Sedat: Biophys. J. 55 (1989) 101.
R. Heintzmann and C. Cremer: J. Microsc. 206 (2002) 7.
Y. Yu, A. Trouvé, B. Chalmond, O. Renaud, and S. L. Shorte: J. Microsc. 242 (2011) 70.
R. J. Skaer and S. Whytock: J. Cell Sci. 19 (1975) 1.
R. Schmidt, C. A. Wurm, S. Jakobs, J. Engelhardt, A. Egner, and S. W. Hell: Nat. Methods 5 (2008) 539.
T. A. Klar, S. Jakobs, M. Dyba, A. Egner, and S. W. Hell: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (2000) 8206.
D. Wildanger, R. Medda, L. Kastrup, and S. W. Hell: J. Microsc. 236 (2009) 35.
K. I. Willig, B. Harke, R. Medda, and S. W. Hell: Nat. Methods 4 (2007) 915.
T. Staudt, M. C. Lang, R. Medda, J. Engelhardt, and S. W. Hell: Microsc. Res. Tech. 70 (2007) 1.
E. H. W. Meijering, W. J. Niessen, and M. A. Viergever: Med. Image Anal. 5 (2001) 111.
B. Schmid, J. Schindelin, A. Cardona, M. Longair, and M. Heisenberg: BMC Bioinformatics 11 (2010) 274.
C. Vonesch and M. Unser: IEEE Trans. Image Process. 17 (2008) 539.
K. I. Willig, J. Keller, M. Bossi, and S. W. Hell: New J. Phys. 8 (2006) 106.
T. Corle and G. Kino: Confocal Scanning Optical Microscopy and Related Imaging Systems (Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deguchi, T., Koho, S., Näreoja, T. et al. Axial super-resolution by mirror-reflected stimulated emission depletion microscopy. OPT REV 21, 389–394 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-014-0060-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-014-0060-7