Abstract
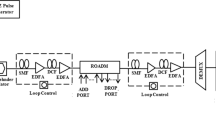
This paper presents design of an electro-optically tunable polymer multi-channel wavelength add drop multiplexer (WADM). The proposed WADM with trapezoidal waveguide geometry and poled electro-optical polymer material in the waveguide cores enables the wavelength tuning speed of WADM as 7.5 ps at the resonance wavelength of 1550 nm and coupling length of 1.5 mm. The device can be electro-optically tuned to add/drop multiple channels. Transmission spectra of the device with varying device parameters are simulated. The proposed WADM with high speed, small size and varying tuning capability makes this device, an important element in faster provisioning and routing of light paths in intelligent optical network.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Zang, P. Jason, L. Sahasrabuddhe, R. Ramamurthy, and B. Mukherjee: IEEE Commun. Mag. 39 (2001) 100.
D. Benjamin, R. Trudel, and S. Shew: IEEE Commun. Mag. 39 (2001) 73.
S. De Maesschalck: IEEE Commun. Mag. 40 (2002) 42.
F. Bilodeau, D. C. Johnson, S. Theriault, B. Malo, J. Albert, and K. O. Hill: IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 7 (1995) 388.
L. Dong, P. Hua, T. A. Birks, L. Reekie, and P. St. J. Russell: IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 8 (1996) 656.
A. S. Kewitsch, G. A. Rakuljic, P. A. Willems, and A. Yariv: Opt. Lett. 23 (1998) 106.
A. V. Tran, W. D. Zhong, R. S. Tucker, and K. Song: IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 13 (2001) 1100.
P. Tang, O. Eknoyan, and H. F. Taylor: J. Lightwave Technol. 21 (2003) 236.
Y. Yamamoto, T. Kamiya, and H. Yanai: IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 14 (1978) 620.
Y. Bai and K. S. Chiang: J. Lightwave Technol. 23 (2005) 4363.
Q. Liu, K. S. Chiang, and V. Rastogi: J. Lightwave Technol. 21 (2003) 3399.
S. Nishimura, H. Inoue, H. Sano, and K. Ishida: IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 4 (1992) 1123.
M. Oh, H. Zhang, H. Erlig, Y. Chang, B. Tsap, D. Chang, A. Szep, W. H. Steier, H. R. Fetterman, and L. R. Dalton: IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 7 (2001) 826.
W. Yuan, S. Kim, W. H. Steier, and H. R. Fetterman: IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 17 (2005) 2568.
T. W. Ang, G. T. Reed, A. Vonsovici, A. G. R. Evans, P. R. Routley, and M. R. Josey: IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 12 (2000) 59.
S. Zhang and T. Tamir: IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 29 (1993) 2813.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponmalar, S., Sundaravadivelu, S. Analysis of reconfigurable multi-channel wavelength add drop multiplexer for intelligent optical networks. OPT REV 18, 305–310 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-011-0060-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-011-0060-9