Abstract
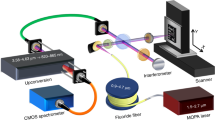
We recently proposed and developed a novel transillumination laser computed tomography (CT) imaging system using a fiber-optic method based on coherent detection imaging (CDI) for biomedical use. Use of optical fibers enables portability and robustness against environmental changes in a room, such as variable temperature, air-flow shifts, and unexpected vibrations. In addition, motion-artifact-free images can be obtained because measurements can be performed with the object fixed. In the present paper, we experimentally investigate in detail the fundamental imaging properties of the system, which has a spatial resolution of 500 μm, a dynamic range of approximately 120 dB, and a minimum-detectable-optical power of 10−14W as a result of the excellent properties of the heterodyne detection. Based on experimental observations, the proposed system can reconstruct tomographic images of highly scattering objects in the transillumination mode, similar to X-ray CT, at sub-millimeter spatial resolution and with quantitativeness. Finally, we demonstrate with experiments using a physical phantom that the imaging system possesses high resolution and quantitative imaging abilities for highly scattering objects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Müller, B. Chance, R. R. Alfano, S. Arridge, J. Beuthan, E. Gratton, M. Kaschke, B. Masters, S. Svanberg and P. van der Zee, eds.: Medical Optical Tomography: Functional Imaging and Monitoring (SPIE Opt. Eng. Press, Bellingham, 1993) Vol. IS11.
R. R. Alfano ed.: OSA Proceedings on Advances in Optical Imaging and Photon Migration (Opt. Soc. Am., Washington DC, 1994) Vol. 21.
J. G. Fujimoto and M. S. Patterson eds.: OSA Trends in Optical and Photonics on Advances in Optical Imaging and Photon Migration (Opt. Soc. Am., Washington DC, 1998) Vol. 21.
Y. Xu, N. Iftimia, H. Jiang, L. L. Key and M. B. Bolster: J. Biomed. Opt. 7 (2002) 88.
S. A. Colak, D. G. Papaioannou, G. W. ‘t Hooft, M. B. van der Mark, H. Schomberg, J. C. J. Paasschens, J. B. M. Melissen and N. A. A. J. van Asten: Appl. Opt. 36 (1997) 180.
S. R. Arridge and M. Schweiger: Opt. Express 2 (1997) 213.
V. Tuchin: Tissue Optics: Light Scattering Methods and Instruments for Medical Diagnosis (SPIE Opt. Eng. Press, Bellingham, 2000) Vol. TT38.
Handbook of Optical Coherence Tomography, eds. B. E. Bouma and G. J. Tearney (Marcel Dekker, New York, 2002).
e.g., A. Yariv: Introduction to Optical Electronics (Holt, Rinehart and Winston, New York, 1985) 3rd ed., Chap. 11.
J. J. Snyder: Appl. Opt. 27 (1988) 4465.
A. E. Siegman: Appl. Opt. 5 (1966) 1558.
H. Inaba: Medical Optical Tomography: Functional Imaging and Monitoring, eds. G. Müller, B. Chance, R. R. Alfano, S. Arridge, J. Beuthan, E. Gratton, M. Kaschke, B. Masters, S. Svanberg and P. van der Zee (SPIE Opt. Eng. Press, Bellingham, 1993) Part IV-4, p. 317.
B. Devaraj, M. Usa, K. P. Chan, T. Akatsuka and H. Inaba: IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2 (1996) 1008.
B. Devaraj, Y. Watanabe, M. Takeda, M. Usa, T. Yuasa, T. Akatsuka and H. Inaba: OSA Trends in Optics and Photonics on Advances in Optical Imaging and Photon Migration, eds. J. G. Fujimoto and M. S. Patterson (Opt. Soc. Am., Washington DC, 1998) Vol. 21, p. 338.
B. Devaraj, M. Takeda, M. Kobayashi, M. Usa, K. P. Chan, Y. Watanabe, T. Yuasa, T. Akatsuka, M. Yamada and H. Inaba: Appl. Phys. Lett. 69 (1996) 3671.
C. Kak and M. Slanery: Principles of Computerized Tomographic Imaging (IEEE Press, New York, 1987).
Y. Sasaki, S. Tanosaki, J. Suzuki, T. Yuasa, M. Takagi, H. Taniguchi, B. Devaraj and T. Akatsuka: Proc. The First IEEE Int. Conf. Sensors, Orlando, Florida, 2002, p. 156.
Y. Sasaki, J. Suzuki, S. Tanosaki, T. Yuasa, M. Takagi, A. Ishikawa, H. Taniguchi, B. Devaraj and T. Akatsuka: Proc: Asian Symposium on Biomedical Optics and Photomedicine (Biomed. Opt. Group in Opt. Soc. Jpn., Sapporo, 2002) p. 270.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasaki, Y., Suzuki, J., Inage, H. et al. Transillumination Laser Computed Tomography System with Fiber-Optic-Based Coherent Detection Imaging Method - High Spatial-Resolution and Quantitative Tomographic Imaging of Highly Scattering Objects -. OPT REV 10, 462–465 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-003-0462-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-003-0462-4