Abstract
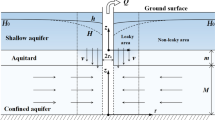
Non-Darcian flow to a partially penetrating well in a confined aquifer with a finite-thickness skin was investigated. The Izbash equation is used to describe the non-Darcian flow in the horizontal direction, and the vertical flow is described as Darcian. The solution for the newly developed non-Darcian flow model can be obtained by applying the linearization procedure in conjunction with the Laplace transform and the finite Fourier cosine transform. The flow model combines the effects of the non-Darcian flow, partial penetration of the well, and the finite thickness of the well skin. The results show that the depression cone spread is larger for the Darcian flow than for the non-Darcian flow. The drawdowns within the skin zone for a fully penetrating well are smaller than those for the partially penetrating well. The skin type and skin thickness have great impact on the drawdown in the skin zone, while they have little influence on drawdown in the formation zone. The sensitivity analysis indicates that the drawdown in the formation zone is sensitive to the power index (n), the length of well screen (w), the apparent radial hydraulic conductivity of the formation zone (K r2), and the specific storage of the formation zone (S s2) at early times, and it is very sensitive to the parameters n, w and K r2 at late times, especially to n, while it is not sensitive to the skin thickness (r s).
Résumé
L’écoulement non-darcéen vers un puits pénétrant partiellement un aquifère captif, avec un effet de peau d’épaisseur finie, a été étudié. L’équation d’Izbash est utilisée pour décrire l’écoulement non-darcéen dans la direction horizontale, et l’écoulement vertical est décrit comme darcéen. La solution pour le modèle d’écoulement non-darcéen nouvellement développé peut être obtenue en appliquant la procédure de linéarisation, conjointement avec la transformée de Laplace et la transformée finie de cosinus de Fourier.Le modèle d’écoulement combine les effets de l’écoulement non-darcéen, de la pénétration partielle du puits et de l’épaisseur finie de l’effet de peau du puits. Les résultats montrent que l’extension du cône de dépression est plus grande pour l’écoulement darcéen que pour l’écoulement non darcéen. Les rabattements dans la zone d’effet de peau pour un puits complet sont plus faibles que ceux pour le puits en pénétration partielle. Le type et l’épaisseur de l’effet de peau ont un fort impact sur le rabattement dans la zone d’effet de peau, alors qu’ils ont une faible influence sur le rabattement dans la formation aquifère. L’analyse de sensibilité indique que le rabattement dans la formation aquifère est sensible, au coefficient de puissance (n), à la longueur crépinée du puits (w), à la conductivité hydraulique radiale apparente de la formation aquifère (K r2) et au coefficient d’emmagasinement spécifique de la formation aquifère (S s2) aux premiers instants, et est très sensible aux paramètres n, w and K r2 aux temps longs, tout particulièrement à n, tandis qu’il n’est pas sensible à l’épaisseur de l’effet de peau (r s).
Resumen
Se investigó el flujo no Darciano en un pozo parcialmente penetrante en un acuífero confinado con una película de espesor finito. La ecuación de Izbash se utiliza para describir el flujo no Darciano en la dirección horizontal y el flujo vertical se describe como Darciano. La solución para el modelo de flujo no Darciano, recientemente desarrollada, se puede obtener mediante la aplicación del procedimiento de linealización en conjunción con la transformada de Laplace y la transformada finita de coseno de Fourier. El modelo de flujo combina los efectos del flujo no Darciano, penetración parcial del pozo, y también el espesor finito de la película. Los resultados muestran que la propagación del cono de depresión es más grande para el flujo Darciano que para el flujo no Darciano. Las depresiones dentro de la zona de la película para un pozo totalmente penetrante son más pequeñas que aquellas en un pozo parcialmente penetrante. El tipo y espesor de la película tienen un gran impacto en la depresión de la zona de la película, mientras que tienen poca influencia en la depresión en la zona de la formación. El análisis de sensibilidad indica que la depresión en la zona de la formación es sensible al índice de potencia (n), la longitud del filtro del pozo (w), la conductividad hidráulica radial aparente de la zona de formación (K r2), y el almacenamiento específico de la zona de la formación (S s2) en los primeros tiempos, y es muy sensible a los parámetros n, w y K r2 en los últimos tiempos, especialmente a n, mientras que no es sensible al espesor de la película (r s).
摘要
在考虑井周有限表皮效应下,研究了承压含水层中非完整井附近非达西渗流问题,采用非达西Izbash定律描述含水层中的径向渗流,同时用达西定律描述流速较小的垂向渗流。利用线性化方法并结合Laplace变换和有限余弦Fourier变换得到该非达西问题的解,该解可同时用来调查非达西作用、井的完整性和有限表皮效应对水位降深的影响。结果表明:达西渗流情况下引起的降落漏斗范围要比非达西情况下要大;完整井抽水情况下的有限厚度表皮层的水位降深要比非完整井抽水引起的降深要小;表皮的类型和厚度对表皮层的水头降深影响较大,而对含水层的降深影响较小。此外,敏感性分析表明,在抽水初期,含水层的水位降深受Izbash定律中的n、滤水管长度w、含水层等效渗透系数K r2和单位储水系数S s2影响明显;在抽水后期,水位降深受n, w 和 K r2影响大,其中尤以受n的影响最大;然而表皮层厚度对含水层水位降深基本没有影响。
Resumo
Fluxo não Darciano foi investigado em um poço parcialmente penetrante com uma película de espessura limitada em aquífero confinado. A equação Izbash é utilizada para descrever o fluxo não Darciano na direção horizontal, e o fluxo vertical é descrito como Darciano. A solução para o modelo de fluxo não Darciano recentemente desenvolvido pode ser obtida mediante a aplicação do processo de linearização em conjunto com a transformada de Laplace e a transformada de Fourier de cosseno finita. O modelo de fluxo combina os efeitos do fluxo não Darciano, em poço parcialmente penetrante, e da película de espessura limitada. Os resultados mostram que a propagação do cone de rebaixamento é maior para o fluxo Darciano do que para o fluxo não Darciano. Os rebaixamentos dentro da zona da película para um poço completamente penetrante são menores do que aqueles para o poço parcialmente penetrante. O tipo de película e espessura da película têm um grande impacto sobre o rebaixamento na zona de película, enquanto eles têm pouca influência sobre o rebaixamento na zona de formação. A análise de sensibilidade indica que o rebaixamento na zona da formação é sensível ao índice de porosidade (n), o comprimento do filtro do poço (w), a condutividade hidráulica radial aparente da zona de formação (K r2), e ao armazenamento específico da zona de formação (S s2) nos tempos iniciais, e é muito sensível aos parâmetros n, w e K r2 em tempos tardios, especialmente a n, enquanto que não é sensível à espessura da película (r s).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bear J (2007) Hydraulics of groundwater. McGraw-Hill, Dover, New York
Bordier C, Zimmer D (2000) Drainage equations and non-Darcian modelling in coarse porous media or geosynthetic materials. J Hydrol 228(3):174–187. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(00)00151-7
Chang CC, Chen CS (2002) An integral transform approach for a mixed boundary problem involving a flowing partially penetrating well with infinitesimal well skin. Water Resour Res 38(6). DOI: 10.1029/2001WR001091
Chen C, Wan J, Zhan H (2003) Theoretical and experimental studies of coupled seepage-pipe flow to a horizontal well. J Hydrol 281:159–171
Chen YF, Hu SH, Hu R, Zhou CB (2015) Estimating hydraulic conductivity of fractured rocks from high-pressure packer tests with an Izbash’s law-based empirical model. Water Resour Res 51:2096–2118. doi:10.1002/2014WR016458
Chiu PY, Yeh HD, Yang SY (2007) A new solution for a partially penetrating constant-rate pumping well with a finite-thickness skin. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 31(15):1659–1674
Feng Q, Zhan H (2015) On the aquitard–aquifer interface flow and the drawdown sensitivity with a partially penetrating pumping well in an anisotropic leaky confined aquifer. J Hydrol 521:74–83
Forchheimer PH (1901) Wasserbewegung durch Boden [Movement of water through soil]. Zeitschr Ver Deutsch Ing 49:1736–1749, and 50:1781–1788
Houben GJ (2015a) Review: Hydraulics of water wells—flow laws and influence of geometry. Hydrogeol J. doi:10.1007/s10040-015-1312-8
Houben GJ (2015b) Review: Hydraulics of water wells—head losses of individual components. Hydrogeol J. doi:10.1007/s10040-015-1313-7
Huang YC, Yeh HD (2007) The use of sensitivity analysis in on-line aquifer parameter estimation. J Hydrol 335(3–4):406–418
Izbash SV (1931) O filtracii v kropnozernstom materiale [Groundwater flow in the material kropnozernstom]. Izv. Nauchnoissled, Inst. Gidrotechniki (NIIG), Leningrad
Malama B, Kuhlman KL, Barrash W (2008) Semi-analytical solution for flow in a leaky unconfined aquifer toward a partially penetrating pumping well. J Hydrol 356(1–2):234–244
Mathias SA, Butler AP, Zhan H (2008) Approximate solutions for Forchheimer flow to a well. J Hydraul Eng 134:1318–1325
Moutsopoulos KN, Tsihrintzis VA (2005) Approximate analytical solutions of the Forchheimer equation. J Hydrol 309:93–103
Moutsopoulos KN, Papaspyros NE, Tsihrintzis VA (2009) Experimental investigation of inertial flow processes in porous media. J Hydrol 374(3–4):242–254
Novakowski KS (1989) A composite analytical model for analysis of pumping tests affected by well bore storage and finite thickness skin. Water Resour Res 25(9):1937–1946
Park E, Zhan H (2002) Hydraulics of a finite-diameter horizontal well with wellbore storage and skin effect. Adv Water Resour 25(4):389–400
Pasandi M, Samani N, Barry DA (2008) Effect of wellbore storage and finite thickness skin on flow to a partially penetrating well in a phreatic aquifer. Adv Water Resour 31(2):383–398
Perina T, Lee TC (2006) General well function for pumping from a confined, leaky, or unconfined aquifer. J Hydrol 317(3–4):239–260
Sedghi-Asl M, Rahimi H, Salehi R (2014) Non-Darcy flow of water through a packed column test. Transp Porous Media 101(2):215–227
Sen Z (1989) Nonlinear flow toward wells. J Hydraul Eng 115(2):193–209
Sen Z (1990) Non-linear radial flow in confined aquifers toward large-diameter wells. Water Resour Res 26(5):1103–1109
Sen Z (2000) Non-Darcian groundwater flow in leaky aquifers. Hydrol Sci J 45(4):595–606
Stehfest H (1970a) Algorithm 368 numerical inversion of Laplace transforms. Commun ACM 13(1):47–49
Stehfest H (1970b) Remark on algorithm 368: numerical inversion of Laplace transforms. Commun ACM 13(10):624–625
Wen Z, Wang Q (2013) Approximate analytical and numerical solutions for radial non-Darcian flow to a well in a leaky aquifer with wellbore storage and skin effect. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 37:1453–1469
Wen Z, Huang G, Zhan H (2008a) An analytical solution for non-Darcian flow in a confined aquifer using the power law function. Adv Water Resour 31(1):44–55
Wen Z, Huang G, Zhan H (2008b) Non-Darcian flow to a well in an aquifer–aquitard system. Adv Water Resour 31(12):1754–1763
Wen Z, Huang G, Zhan H (2009) A numerical solution for non-Darcian flow to a well in a confined aquifer using the power law function. J Hydrol 364:99–106
Wen Z, Huang G, Zhan H (2011) Non-Darcian flow to a well in leaky aquifers using the Forchheimer equation. Hydrogeol J 19:563–572
Wen Z, Liu K, Chen X (2013) Approximate analytical solutions for non-Darcian flow toward a partially penetrating well in a confined aquifer. J Hydrol 498:124–131
Wen Z, Liu K, Zhan H (2014) Non-Darcian flow toward a larger-diameter partially penetrating well in a confined aquifer. Environ Earth Sci 72:4617–4625
Yang SY, Yeh HD (2007) On the solutions of modeling a slug test performed in a two-zone confined aquifer. Hydrogeol J 15:297–305
Yang SY, Yeh HD, Chiu PY (2006) A closed form solution for constant flux pumping in a well under partial penetration condition. Water Resour Res 42(5). doi:10.1029/2004WR003889
Yang SY, Huang CS, Liu CH, Yeh HD (2014) Approximate solution for a transient hydraulic head distribution induced by a constant-head test at a partially penetrating well in a two-zone confined aquifer. J Hydraul Eng 140. doi:10.1061/(ASCEHY.1943-7900.0000884)
Yeh HD, Chang YC (2013) Recent advances in modeling of well hydraulics. Adv Water Resour 51:27–51
Yeh HD, Yang SY (2006) A novel analytical solution for a slug test conducted in a well with a finite-thickness skin. Adv Water Resour 29:1479–1489
Yeh HD, Yang SY, Peng HY (2003) A new closed-form solution for a radial two-layer drawdown equation for groundwater under constant-flux pumping in a finite-radius well. Adv Water Resour 26(7):747–757
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers: 41372253, 41521001), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) (Grant Number: CUG140503). We also would like to thank the editor (Prof. Maria-Theresia Schafmeister), the associate editor (Dr. Georg J. Houben), the technical editorial advisor (Mrs. Sue Duncan) and two anonymous reviewers for providing valuable comments and suggestions in improving this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Q., Wen, Z. Non-Darcian flow to a partially penetrating well in a confined aquifer with a finite-thickness skin. Hydrogeol J 24, 1287–1296 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-016-1389-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-016-1389-8