Abstract
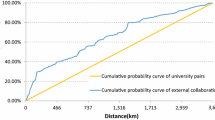
Scientific research has increasingly been becoming a group effort, which has been the main driving force in the growth of scientific productivity. While there have been multiple contributions toward intercity and interregional interactions in the analysis of these collaborations, intracity studies have been lagging. This study addresses this gap with the example of Istanbul, Turkey. Turkey has implemented a radical expansion policy in the spatial organization of universities after 2006 during which Istanbul has further strengthened its role as a science hub for the country. However, despite the increase in the number of universities and their personnel, the role of their collaborations in knowledge production has not been studied. In this setting, the study uses a gravity model for the measurement of Istanbul’s intracity collaborations in six research fields. The study measures intracity coauthorship chances by spatial proximity, domestic coauthorships, international coauthorships, institutional distance based on public-private university coauthorships and the difference between founding years. The results show that spatial proximity within the city is mostly relevant for soft science fields such as humanities and social sciences. In comparison, intracity coauthorships in hard science fields grow with domestic coauthorships beyond Istanbul. Additionally, coauthorships between public and private universities did not have a positive association with higher coauthorship chances while differences in founding years did not prevent the growth of coauthorships despite organisational differences between new and old universities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akçiğit U, Özcan-Tok E (2020) Türkiye Bilim Raporu. Türkiye Bilimler Akademisi Yayınları, TÜBA Raporları, vol 43. Berk Grup Matbaacılık, Ankara (Report on Turkish science, https://www.tuba.gov.tr/files/yayinlar/raporlar/Tu%CC%88rkiye%20Bilim%20Raporu.pdf)
Alpkokin P, Kiremitci ST, Black JA, Cetinavci S (2016) LRT and street tram policies and implementation in Turkish cities. J Transp Geogr 54:476–487
Benneworth P, Charles D, Madanipour A (2010) Building localized interactions between universities and cities through university spatial development. Eur Plan Stud 18(10):1611–1629. https://doi.org/10.1080/09654313.2010.504345
Boschma R (2005) Proximity and innovation: a critical assessment. Reg Stud 39(1):61–74. https://doi.org/10.1080/0034340052000320887
Boucher G, Conway C, Van Der Meer E (2003) Tiers of engagement by universities in their region’s development. Reg Stud 37(9):887–897. https://doi.org/10.1080/0034340032000143896
Csomós G (2020) On the challenges ahead of spatial scientometrics focusing on the city level. Aslib J Inf Manag 72(1):67–87. https://doi.org/10.1108/AJIM-06-2019-0152
Dai L, Derudder B, Cao Z, Ji Y (2022) Examining the evolving structures of intercity knowledge networks: the case of scientific collaboration in China. Int J Urban Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/12265934.2022.2042365
Elsevier (2019) Research metrics guidebook (https://www.elsevier.com/research-intelligence/resource-library/research-metrics-guidebook)
Frenken K, Hardeman S, Hoekman J (2009) Spatial scientometrics: towards a cumulative research program. J Informetr 3(3):222–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2009.03.005
Gieryn TF (2006) City as truth-spot: laboratories and field-sites in urban studies. Soc Stud Sci 36(1):5–38. https://doi.org/10.1177/0306312705054526
Gossart C, Özman M (2009) Co-authorship networks in social sciences: the case of Turkey. Scientometrics 78(2):323–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-007-1963-x
Grossetti M, Eckert D, Maisonobe M, Tallec J (2016) Four commonly held beliefs about the geography of scientific activities. In: Shearmur R, Carrincazeaux C, Doloreux D (eds) Handbook on the geographies of innovation. Edward Elgar, pp 223–240 https://doi.org/10.4337/9781784710774.00026
Grossetti M, Maisonobe M, Jégou L, Milard B, Cabanac G (2020) Spatial organisation of French research from the scholarly publication standpoint (1999–2017): long-standing dynamics and policy-induced disorder. EPJ Web Conf 244:1005. https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/202024401005
Henkel M (2000) Academic identity and policy change. Jessica Kingsley, London
Hočevar M, Bartol T (2021) Cities as places and topics of studies: mapping research clusters across disciplines. Urbani Izziv 32(1):123–137 (https://www.jstor.org/stable/27043406)
Hoekman J, Frenken K, Tijssen RJ (2010) Research collaboration at a distance: changing spatial patterns of scientific collaboration within Europe. Res Policy 39(5):662–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2010.01.012
Hornyak T, Casassus B (2016) Old bonds and elemental connections. Nature 539(7629):S14–S19. https://doi.org/10.1038/539S14a
Karataş Acer E, Güçlü N (2017) An analysis of the expansion of higher education in Turkey using the new institutional theory. Educ Sci Theory Pract 17(6):1911–1933. https://doi.org/10.12738/estp.2017.6.0031
Kepenek Y (2016) Türkiye’nin 1980 Öncesi Bilim ve Teknoloji Politikaları. In: Akçomak İS, Erdil E, Tiryakioğlu M, Pamukçu MT (eds) Bilim Teknoloji ve Yenilik: Kavramlar Kuramlar ve Politika. Bilgi Üniversitesi Yayınları, (Science and technology policies of Turkey before 1980)
Kocatürk HE, Karadağ E (2021) Organizational functioning in Turkish higher education system: Birnbaum’s five models of institutional governance. J Pedagog Res 5(4):230–250. https://doi.org/10.33902/JPR.2021474637
Liefner I, Hennemann S (2011) Structural holes and new dimensions of distance: the spatial configuration of the scientific knowledge network of China’s optical technology sector. Environ Plan A 43(4):810–829. https://doi.org/10.1068/a43100
Ma H, Li Y, Huang X (2021) Proximity and the evolving knowledge polycentricity of megalopolitan science: evidence from China’s Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay area, 1990–2016. Urban Stud 58(12):2405–2423. https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098020942665
Maisonobe M, Eckert D, Grossetti M, Jégou L, Milard B (2016) The world network of scientific collaborations between cities: domestic or international dynamics? J Informetr 10(4):1025–1036
Maisonobe M, Grossetti M, Milard B, Jégou L, Eckert D (2017) The global geography of scientific visibility: a deconcentration process (1999–2011). Scientometrics 113(1):479–493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2463-2
Matthiessen CW, Schwarz AW, Find S (2010) World cities of scientific knowledge: systems, networks and potential dynamics. An analysis based on bibliometric indicators. Urban Stud 47(9):1879–1897. https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098010372683
OECD (2015) Chapter 3, the measurement of scientific, technological and innovation activities. In: Frascati manual 2015: guidelines for collecting and reporting data on research and experimental development. OECD, Paris
Olechnicka A, Ploszaj A, Celińska-Janowicz D (2018) The geography of scientific collaboration, 1st edn. Routledge https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315471938
Rosenberg N, Nelson RR (1994) American universities and technical advance in industry. Res Policy 23(3):323–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-7333(94)90042-6
Scherngell T, Hu Y (2011) Collaborative knowledge production in China: regional evidence from a gravity model approach. Reg Stud 45(6):755–772. https://doi.org/10.1080/00343401003713373
Therrien P (2005) City and innovation: different size, different strategy. Eur Plan Stud 13(6):853–877. https://doi.org/10.1080/09654310500187961
Unutulmaz Gürlek S, Dulupçu MA (2022) Coğrafi ve Sistemik Yakınlık Üniversitelerde Bilimsel İşbirliğinin İtici Faktörleri Midir? Ar-Ge Projeleri ile Ampirik Bir Çalışma. İDEALKENT 14:131–157. https://doi.org/10.31198/idealkent.1127103 (Are geographical and systemic proximity driving factors for scientific collaboration in universities? An empirical study with R&D projects)
Yükseköğretim Kurulu (2021) Vakıf Yükseköğretim Kurumları 2021 (Foundation higher education institutions 2021, https://www.yok.gov.tr/Documents/Yayinlar/Yayinlarimiz/2021/vakif-yuksekogretim-kurumlari-raporu-2021.pdf)
Acknowledgements
This research is part of an on-going doctoral dissertation of the corresponding author Arda Tuncer, supervised by Prof. Dr. Ferhan Gezici (the co-author of the paper)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A. Tuncer and F. Gezici declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tuncer, A., Gezici, F. Scientific collaborations within urban areas: the case of İstanbul. Rev Reg Res (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10037-023-00197-2
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10037-023-00197-2