Abstract
This paper investigates the one-dimensional planar piston problem in dilute granular-gaseous mixture using both analytical and numerical approaches. Starting from the Euler equations of the two-fluid model, a one-way coupling model for dilute granular flow was derived assuming that the piston speed is higher than the sound speed of the granular phase, but much smaller than that of the gaseous phase—which results in a shock wave propagating in the granular phase. It was shown that the dissipation terms of this model—the drag force and inelastic collisions—affect the shock wave structure. A reference analytical solution for fully elastic particles assuming that the linear drag is the only dissipation mechanism predicted a shock wave structure that is similar to ideal molecular gas but decays exponentially with time. The nonlinear drag component resulted in decreasing velocity and density behind the shock while the temperature increases, in an opposite trend to the effect of inelastic collisions. It was shown that the combined effects of both nonlinear drag and inelastic collisions could result in either two regimes depending on the values of their corresponding parameters.
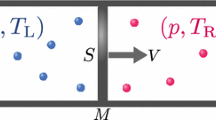
Graphical abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell, C.S.: Rapid granular flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 22(1), 57–90 (1990)
Chou, P.C., Huang, S.L.: Late-stage equivalence in spherical blasts as calculated by the method of characteristics. J. Appl. Phys. 40(2), 752–759 (1969)
Chou, P.C., Karpp, R.R., Huang, S.L.: Numerical calculation of blast waves by the method of characteristics. AIAA J 5(4), 618–623 (1967)
Fouda, Y.M.: Shock-contact-shock solutions of the Riemann problem for dilute granular gas. J. Fluid Mech. 915, A48 (2021)
Gidaspow, D.: Multiphase Flow and Fluidization: Continuum and Kinetic Theory Descriptions. Academic press, Cambridge (1994)
Goldhirsch, I.: Rapid granular flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 35(1), 267–293 (2003)
Goldhirsch, I.: Introduction to granular temperature. Powder Technol. 182(2), 130–136 (2008)
Goldshtein, A., Shapiro, M., Gutfinger, C.: Mechanics of collisional motion of granular materials. Part 3. Self-similar shock wave propagation. J. Fluid Mech. 316, 29–51 (1996)
Higashino, F.: Characteristic method applied to blast waves in a dusty gas. Z. Naturforsch. A 38(4), 399–406 (1983)
Houim, R.W., Oran, E.S.: A multiphase model for compressible granular-gaseous flows: formulation and initial tests. J. Fluid Mech. 789, 166–220 (2016)
Kamenetsky, V., Goldshtein, A., Shapiro, M., Degani, D.: Evolution of a shock wave in a granular gas. Phys. Fluids 12(11), 3036–3049 (2000)
Koch, D.L., Sangani, A.S.: Particle pressure and marginal stability limits for a homogeneous monodisperse gasfluidized bed: kinetic theory and numerical simulations. J. Fluid Mech. 400, 229–263 (1999)
LeVeque, R.J.: Finite Volume Methods for Hyperbolic Problems. Cambridge Texts in Applied Mathematics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2002)
Moretti, G.: Thirty-six years of shock fitting. Comput. Fluids 31(4), 719–723 (2002)
Nakamura, Y.: Analysis of self-similar problems of imploding shock waves by the method of characteristics. Phys. Fluids 26(5), 1234–1239 (1983)
Panicker, N., Passalacqua, A., Fox, R.: On the hyperbolicity of the two-fluid model for gas-liquid bubbly flows. Appl. Math. Model. 57, 432–447 (2018)
Reddy, M.H.L., Alam, M.: Plane shock waves and Haff’s law in a granular gas. J. Fluid Mech. 779, R2 (2015)
Sirmas, N., Radulescu, M.I.: Evolution and stability of shock waves in dissipative gases characterized by activated inelastic collisions. Phys. Rev. E 91(2), 023003 (2015)
Sirmas, N., Radulescu, M.I.: Structure and stability of shock waves in granular gases. J. Fluid Mech. 873, 568–607 (2019)
Toro, E.F.: Riemann Solvers and Numerical Methods for Fluid Dynamics: A Practical Introduction. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Vardy, A.E., Tijsseling, A.S.: Method of characteristics for transient, spherical flows. Appl. Math. Model. 77, 810–828 (2020)
Zeidan, D., Slaouti, A., Romenski, E., Toro, E.F.: Numerical solution for hyperbolic conservative two-phase flow equations. Int. J. Comput. Methods 04(02), 299–333 (2007)
Zeidan, D., Slaouti, A., Touma, R.: Compressible gassolid mixture conservation laws simulations. AIP Conf. Proc. 1479(1), 165–168 (2012)
Zhang, Q., He, F.: The exact Riemann solutions to the generalized pressureless Euler equations with dissipation. Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc. 43, 4361–4374 (2020)
Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y.: The Riemann problem for the Eulerian droplet model with buoyancy and gravity forces. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135(2), 171 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fouda, Y.M. Planar piston motion in dilute granular-gaseous mixture. Granular Matter 23, 85 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-021-01145-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-021-01145-y