Abstract
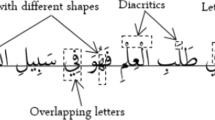
Much work on Arabic language optical character recognition (OCR) has been on Naskh writing style. Nastalique style, used for most of languages using Arabic script across Southern Asia, is much more challenging to process due to its compactness, cursiveness, higher context sensitivity and diagonality. This makes the Nastalique writing more complex with multiple letters horizontally overlapping each other. Due to these reasons, existing methods used for Naskh would not work for Nastalique and therefore most work on Nastalique has used non-segmentation methods. The current paper presents new approach for segmentation-based analysis for Nastalique style. The paper explains the complexity of Nastalique, why Naskh based techniques cannot work for Nastalique, and proposes a segmentation-based method for developing Nastalique OCR, deriving principles and techniques for the pre-processing and recognition. The OCR is developed for Urdu language. The system is optimized using 79,093 instances of 5249 main bodies derived from a corpus of 18 million words, giving recognition accuracy of 97.11 %. The system is then tested on document images of books with 87.44 % main body recognition accuracy. The work is extensible to other languages using Nastalique.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Population collated from http://www.ethnologue.com/region/SAS.
Based on the graphemes used for Nafees Nastalique font for Urdu.
Semi circular stroke having end point traversal path in reverse order of normal writing style.
References
Davis, M., Iancu, L.: Unicode Text Segmentation. Unicode Consortium, Mountain View, USA (2015)
Naseem, T., Hussain, S.: A novel approach for ranking spelling error corrections for Urdu. Language resources and evaluation, Springer 41, (2007)
Akram, M., Hussain, S.: Word Segmentation for Urdu OCR System. In: 8th Workshop on Asian language resources, COLIG 2010. Beijing (2010)
Hussain, S.: In 12th AMIC Annual Conference on E-Worlds: Governments, Business and Civil Society, Asian Media Information Center, Singapore. www.LICT4D.asia/Fonts/Nafees_Nastalique (2003)
Wali, A., Hussain, S.: Context sensitive shape-substitution in nastaliq writing system: analysis and formulation. In: International joint conferences on computer, information, and systems sciences, and engineering (2006)
Hussain, S., Rahman, S., Wali, A., Gulzar, A., Rahman, S.J.: Grammatical analysis of Nastalique writing style of Urdu. Center for Research in Urdu language processing, FAST-nu, Lahore, Pakistan (2002)
Ijaz, M., Hussain, S.: Corpus based Urdu Lexicon development. In Conference on Language Technology, Peshawar (2007)
Shaw, B., Parui, S.K., Shridhar, M.: Offline handwritten Devanagari word recognition: a segmentation based approach. In: 19th international conference on pattern recognition (2008)
Lorigo, L., Govindaraju, V.: Segmentation and pre-recognition of Arabic handwriting. In: Eight international conference on document analysis and recognition (2005)
Cheung, A., Bennamoun, M., Bergmann, N.M.: An Arabic optical character recognition system using recognition-based segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 34(2), 215–233 (2001)
Mehran, R., Pirsiavash, H., Razzazi, F.: A front-end OCR for omni-font Persian/Arabic cursive printed documents. In: Digital image computing on techniques and applications. DC, Washington (2005)
Safabakhsh, R., Abidi, P.: Nastaaligh handwritten word recognition using a continuous-density variable-duration HMM. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 30, 95–118 (2005)
Javed, S.T., Hussain, S.: ”Segmentation Based Urdu Nastalique OCR,” in 18th Iberoamerican Congress on Pattern Recognition, Havana CUBA, (2013)
Muaz, A.: Urdu optical character recognition system. MS Thesis Report, National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore (2010)
Sankaran, N., Jawahar, C.V.: Recognition of printed Devanagari text using BLSTM Neural Network. In: 21st international conference on pattern recognition (2012)
Al-Muhtaseb, H.A., Mahmoud, S.A., Qahwaji, R.S.: Recognition of off-line printed Arabic text using Hidden Markov models. Signal Process. 88(12), 2902–2912 (2008)
AlKhateeb, J.H., Jiang, J., Ren, J., Khelifi, F., Ipson, S.S.: Multiclass classification of unconstrained handwritten arabic words using machine learning approaches. Open Signal Process. J. 2(1), 21–28 (2009)
AlKhateeb, J.H., Ren, J., Jiang, J., Al-Muhtaseb, H.: Offline handwritten Arabic cursive text recognition using Hidden Markov models and re-ranking. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 32(8), 1081–1088 (2011)
Khorsheed, M.S.: Offline recognition of omnifont Arabic text usingthe HMM ToolKit (HTK). Pattern Recognit. Lett. 28(12), 1563–1571 (2007)
Ul-Hasan, A., Ahmed, S.B., Rashid, S.F., Shafait, F., Breuel, T.M.: Offline printed Urdu Nastaleeq script recognition with bidirectional LSTM networks. In: International conference on document analysis and recognition (2013)
Sabbour, N., Shafait, F.: A segmentation free approach to Arabic and Urdu OCR. In: SPIE 8658, (2013)
Javed, S.T., Hussain, S., Maqbool, A., Asloob, S., Jamil, S., Mohsin, H.: Segmentation Free Nastalique Urdu OCR, vol. 46, pp. 456–461. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology (2010)
Shah, Z., Saleem, F.: Ligature based optical character recognition of Urdu, Nastaleeq font. In: International multi topic conference. Karachi (2002)
Lehal, G.S., Rana, A.: Recognition of Nastalique Urdu ligatures. In: 4th International workshop on multilingual OCR. NY, New York (2013)
Sattar, S.A.: A technique for the design and implementation of an OCR for printed Nastalique text. Degree of Doctor of Philosophy Thesis Report. N.E.D University of Engineering and Technology, Karachi (2009)
Satti, D.A.: Offline Urdu Nastaliq OCR for printed text using analytical approach. MS Thesis report, Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad (2013)
Akram, Q., Hussain, S., Niazi, A., Anjum, U., Irfan, F.: Adapting Tesseract for complex scripts: an example for Urdu Nastalique. In: 11th IAPR Workshop on document analysis systems. Tours (2014)
Rashwan, M.A., Fakhr, M.W., Attia, M., El-Mahallawy, M.: Arabic OCR system analogous to HMM-based ASR systems; implementation and evaluation. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. Cairo 54(6), 653–672 (2007)
Naz, M., Akram, Q., Hussain, S.: Binarization and its evaluation for Urdu Nastalique document images. In: Proceedings of the 16th international multi topic conference, Lahore (2013)
Huang, L., Wan, G., Liu, C.: An improved parallel thinning algorithm. In: Seventh international conference on document analysis and recognition (2003)
Jiang, Y., Hongwei, G., Chao, L.: A filtering algorithm for removing salt and pepper noise and preserving details of images. In: 6th international conference on wireless communications networking and mobile computing (2010)
Li, F., Fan, J.: Salt and pepper noise removal by adaptive median filter and minimal surface inpainting. In: 2nd international congress on image and signal processing (2009)
Al-Khaffaf, H.S., Talib, A.Z., Abdul, R.: Salt and pepper noise removal from document images. In: Proceedings of the 1st international visual informatics conference on visual informatics (2009)
Ahmed, N., Natarajan, T., Rao, K.R.: Discrete cosine transform. IEEE Trans. Comput. C–25, 90–93 (1974)
Rabiner, L.R.: Mathematical foundations of hidden Markov models. In: Proceedings of the NATO advanced study institute on recent advances in speech understanding and dialog systems (1988)
Walker, W., Lamere, P., Kwok, P., Raj, B., Singh, R., Gouvea, E., Wolf, P., Woelfel, J.: Sphinx-4: a flexible open source framework for speech recognition. Sun Microsystems Inc, Mountain View, CA (2004)
CLE, Text corpora. In: Center for Language Engineering, 10 December 2014. http://www.cle.org.pk/clestore/index.htm (2014). Accessed 11 May 2015
Urooj, S., Hussain, S., Adeeba, F., Jabeen, F., Parveen, R.: CLE Urdu digest corpus. In: Conference on language and technology 2012 (CLT12), Lahore (2012)
CLE, CLE Urdu image corpus 14 point size. In: Center for Language Engineering, 12 July 2012. http://www.cle.org.pk/clestore/cleurduimagecorpus14pt.htm (2012). Accessed 11 May 2015
Acknowledgments
This work is available at www.UrduOCR.net and has been supported by Urdu Nastalique OCR research project Grant by ICTR&D Fund, Ministry of IT, Govt. of Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, S., Ali, S. & Akram, Q.u.A. Nastalique segmentation-based approach for Urdu OCR. IJDAR 18, 357–374 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10032-015-0250-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10032-015-0250-2