Abstract
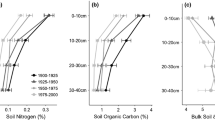
Urbanization represents the extreme case of human influence on an ecosystem. Biogeochemical cycling of nitrogen (N) in cities is very different from that of non-urban landscapes due to the large input of reactive forms of N and the heterogeneous distribution of various land uses that alters landscape connections. To quantify the likely effects of human activities on soil N and other soil properties in urban ecosystems, we conducted a probability-based study to sample 203 plots randomly distributed over the 6,400 km2 Central Arizona-Phoenix Long-Term Ecological Research (CAP LTER) area, which encompasses metropolitan Phoenix with its 3.5 million inhabitants. Soil inorganic N concentrations were significantly higher in urban residential, non-residential, agricultural, transportation, and mixed sites than in the desert sites. Soil water content and organic matter were both significantly higher under urban and agricultural land uses, whereas bulk density was lower compared to undeveloped desert. We calculated that farming and urbanization on average had caused an accumulation of 7.23 g m−2 in soil inorganic N across the CAP study area. Average soil inorganic N of the sampled desert sites (3.23 g m−2) was much higher than the natural background level reported in the literature. Laboratory incubation studies showed that many urban soils exhibited net immobilization of inorganic N, whereas desert and agricultural soils showed small, but positive, net N mineralization. The large accumulation of inorganic N in soils (mostly as nitrate) was highly unusual in terrestrial ecosystems, suggesting that in this arid urban ecosystem, N is likely no longer the primary limiting resource affecting plants, but instead poses a threat to surface and groundwater contamination, and influences other N cycling processes such as denitrification.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber J, McDowell W, Nadelhoffer K, Magill A, Berntson G, Kamakea M, McNulty S, Currie W, Rustad L, Fernandez I. 1998. Nitrogen saturation in temperate forest ecosystems: hypotheses revisited. Bioscience 48:921–34
Baker LA, Hope D, Xu Y, Edmonds J, Lauver L. 2001. Nitrogen balance for the central Arizona-Phoenix (CAP) ecosystem. Ecosystems 4:582–602
Boyle CA, Lavkulich L, Schreier H, Kiss E. 1997. Changes in land cover and subsequent effects on lower Fraser basin ecosystems from 1827 to 1990. Environ Manage 21:185–96
Collins JP, Kinzig AP, Grimm NB, Fagan WB, Hope D, Wu J, Borer ET. 2000. A new urban ecology. Am Sci 88:416–25
Effland WR, Pouyat RV. 1997. The genesis, classification, and mapping of soils in urban areas. Urban Ecosys 1:217–28
Elliott ET, Heill JW, Kelly EF, Monger HC. 1999. Soil structural and other physical properties. In: Robertson GP, Coleman DC, Bledsoe CS, Sollins P, Eds. Standard soil methods for long-term ecological research. New York: Oxford University Press
Ellis AW, Hildebrandt ML, Fernando HJS. 1999. Evidence of lower-atmospheric ozone “sloshing” in an urbanized valley. Phys Geogr 20:520–36
Ellis BA, Verfaillie JR, Kummerow J. 1983. Nutrient gain from wet and dry atmospheric deposition and rainfall acidity in southern California chaparral. Oecologia 60:118–21
Fenn ME, Haebuer R, Tonnesen GS, Baron JS, Grossman-Clarke S, Hope D, Jaffe DA, Copeland S, Geiser L, Rueth HM, Sickman JO. 2003a. Nitrogen emissions, deposition and monitoring in the Western United States. Bioscience 53:391–403
Fenn ME, Baron JS, Allen EB, Rueth HM, Nydick KR, Geiser L, Bowman WD, Sickman JO, Meixner T, Johnson DW, Neitlich P. 2003b. Ecological effects of nitrogen deposition in the western United States. Bioscience 53:404–20
Fisher SG, Grimm NB. 1985. Hydrologic and material budgets for a small Sonoran Desert watershed during three consecutive cloudburst floods. J Arid Environ 9:105–118
Folke C, Jansson A, Larsson J, Costanza R. 1997. Ecosystem appropriation by cities. Ambio 26:167–72
Grimm NB, Grove JM, Pickett STA, Redman CL. 2000. Integrated approaches to long-term studies of urban ecological systems. Bioscience 50:571–84
Hope D, Gries C, Zhu W, Fagan WF, Redman CL, Grimm NB, Nelson AL, Martin C, Kinzig A. 2003. Socioeconomics drive urban plant diversity. Proc Nat Acad Sci 100:8788–92
Hope D, Zhu W, Gries C, Oleson J, Kaye J, Grimm NB, Baker LA. 2005. Spatial variation in soil inorganic nitrogen across an arid urban ecosystem. Urban Ecosyst 8:251–273
Howarth RW, Billen G, Swaney D, Townsend A, Jaworski N, Lajtha K, Downing JA, Elmgren R, Caroco N, Jordan T, Berendse F, Freney J, Kudeyarov V, Murdoch P, Zhu ZL. 1996. Regional nitrogen budget and riverine N & P fluxes for the drainages to the North Atlantic Ocean: Natural and human influences. Biogeochemistry 35:75–139
Lovett GM, Traynor MM, Pouyat RV, Carreiro MM, Zhu WX, Baxter JW. 2000. Atmospheric deposition to oak forests along an urban–rural gradient. Environ Sci Technol 34:4294–300
Luck M, Wu JG. 2002. A gradient analysis of urban landscape pattern: a case study from the Phoenix metropolitan region, Arizona, USA. Lands Ecol 17:327–39
Luck MA, Jenerette GD, Wu J, Grimm NB. 2001. The urban funnel model and the spatially heterogeneous ecological footprint. Ecosystems 4:782–96
McDonnell MJ, Pickett STA. 1990. Ecosystem structure and function along urban–rural gradients: an unexploited opportunity for ecology. Ecology 71:1232–37
McDonnell MJ, Pickett STA. 1993. Humans as components of ecosystems: the ecology of subtle human effects and populated areas. Berlin Heidelberg, New York: Springer
McDonnell MJ, Pickett STA, Groffman P, Bohlen P, Pouyat RV, Zipperer WC, Parmelee RE, Carreiro MM, Medley K. 1997. Ecosystem processes along an urban-to-rural gradient. Urban Ecosyst 1:21–36
Mun HT, Whitford WG. 1989. Effects of nitrogen amendment on annual plants in the Chihuahuan Desert. Plant Soil 120:225–31
Padgett PE, Allen EB, Bytnerowicz A, Minich RA. 1999. Changes in soil inorganic nitrogen as related to atmospheric nitrogenous pollutants in southern California. Atmas Environ 33:769–81
Paul EA, Clark FE. 1996. Soil microbiology and biochemistry, 2nd ed. New York: Academic
Peterjohn WT, Schlesinger WH. 1990. Nitrogen loss from deserts in the southwestern United States. Biogeochemistry 10:67–79
Peterjohn WT, Schlesinger WH. 1991. Factors controlling denitrification in a Chihuahuan desert ecosystem. Soil Sci Soc Am J 55:1694–701
Peterson SA, Urquhart NS, Welch EB. 1999. Sample representativeness: a must for reliable regional lake condition estimates. Envrion Sci Technol 33:1559–65
Pickett STA, Cadenasso ML, Grove JM, Nilon CH, Pouyat RV, Zipperer WC, Costanza R. 2001. Urban ecological systems: linking terrestrial ecological, physical, and socioeconomic components of Metropolitan areas. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 32:127–57
Pouyat RV, Carreiro MM, McDonnell MJ, Pickett STA, Groffman PM, Parmelee RW, Medley KE, Zipperer WC. 1995. Carbon and nitrogen dynamics in oak stands along an urban–rural gradient. In: McFee WW, Kelly JM, Eds. Carbon forms and function in forest soils. Madison (Wisconsin, USA): Soil Science Society America, p 569–87
Rebele F. 1994. Urban ecology and special features of urban ecosystems. Glob Ecol Biogeogr Lett 4:173–87
Reynolds JF, Viginia RA, Kemp PR, de Soyza AG, Tremmel DC. 1999. Impact of drought on desert shrubs: effects of seasonality and degree of resource island development. Ecol Monogr 69:60–106
Robertson GP, Wedin D, Groffman PM, Blair JM, Holland EA, Nadelhoffer KJ, Harris D. 1999. Soil carbon and nitrogen availability: nitrogen mineralization, nitrification, and soil respiration potentials. In: Robertson GP, Coleman DC, Bledsoe CS, Sollins P, Eds. Standard soil methods for long-term ecological research. New York: Oxford University Press
Schlesinger WH, Gray JT, Gilliam FS. 1982. Atmospheric deposition processes and their importance as sources of nutrients in a chaparral ecosystem of southern California. Wat Res Res 18:623–29
Schlesinger WH, Raikes JA, Hartley AE, Cross AF. 1996. On the spatial pattern of soil nutrients in desert ecosystems. Ecology 77:364–74
Stevens DL Jr. 1997. Variable density grid-based sampling designs for continuous spatial populations. Environmetrics 8:167–95
Townsend AR, Howarth RW, Bazzaz FA, Booth MS, Cleveland CC, Collinge SK, Dobson AP, Epstein PR, Keeney DR, Mallin MA, Rogers CA, Wayne P, Wolfe AH. 2003. Human health effects of a changing global nitrogen cycle. Front Ecol Environ 1:240–46
Virginia RA, Jarrell WM, Franco-Vizcaino E. 1982. Direct measurement of denitrification in a Prosopis (Mesquite) dominated Sonoran desert ecosystem. Oecologia 53:120–22
Vitousek PM, Mooney HA, Lubchenco J, Melillo JM. 1997. Human domination of earth’s ecosystems. Science 277:494–9
Walvoord MA, Phillips FM, Stonestrom DA, Evans RD, Hartsough PC, Newman BD, Striegl RG. 2003. A reservoir of nitrate beneath desert soils. Science 302:1021–24
West NE, Klemmedson JO. 1978. Structural distribution of nitrogen in desert ecosystems. In: West NE, Skujins J, Eds. Nitrogen in desert ecosystems. Stroundsburg: Dowden, Hutchinson & Ross, pp 1–16
Whitford WG. 2002. Ecology of desert systems. San Diego: Academic
Zar JH. 1999. Biostatistical analysis. Upper Saddle River (New Jersey): Prentice Hall
Zhu WX, Carriero MM. 2004. Temporal and spatial variations in nitrogen cycling in deciduous forest ecosystems along an urban-rural gradient. Soil Biol Biochem 36:267–78
Zhu WX, Dillard ND, Grimm NB. 2004. Urban nitrogen biogeochemistry: status and processes in green retention basins. Biogeochemistry 71:177–96
Zipperer WC, Wu J, Pouyat RV, Pickett STA. 2000. The application of ecological principles to urban and urbanization landscapes. Ecol Appl 10:685–88
Acknowledgements
This project is supported by the National Science Foundation Grant nos. DEB-9714833 and DEB-0423704. We are grateful to the entire 2000 sampling crew for their dedicated work both in the field and in the laboratory. We are indebted to the editors and reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions. We thank Dr. Doug Green for providing consultation on soil sampling and soil processing and Dr. Jason Kaye for comments on writing. This paper is a contribution from the Central Arizona-Phoenix Long-Term Ecological Research Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, WX., Hope, D., Gries, C. et al. Soil Characteristics and the Accumulation of Inorganic Nitrogen in an Arid Urban Ecosystem. Ecosystems 9, 711–724 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-006-0078-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-006-0078-1