Abstract
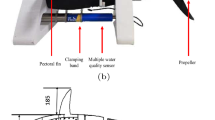
Robotic fish are nowadays developed for various types of research, such as bio-inspiredrobotics, biomimetics and animal behavior studies. In the context of our research on the social interactions of the zebrafish Danio Rerio, we developed a miniature robotic fish lure for direct underwater interaction with the living fish. This remotely controlled and waterproof device has a total length of 7.5 cm with the same size ratio as zebrafish and is able to beat its tail with different frequencies and amplitudes, while following the group of living animals using a mobile robot moving outside water that is coupled with the robotic lure using magnets. The robotic lure is also equipped with a rechargeable battery and can be used autonomously underwater for experiments of up to 1 h. We performed experiments with the robot moving inside an aquarium with living fish to analyze its impact on the zebrafish behavior. We found that the beating rate of the tail increased the attractiveness of the lure among the zebrafish shoal. We also demonstrated that the lure could influence a collective decision of the zebrafish shoal, the swimming direction, when moving with a constant linear speed inside a circular corridor. This new robotic fish design and the experimental results are promising for the field of fish–robot interaction.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mondada F, Martinoli A, Correll N, Gribovskiy A, Halloy J, Siegwart R, Deneubourg J-L (2013) A general methodology for the control of mixed natural-artificial societies. In: Kernbach S (ed) Handbook of collective robotics, Chapter 15. Pan Stanford Publishing, Singapore, pp 547–586
Halloy J et al (2007) Social integration of robots into groups of cockroaches to control self-organized choices. Science 318(5853):1155–1158
Krause J, Winfield A, Deneubourg J-L (2011) Interactive robots in experimental biology. Trends Ecol Evol 26(7):369–375
Kawabata K, Aonuma H, Hosoda K, Xue J (2013) A system for automated interaction with the cricket utilizing a micro mobile robot. J Robot Mechatron 25(2):333–339
Gribovksiy A, Halloy J, Deneubourg J.-L., Mondada F (2010) The poulbot, a mobile robot for ethological studies on domestic chickens. Symposium on AI-Inspired Biology
Reed B, Jennings M (2010) Guidance on the housing and care of Zebrafish Danio Rerio. Research Animals Department, Science Group, RSPCA
Abaid A, Bartolini T, Macri S, Porfiri M (2012) Zebrafish responds differentially to a robotic fish of varying aspect ratio, tail beat frequency, noise and color. Behav Brain Res 233:545–553
Aureli M, Fiorilli F, Porfiri M (2012) Portraits of self-organization in fish schools interacting with robots. Phys D: Nonlinear Phenom 241(9):908–920
Marras S, Porfiri M (2012) Fish and robots swimming together: attraction towards the robot demands biomimetic locomotion. J R Soc Interface 9(73):1856–1868
Faria J, Dyer J, Clment R, Couzin I, Holt N, Ward A, Waters D, Krause J (2010) A novel method for investigating the collective behaviour of fish: Introducing Robofish. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 64:1211–1218
Swain D, Couzin I, Leonard N (2012) Real-time feedbackcontrolled robotic fish for behavioral experiments with fish schools. Proc IEEE 100(1):150–163
Landgraf T, Nguyen H, Forgo S, Schneider J, Schrer J, Krger C, Matzke H, Clment R, Krause J, Rojas R (2013) Interactive robotic fish for the analysis of swarm behavior. In: Tan Y, Shi Y, Mo H (eds) ICSI (1), ser. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. vol. 7928, pp 1–10
Bonnet F, Rétornaz P, Halloy J, Gribovskiy A, Mondada F (2012) Development of a mobile robot to study the collective behavior of zebrafish. Proc IEEE Int Conf Biomed Robot Biomechatron BioRob 4:437–442
Bonnet F, Binder S, Elias de Oliveira M, Halloy J and Mondada F (2014) A Miniature mobile robot developed to be socially integrated with species of small fish. IEEE international conference on robotics and biomimetics, Bali, Indonesia
Bandyopadhyay PR (2005) Trends in biorobotic autonomous undersea vehicles. IEEE J Ocean Eng 30:109–139
Heo S, Wiguna T, Park HC, Goo NS (2007) Effect of an artificial caudal fin on the performance of a biomimetic fish robot propelled by piezoelectric actuators. J Bionic Eng 4:151–158
Wang Z, Hanga G, Li J, Wang Y, Xiao K (2008) A micro-robot fish with embedded SMA wire actuated flexible biomimetic. Sens Actuators A 144:354–360
Rosenthal GG, Ryan MJ (2005) Assortative preferences for stripes in danios. Anim Behav 70(5):1063–1066
Saverino C, Gerlai R (2008) The social zebrafish: Behavioral responses to conspecific, heterospecific, and computer animated fish. Behav Brain Res 191(1):77–87
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the EU-ICT project ASSISIbf, No. 601074. The information provided is the sole responsibility of the authors and does not reflect the European Commissions opinion. The European Commission is not responsible for any use that might be made of data appearing in this publication. We also thank Daniel Burnier and Norbert Crot (LSRO) for the technical support during RiBot design and production.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented in part at the 1st International Symposium on Swarm Behavior and Bio-Inspired Robotics, Kyoto, Japan, October 28–30, 2015.
About this article
Cite this article
Bonnet, F., Kato, Y., Halloy, J. et al. Infiltrating the zebrafish swarm: design, implementation and experimental tests of a miniature robotic fish lure for fish–robot interaction studies. Artif Life Robotics 21, 239–246 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-016-0291-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10015-016-0291-8